During which seasons are hurricanes most likely to appear in the northern ? [ MCQ aircraft ]
Question 159-1 : Summer and autumn winter all seasons winter and spring
 Summer and autumn.
Summer and autumn. At what time of the year are typhoons most likely to occur over the southern ?
Question 159-2 : July to november september to january january to may may to july
 July to november.
July to november. On which coast of north america is the danger of tropical revolving storms the ?
Question 159-3 : Se coast w coast n coast ne coast
 Se coast.
Se coast. What is characteristic of the pamperos ?
Question 159-4 : A marked advance of cold air in south america katabatic winds in the atlas mountains a marked advance of cold arctic air in north america foehn conditions in the spanish pyrenees
 A marked advance of cold air in south america
A marked advance of cold air in south america Where during a flight from marseille to dakar in july may the itcz be ?
Question 159-5 : In the vicinity of dakar at the latitudes of gibraltar at the latitudes of algeria near the canary islands
 In the vicinity of dakar.
In the vicinity of dakar. Which wind systems converge on the itcz when it lies at the equator ?
Question 159-6 : Se trade winds and ne trade winds sw monsoon and nw monsoon sw monsoon and nw trade winds nw monsoon and sw trade winds
 Se trade winds and ne trade winds
Se trade winds and ne trade winds From which direction do the trade winds blow in the southern hemisphere ?
Question 159-7 : Se ne sw n
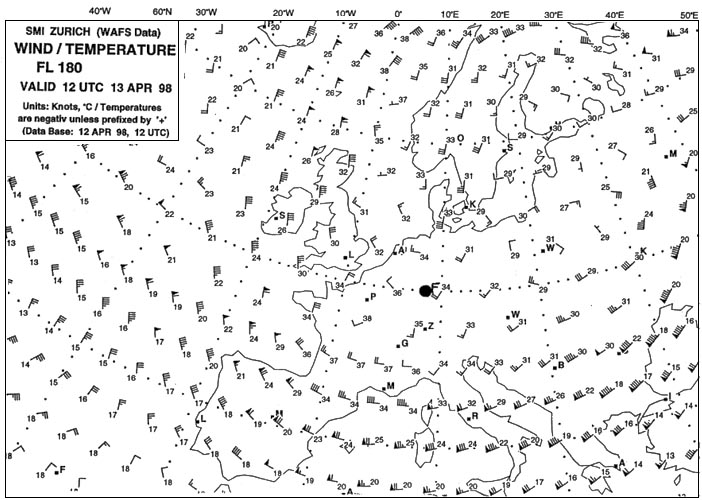 Se
Se Considering the route indicates from lisbon to freetown the harmattan is a . 290 ?
Question 159-8 : Ne wind affecting north west africa during november to april reducing visibility in rising dust sw monsoonal wind causing extensive areas of advection fog along the west african coast south of 15°n warm southerly dust bearing wind affecting the coast of north africa localised depression giving squally winds
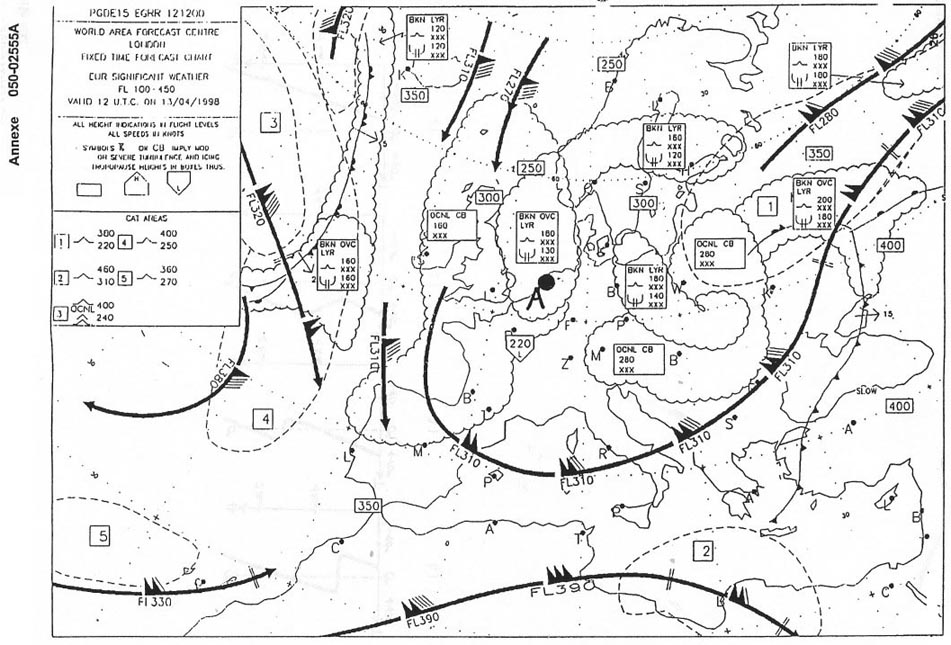 Ne wind affecting north-west africa during november to april reducing visibility in rising dust.
