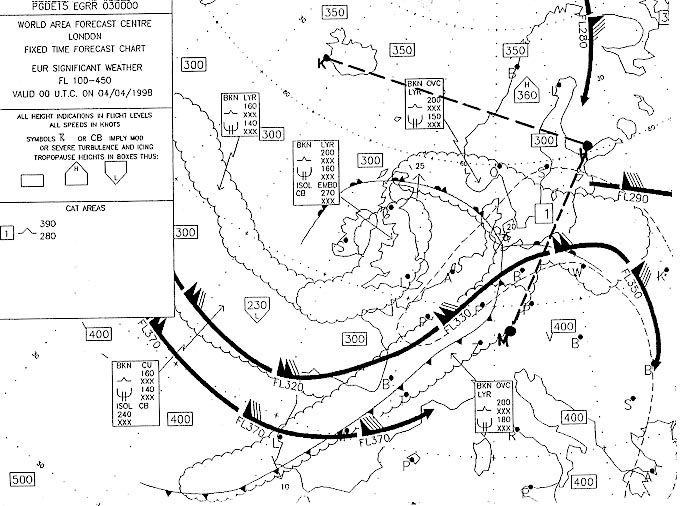
What is the lowest visibility that may be expected during an approach into ? [ MCQ aircraft ]
Question 151-1 : 4 km 10 km or more 7 km 6000 m
 4 km.
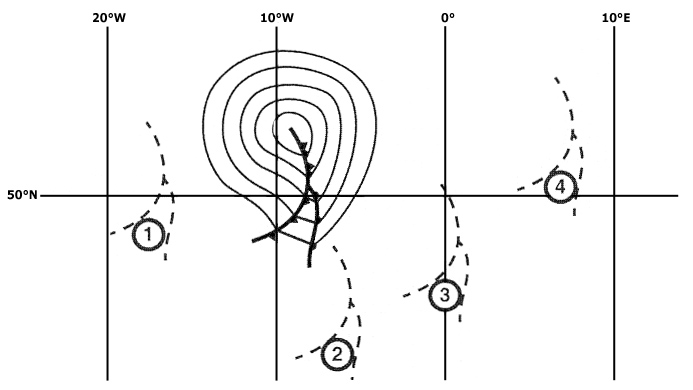
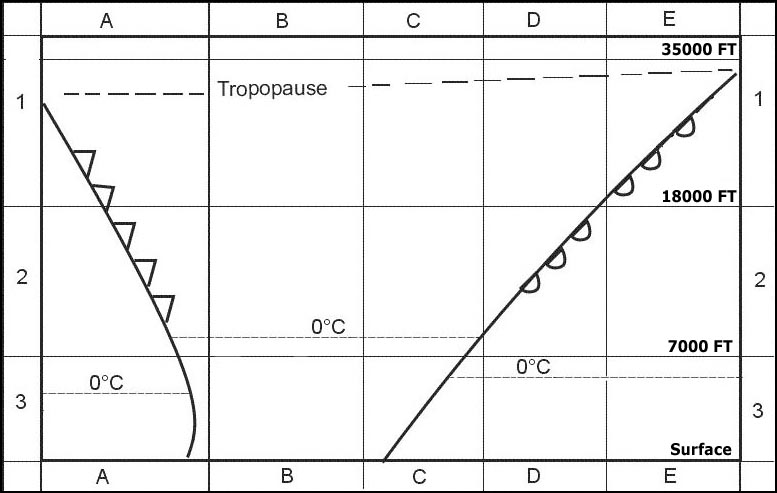
4 km. In which squares are conditions most likely to cause the occurrence of low ?
Question 151-2 : 3 a and 3 c 3 a and 3 b 3 b and 3 c 3 b and 3 d
 3 a and 3 c.
3 a and 3 c. For an aircraft making an approach to an airfield which is not situated near ?
Question 151-3 : Low level wind shear radiation fog rotor streaming clear air turbulence cat
 Low level wind shear.
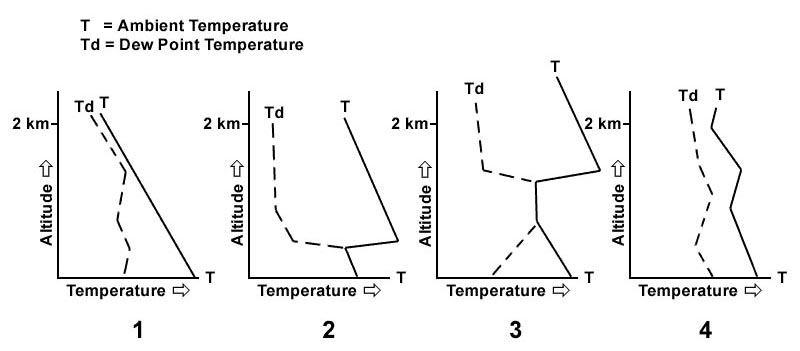
Low level wind shear. The occurrence of freezing rain at fl 60 is most likely in square . 347 ?
Question 151-4 : 3c 2d 3b 2a
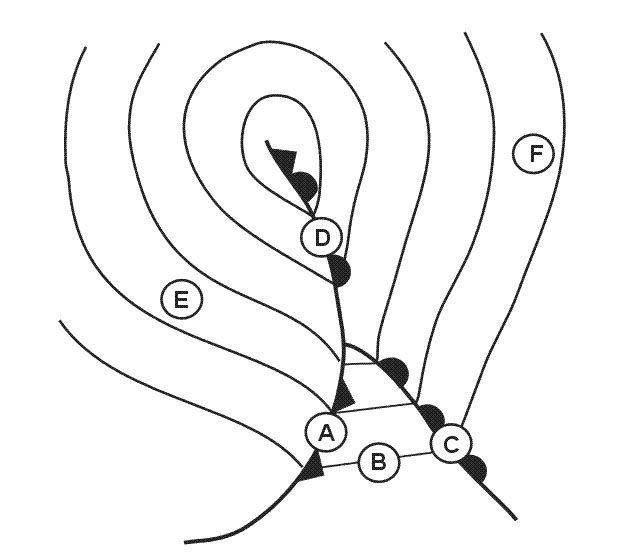 3c.
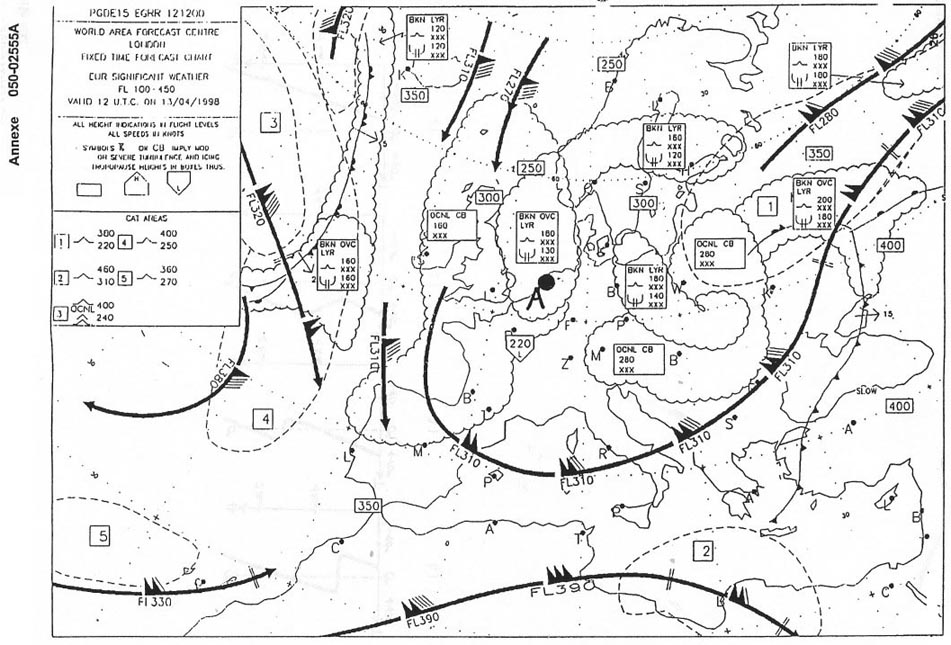
3c. For an aircraft at fl 40 approaching the front square 3c from the direction of ?
Question 151-5 : Clear ice accretion to the airframe severe turbulence associated with cb severe turbulence and wind shear severe downdrafts from subsiding air
 Clear ice accretion to the airframe.