Ne wind affecting north-west africa during november to april reducing visibility in rising dust. In which month does the humid monsoon in india start ?
Question 159-9 : In june in october in december in march
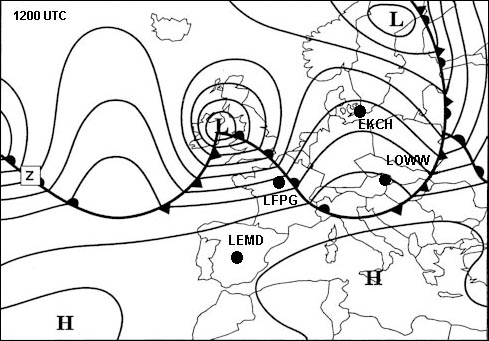 In june.
In june. The intertropical convergence zone itcz particularly affects ?
Question 159-10 : Western africa between 10°n and 20°n and the northern coasts of the arabian sea in july western africa at a latitude of 25°n in july the atlantic ocean between latitudes 10°n and 30°n depending on the time of year western africa where it is situated between the 10°n and 30°n parallels depending on the time of the year
 Western africa between 10°n and 20°n and the northern coasts of the arabian sea in july.
Western africa between 10°n and 20°n and the northern coasts of the arabian sea in july. The chinook is a ?
Question 159-11 : Warm and dry wind that forms as air descends on the leeward side of the rocky mountains very cold wind with blowing snow downslope wind that occurs particularly at night as air cools along mountain slopes warm anabatic wind up the slopes of snowfields or glaciers
 Warm and dry wind that forms as air descends on the leeward side of the rocky mountains.
Warm and dry wind that forms as air descends on the leeward side of the rocky mountains. A dry sand and dust laden north easterly wind that blows in winter over large ?
Question 159-12 : Harmattan scirocco pampero khamsin
 Harmattan
Harmattan The transition from sw to ne monsoon in india occurs in ?
Question 159-13 : September october november july august september december january february february march april
 September, october, november.
September, october, november. Which of the following statements concerning the intertropical convergence zone ?
Question 159-14 : There are frequent occurrences of cb it lies totally in the northern hemisphere in july and totally in the southern hemisphere in january it does not change its position over the oceans during the year it is an area of low pressure and low relative humidity
 There are frequent occurrences of cb.
There are frequent occurrences of cb. An easterly wave is a ?
Question 159-15 : Wave in a trade wind belt moving from east to west with severe convective activity in rear of its trough wave like disturbance in the monsoon regime of india moving from east to west with severe convective activity ahead of its trough small scale wave disturbance in the tropics moving from east to west with severe convective activity ahead of its trough disturbance in the higher levels associated with the equatorial easterly jet moving from east to west with severe convective activity in rear of its trough
 Wave in a trade wind belt, moving from east to west, with severe convective activity in rear of its trough.
Wave in a trade wind belt, moving from east to west, with severe convective activity in rear of its trough. The prevailing surface wind in the area of the west coast of africa north of ?
Question 159-16 : Sw monsoon in summer and ne tradewind in winter ne monsoon in winter and se tradewind in summer sw monsoon in winter and ne monsoon in summer ne tradewind in summer and se tradewind in winter
 Sw monsoon in summer and ne tradewind in winter.
Sw monsoon in summer and ne tradewind in winter. Which of the following statements concerning trade winds is correct ?
Question 159-17 : They occur only in the lower part of the troposphere and more pronounced over the oceans they reach up to the tropopause and are more pronounced over the continents they reach up to the tropopause and are more pronounced over the oceans they occur only in the lower part of the troposphere and are more pronounced over the continents
 They occur only in the lower part of the troposphere and more pronounced over the oceans.
They occur only in the lower part of the troposphere and more pronounced over the oceans. In the central part of the atlantic ocean between 10°n and 20°n the ?