Clear ice accretion to the airframe. What are the characteristics of rime ice and what conditions are most ?
Question 151-6 : Milky granular appearance forming on leading edges and accumulating forward into the air stream stratiform clouds at temperatures of 10°c to 20°c are most conducive to its formation opaque rough appearance tending to spread back over an aircraft surface most frequently encountered in cumuliform clouds at temperatures slightly below freezing smooth appearance and builds forward from leading surfaces into a sharp edge most common in cumuliform clouds at temperatures of 20°c to 25°c transparent appearance and tendency to take the shape of the surface on which it freezes stratiform clouds and temperatures only slightly below freezing promote its formation
 Milky granular appearance, forming on leading edges and accumulating forward into the air stream. stratiform clouds at temperatures of -10°c to -20°c are most conducive to its formation.
Milky granular appearance, forming on leading edges and accumulating forward into the air stream. stratiform clouds at temperatures of -10°c to -20°c are most conducive to its formation. What intensity and type of aircraft icing is likely to occur at fl 100 in a ?
Question 151-7 : Moderate to severe icing due to clear ice light icing due to rime ice moderate to severe icing due to rime ice light icing due to clear ice
 Moderate to severe icing due to clear ice.
Moderate to severe icing due to clear ice. The presence of ice pellets at the surface is the evidence that ?
Question 151-8 : Temperatures are above freezing at some higher altitudes a cold front has passed there are thunderstorms in the area after take offyou can climb to a higher altitude without encountering more than light icing conditions
 Temperatures are above freezing at some higher altitudes.
Temperatures are above freezing at some higher altitudes. At the surface the lifetime of a typical microburst and the diameter of the ?
Question 151-9 : 1 5 minutes and 4 km 30 40 minutes and 4 km 5 15 minutes and 8 km 5 10 minutes and 12 km
 1-5 minutes and 4 km.
1-5 minutes and 4 km. In mature cb's the probability of severe icing according to meteorological ?
Question 151-10 : 0°c to 23°c +5°c to 0°c 23°c to 40°c 40°c to 60°c
 0°c to -23°c.
0°c to -23°c. In which environment is aircraft structural ice most likely to have the highest ?
Question 151-11 : Freezing rain stratus clouds cirrus clouds snow
 Freezing rain.
Freezing rain. An aircraft descends in layered clouds the freezing level is situated at fl 60 ?
Question 151-12 : Between fl 120 and fl 60 between fl 60 and fl 20 between fl 120 and fl 180 at fl 140
 Between fl 120 and fl 60.
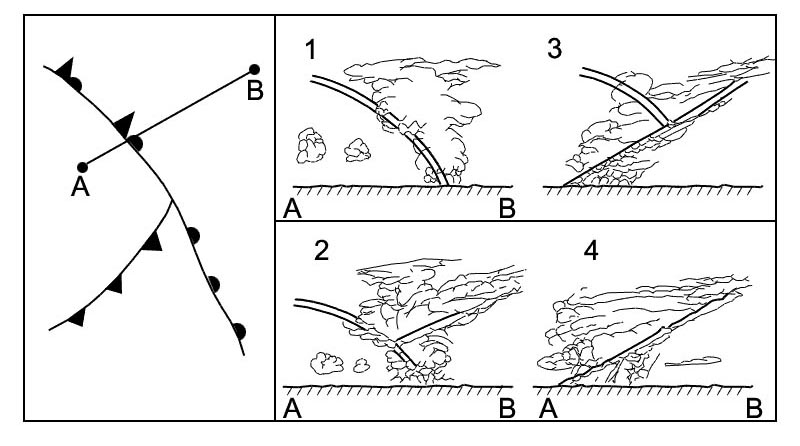
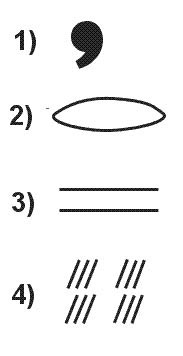
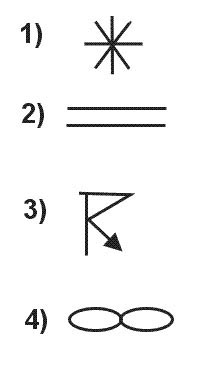
Between fl 120 and fl 60. According to icao which symbol indicates danger to an aircraft flying according ?
Question 151-13 : Symbol 2 symbol 4 symbol 1 symbol 3
 Symbol 2.
Symbol 2. In which of the following situations is the probability for severe ?
Question 151-14 : Advection of maritime cold air over a warm sea surface advection of warm air over a cold land surface advection of continental cold air over a warm land surface advection of maritime warm air over a cold sea surface
 Advection of maritime cold air over a warm sea surface.
Advection of maritime cold air over a warm sea surface. In which of these cloud types can icing be virtually ruled out ?
Question 151-15 : Cs as sc ns
 Cs
Cs According to icao which symbol indicates danger to an aircraft flying according ?
Question 151-16 : Symbol 3 symbol 4 symbol 1 symbol 2
 Symbol 3.
Symbol 3. In which conditions would you most likely encounter clear icing and how would ?
Question 151-17 : Cumuliform clouds large water droplets temperatures between 0°c and 15°c appears smooth and tends to spread back over an aircraft wing stratiform clouds small water droplets temperatures between 10°c and 20°c appears granular and tends to accumulate forward into the air stream cumuliform clouds small water droplets temperatures between 20°c and 25°c appears transparent and tends to take the shape of the surface on which it freezes stratiform clouds large water droplets temperatures well below freezing appears opaque and builds forward from leading surface into a sharp edge
 Cumuliform clouds, large water droplets, temperatures between 0°c and -15°c. appears smooth and tends to spread back over an aircraft wing.
Cumuliform clouds, large water droplets, temperatures between 0°c and -15°c. appears smooth and tends to spread back over an aircraft wing. A cb with thunderstorm has reached the mature stage which statement is correct ?
Question 151-18 : In temperatures lower than 23°c icing is still possible the freezing level in the whole cloud lies lower than outside the cloud if hail occurs it only occurs in downdrafts severe turbulence occurs in the cloud but hardly ever below the cloud
 In temperatures lower than -23°c icing is still possible.
In temperatures lower than -23°c icing is still possible. Which of the following statements is true with regard to mountain waves ?
Question 151-19 : Flight with headwind toward high ground is likely to be more hazardous than flight with tailwind toward high ground mountain waves are not experienced beyond 100 miles downwind from initiating high ground regardless of the height of the ground the absence of cloud over high ground indicates the absence of mountain waves flight with tailwind toward high ground is likely to be more hazardous than flight with headwind toward high ground
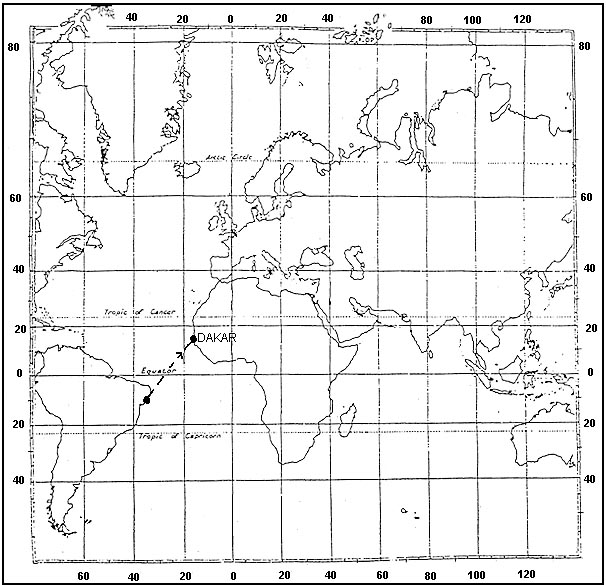 Flight with headwind toward high ground is likely to be more hazardous than flight with tailwind toward high ground.
Flight with headwind toward high ground is likely to be more hazardous than flight with tailwind toward high ground. The correct statement is ?