Question 159-18 : Ne trade winds ne monsoon in winter and sw monsoon in summer se trade winds sw winds throughout the whole year
 Ne trade winds.
Ne trade winds. Along the west coast of india the prevailing winds are the ?
Question 159-19 : Sw monsoon in july and a ne monsoon in january ne monsoon in july and a sw monsoon in january sw monsoon in july and a se monsoon in january se monsoon in july and a sw monsoon in january
 Sw monsoon in july and a ne monsoon in january.
Sw monsoon in july and a ne monsoon in january. The bora is a ?
Question 159-20 : Cold catabatic wind with the possibility of violent gusts squally warm catabatic wind which occurs mainly in summer cold catabatic wind with gusts associated with a maritime air mass cold catabatic wind always associated with clouds and heavy showers
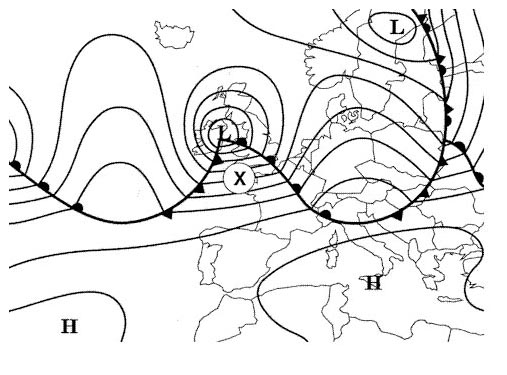 Cold catabatic wind with the possibility of violent gusts.
Cold catabatic wind with the possibility of violent gusts. What is the name of the northerly cold and strong wind that sometimes blows ?
Question 159-21 : Mistral foehn sirocco typhoon
 Mistral.
Mistral. What are the characteristics of the bora ?
Question 159-22 : It is a cold and very strong wind that blows mainly in winter from a tableland downwards to the adriatic it is a very cold wind that blows mainly in winter from a north westerly direction in the mediterranean it is a warm and moist south westerly wind experienced in the eastern mediterranean that usually carries precipitation it is a dry and hot southerly wind experienced in the sahara desert that often carries dust
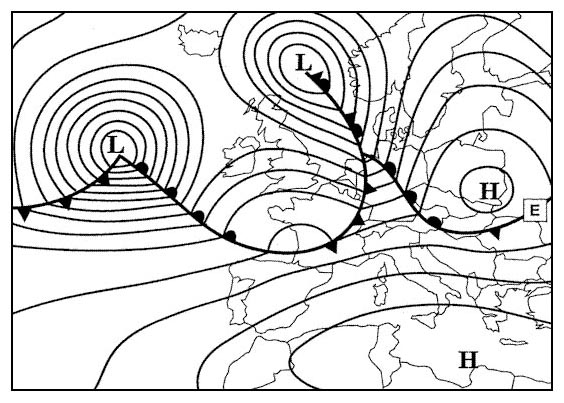 It is a cold and very strong wind that blows mainly in winter from a tableland downwards to the adriatic
It is a cold and very strong wind that blows mainly in winter from a tableland downwards to the adriatic Which one of the following statements is correct concerning the movement of the ?
Question 159-23 : It reaches its maximum northerly position of 15° 20°n in july it reaches its maximum southerly position of 5°s in january it oscillates during the year between 10 degrees north and 10 degrees south it oscillates during the year between the equator and 10 degrees north
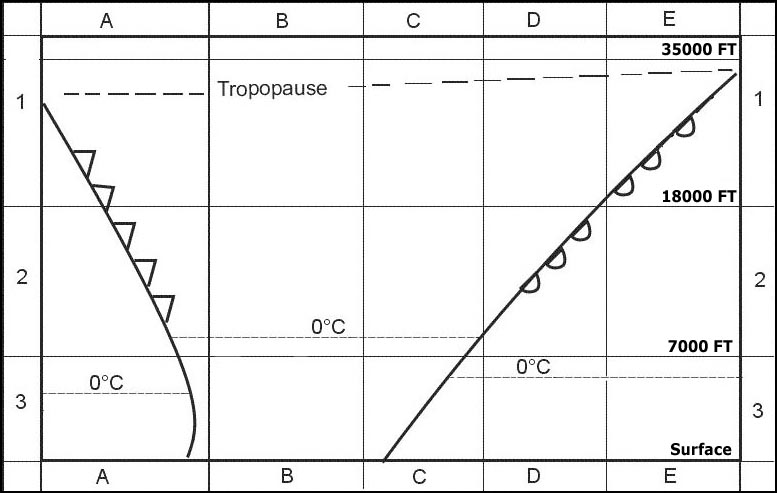 It reaches its maximum northerly position of 15° - 20°n in july.