Question 151-20 : Airframe icing can occur in clear air haze is a reduction of visibility due to the presence of water vapour mountain waves are always accompanied by rotor clouds above the tropopause no turbulence occurs
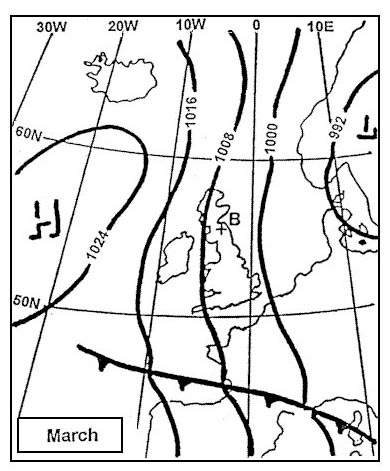 Airframe icing can occur in clear air.
Airframe icing can occur in clear air. Flight from bordeaux to amsterdam eta 2100 utc what is the minimum visibility ?
Question 151-21 : 3 km 5 km 5 nm 6 km
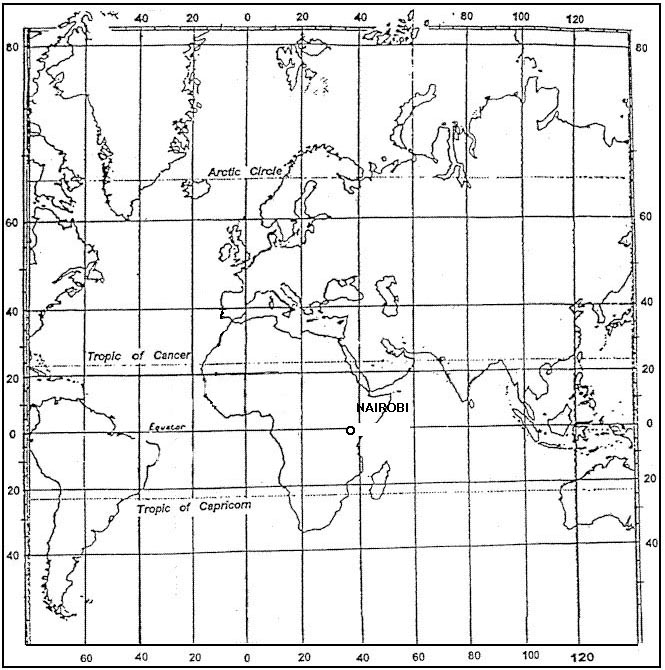 3 km.
3 km. What are the conditions required for the formation of hoar frost ?
Question 151-22 : The temperature of the surface is lower than the dew point of the air and the dew point is lower than 0°c falling droplets on a surface while the air temperature is below freezing the temperature of the surface is higher than the dew point of the air and the dew point is lower than 0°c falling droplets on a surface with a temperature below freezing
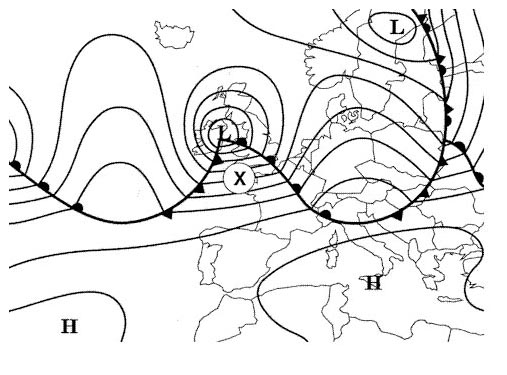 The temperature of the surface is lower than the dew point of the air and the dew point is lower than 0°c.
The temperature of the surface is lower than the dew point of the air and the dew point is lower than 0°c. Imagine an airfield during summer with sunny days and clear nights and with a ?
Question 151-23 : A strong sea breeze blowing more or less perpendicular to the runway a radiation inversion due to surface cooling during the clear night a subsidence inversion typical for summer anticyclones causing variations in wind speed and direction near the surface a strong land breeze blowing more or less perpendicular to the runway
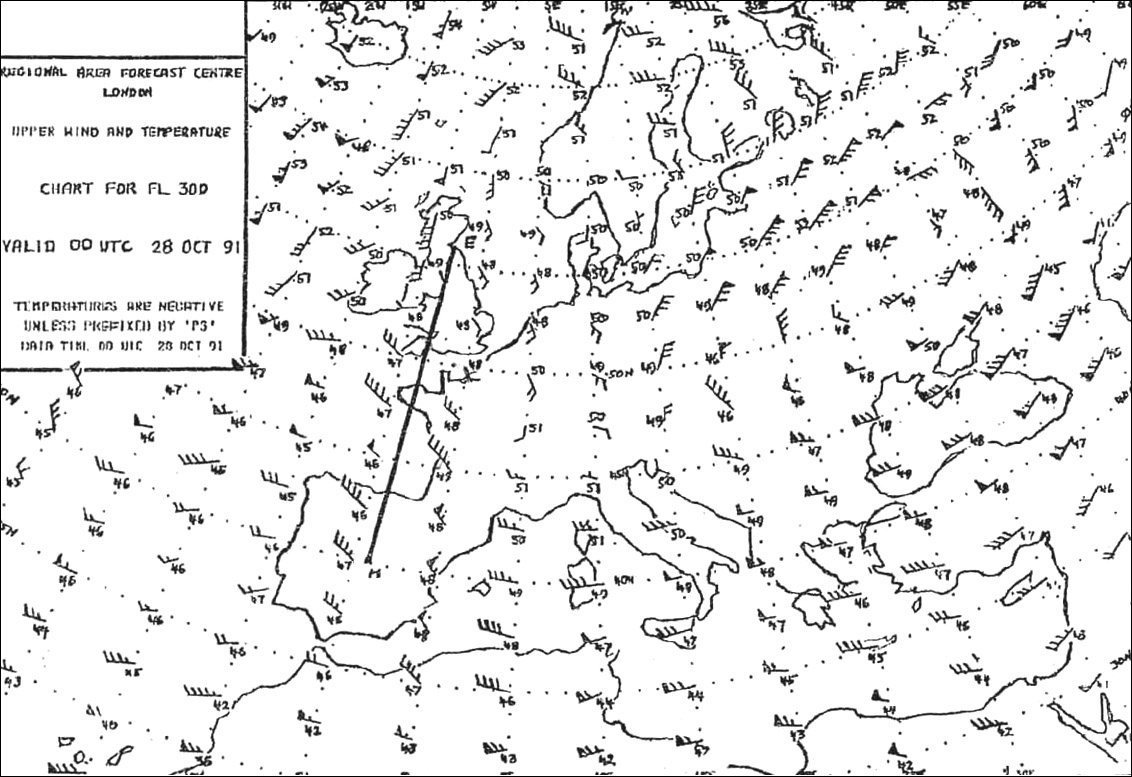 A strong sea breeze blowing more or less perpendicular to the runway.
A strong sea breeze blowing more or less perpendicular to the runway. Which of the following situations favours the formation of heavy thunderstorms ?
Question 151-24 : A cold front approaching a mountain range in the evening the passage of a warm front in the morning a cold front on the leeward side of a mountain range a warm sector moving over a snow covered ground
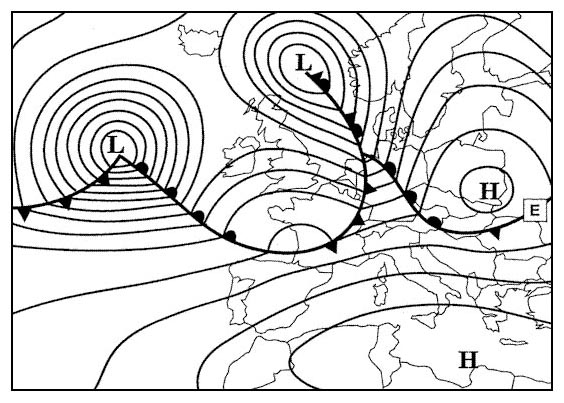 A cold front approaching a mountain range in the evening.
A cold front approaching a mountain range in the evening. The wind at 500ft above ground is 290/15kt and at the same position at 600ft ?