It reaches its maximum northerly position of 15° - 20°n in july. What is the name of the wind or air mass which gives to the main part of india ?
Question 159-24 : South west monsoon south east trade wind indian maritime tropical air mass winter monsoon
 South-west monsoon.
South-west monsoon. What is the type intensity and seasonal variation of precipitation in the ?
Question 159-25 : Rainshowers hail showers and thunderstorms occur the whole year but frequency is highest during two periods april may and october november warm fronts are common with continuous rain the frequency is the same throughout the year precipitation is generally in the form of showers but continuous rain occurs also the greatest intensity is in july showers of rain or hail occur throughout the year the frequency is highest in january
 Rainshowers, hail showers and thunderstorms occur the whole year, but frequency is highest during two periods: april-may and october-november.
Rainshowers, hail showers and thunderstorms occur the whole year, but frequency is highest during two periods: april-may and october-november. Assuming a generalised zonal system of world wind circulation the se trade ?
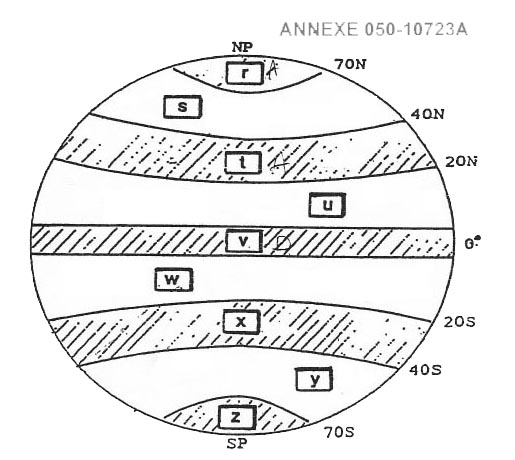
Question 159-26 : W t u v
 W
W Assuming a generalised zonal system of world climatic and wind circulation zone ?
Question 159-27 : Subtropical high pressure systems se trade winds travelling low pressure systems ne trade winds
 Subtropical high pressure systems.
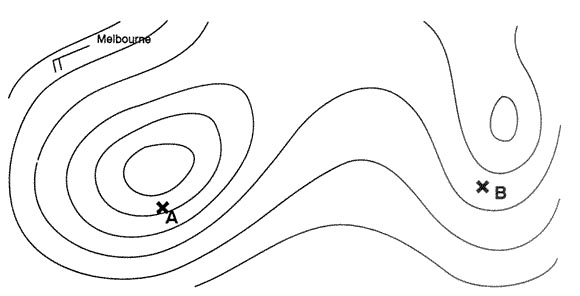
Subtropical high pressure systems. Considering melbourne c in july the weather is predominantly influenced by the ?
Question 159-28 : Subtropical high pressure with the occasional passage of fronts originating in the adjacent zone of westerly waves antarctic high pressure due to the absence of any protective land mass between south australia and antarctica disturbed temperate low pressure bringing an almost continuous succession of fronts resulting in strong winds low cloud and rain equatorial low pressure due to the proximity of the intertropical convergence zone over central australia
 Subtropical high pressure, with the occasional passage of fronts originating in the adjacent zone of westerly waves.
Subtropical high pressure, with the occasional passage of fronts originating in the adjacent zone of westerly waves. Assuming a generalised zonal system of world climatic and wind circulation zone ?
Question 159-29 : Travelling low pressure systems ne trade winds se trade winds subtropical high pressure systems
 Travelling low pressure systems.
Travelling low pressure systems. Assuming a generalised zonal system of world wind circulation the ne trade ?
Question 159-30 : U w v t
 U.
U. Assuming a generalised zonal system of world climatic and wind circulation zone ?
Question 159-31 : Ne trade winds travelling depressions sw trade winds subtropical high pressure
 Ne trade winds.
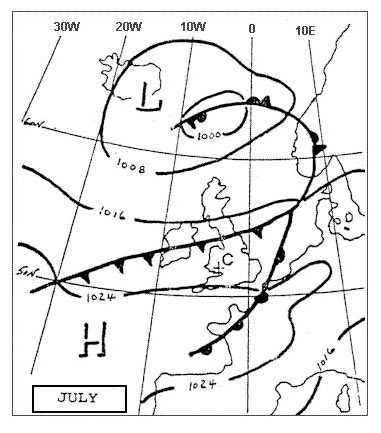
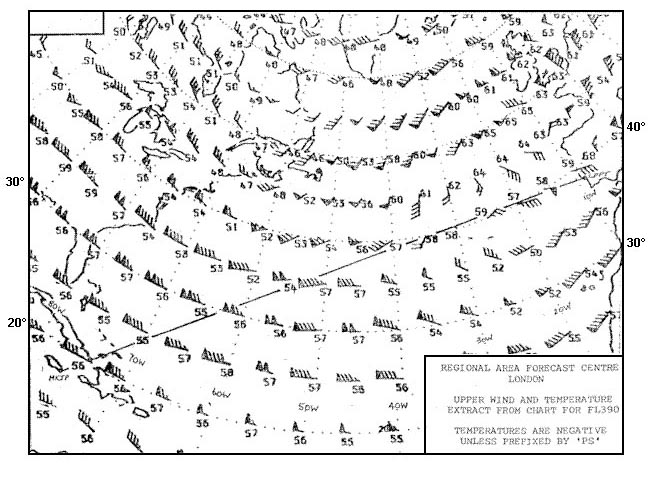
Ne trade winds. The dotted line labelled 'y' represents the . 322 ?
Question 159-32 : Mean position of the intertropical convergence zone itcz during january axis of the subtropical jet stream during january mean position of the intertropical convergence zone itcz during july axis of the equatorial jet stream during july
 Mean position of the intertropical convergence zone (itcz) during january.
Mean position of the intertropical convergence zone (itcz) during january. What weather conditions are most likely to affect an approach to dakar during ?
Question 159-33 : Wet and thundery due to the proximity of the intertropical convergence zone itcz dry and clear due to the influence of the azores high pressure system generally clear skies nw trade winds reduced visibility due to the rising sand of the harmattan
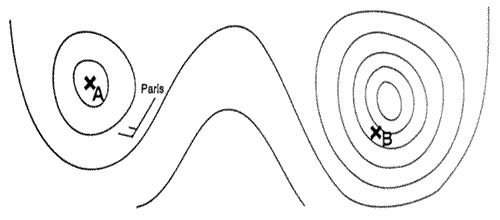 Wet and thundery due to the proximity of the intertropical convergence zone (itcz)
Wet and thundery due to the proximity of the intertropical convergence zone (itcz) Weather conditions at bombay during early july are mainly influenced by the . ?
Question 159-34 : Sw monsoon ne monsoon and the proximity of the itcz passage of frontal system generated in the south indian ocean high incidence of tropical revolving storms originating in the persian gulf
 Sw monsoon.
Sw monsoon. Weather conditions at bombay during january are mainly influenced by the . 325 ?
Question 159-35 : Ne monsoon sw monsoon nw monsoon se monsoon
 Ne monsoon
Ne monsoon Which one of the following local winds is a foehn wind ?
Question 159-36 : Chinook scirocco harmattan bora
 Chinook.
Chinook. During the approach to mumbai 19°n 73°e on the west coast of india you are ?
Question 159-37 : 25014kt 4500 shra sct015 bkn025cb 25/24 q1006 nosig= 05013kt 3500 mifg sct003 bkn005 19/14 q1012 becmg 8000= 02005kt cavok 24/09 q1030 nosig= 30012kt 9999 sct030 sct200 20/16 q1025 tempo 4000=
 25014kt 4500 shra sct015 bkn025cb 25/24 q1006 nosig=
25014kt 4500 shra sct015 bkn025cb 25/24 q1006 nosig= On the west coast of india it can be said in general that the wind blows ?
Question 159-38 : For six month from the north east and for six month from the south west for six month from the north west and for six month from the south east the whole year from the north east the whole year from the south east
 For six month from the north east and for six month from the south west
For six month from the north east and for six month from the south west What name is given to the low level wind system between the subtropical high ?
Question 159-39 : Trade winds doldrums westerly winds monsoon
 Trade winds.
Trade winds. What is a favourable synoptic situation for the development of a scirocco ?
Question 159-40 : Low pressure area in the western part of the mediterranean sea high pressure area over italy extension of the azores high pressure area over the alps high pressure area in the western part of the mediterranean sea
 Low pressure area in the western part of the mediterranean sea.
Low pressure area in the western part of the mediterranean sea. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6319 Free Training Exam