Question 151-25 : Moderate vertical wind shear severe horizontal wind shear gradual horizontal wind shear severe low level turbulence
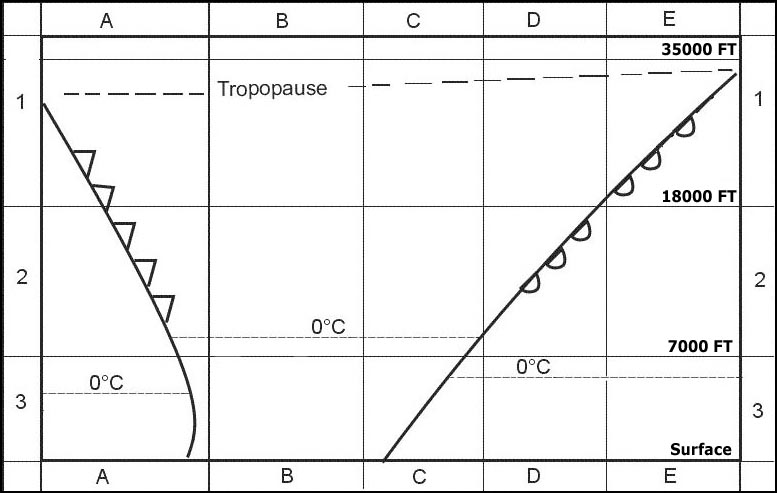 Moderate vertical wind shear.
Moderate vertical wind shear. Imagine an aircraft during approach to an airfield which is located in a basin ?
Question 151-26 : While approaching the airfield in the early morning after a short period of bumpiness the engines of the aircraft will deliver more thrust after breaking through the inversion layer if the pilot does not intervene while approaching the airfield shortly before sunrise the pilot has to consider turbulence because at first lift will be decreased due to katabatic winds and after breaking through a valley inversion layer lift is likely to improve due to anabatic wind while approaching the airfield in the late evening hours without the pilot's intervention the engines of the aircraft are most likely to provide less thrust after breaking through the inversion layer while approaching the airfield in the early morning hours these conditions apply for the possibility of a marked valley inversion which has to be considered as a potential flight hazard due to a decreased lift after breaking through the inversion layer
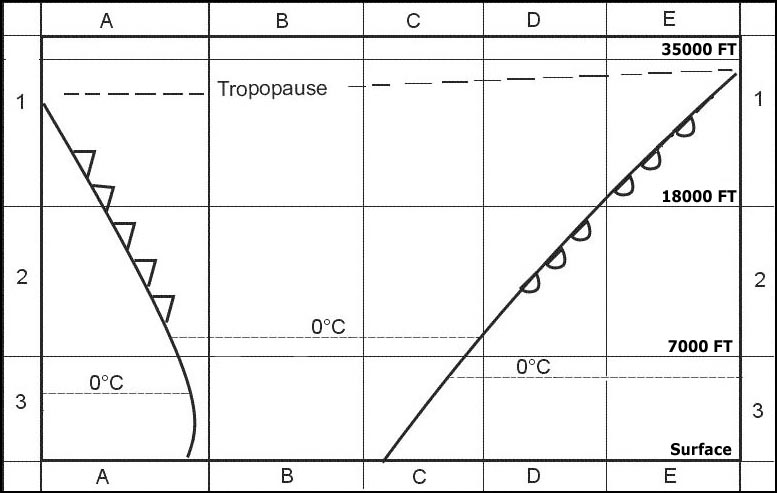 While approaching the airfield in the early morning, after a short period of bumpiness the engines of the aircraft will deliver more thrust after breaking through the inversion layer if the pilot does not intervene.
While approaching the airfield in the early morning, after a short period of bumpiness the engines of the aircraft will deliver more thrust after breaking through the inversion layer if the pilot does not intervene. Mark the statement most reasonable regarding a valley inversion ?
Question 151-27 : Over night cool dense air as a result of radiation cooling will descend along the mountain slopes into the basin and lead to the development of a valley inversion if the incident solar radiation is non uniform because of orographic conditions the development of a valley inversion is very likely during daytime provided that the lee side winds are able to displace the air at the bottom of the basin the foehn effect is the predominant factor in the development of a valley inversion small scale density variations due to turbulent mixing mainly caused by the roughness of rocks are a significant prerequisite for the formation of valley inversions
 Over night, cool dense air as a result of radiation cooling will descend along the mountain slopes into the basin and lead to the development of a valley inversion.
Over night, cool dense air as a result of radiation cooling will descend along the mountain slopes into the basin and lead to the development of a valley inversion. Which of the following statements is correct concerning the weather in a warm ?
Question 151-28 : Isolated thunderstorms are sometimes possible over continental areas during the summer no thunderstorms can occur in mid and high latitudes thunderstorms may occur only over open sea during the summer isolated air mass thunderstorms are common during all seasons over continental areas
 Isolated thunderstorms are sometimes possible over continental areas during the summer.
Isolated thunderstorms are sometimes possible over continental areas during the summer. With which meteorological phenomena are wind shear conditions mostly associated ?
Question 151-29 : Gust fronts low level temperature inversions frontal surfaces gust fronts sea breeze fronts high stratiform clouds strong surface winds coupled with local topography anticyclones light precipitation thunderstorms drizzle conditional instability
 Gust fronts, low level temperature inversions, frontal surfaces.
Gust fronts, low level temperature inversions, frontal surfaces. In winter after breaking through a low level inversion during descent and ?
Question 151-30 : Thrust most likely will increase and visibility is likely to deteriorate lift most likely will increase and visibility is likely to improve thrust most likely will decrease and visibility is likely to improve lift most likely will decrease and visibility is likely to deteriorate
 Thrust most likely will increase and visibility is likely to deteriorate.
Thrust most likely will increase and visibility is likely to deteriorate. The presence of ice pellets at the surface is the evidence that ?
Question 151-31 : Temperatures are above freezing at some higher altitudes a cold front has passed there are thunderstorms in the area after take off you can climb to a higher altitude without encountering more than light icing conditions
 Temperatures are above freezing at some higher altitudes.
Temperatures are above freezing at some higher altitudes. Mark the correct statement concerning lightning discharge ?
Question 151-32 : While flying through air that is electrically charged the aircraft is likely to become a charge carrier itself and can initiate a lightning discharge the probability of a lightning discharge is reciprocally proportional to the strength of the electric field the aircraft intruded the set of possible effects of a lightning discharge does not include welding of aircraft parts such as joints or bearings because an aircraft acts as a 'faraday's cage' the magnetisation associated with a lightning discharge hardly has an effect on the magnetic compass
 While flying through air that is electrically charged the aircraft is likely to become a charge carrier itself and can initiate a lightning discharge.
While flying through air that is electrically charged the aircraft is likely to become a charge carrier itself and can initiate a lightning discharge. Most tornadoes have a life span that lasts for ?
Question 151-33 : A few minutes up to 30 minutes approximately one hour several hours not more than one minute
 A few minutes up to 30 minutes.
A few minutes up to 30 minutes. During an ils approach on rwy 33 a northwesterly wind is blowing parallel to ?
Question 151-34 : Without the pilot's intervention the aircraft is likely to fly below the designated glide path with increasing deviation from it without the pilot's intervention the aircraft is likely to fly above the designated glide path with increasing deviation from it a deviation from the glide path will not have to be considered since there is no significant wind shear to be expected without the pilot's intervention the aircraft is likely to fly above the designated glide path with decreasing deviation from it
 Without the pilot's intervention, the aircraft is likely to fly below the designated glide path with increasing deviation from it.
Without the pilot's intervention, the aircraft is likely to fly below the designated glide path with increasing deviation from it. Mark the correct statement concerning the flight through an inversion caused by ?
Question 151-35 : During climb the reduced air density above the inversion layer will cause a certain decrease in the aircraft performance ie lift and thrust and the pilot will experience a sudden improvement of visibility during climb the increased air density above the inversion layer will cause a certain increase in the aircraft performance ie lift and thrust and the pilot will experience a gradual change of the cross wind component during climb the pilot of an aircraft probably will experience a slight deterioration of flight visibility when breaking through the top of the inversion layer and the general aircraft performance will decrease the pilot of an aircraft probably will experience a gradual increase of the cross wind component and a gradual improvement of flight visibility when breaking through the base of the inversion layer during descent
 During climb, the reduced air density above the inversion layer will cause a certain decrease in the aircraft performance (ie: lift and thrust) and the pilot will experience a sudden improvement of visibility.
During climb, the reduced air density above the inversion layer will cause a certain decrease in the aircraft performance (ie: lift and thrust) and the pilot will experience a sudden improvement of visibility. Clouds will mainly consist of supercooled water droplets when the temperature is ?
Question 151-36 : Between 0°c and 15°c between 5°c and 30°c between 30°c and 40°c below 40°c
 Between 0°c and -15°c.
Between 0°c and -15°c. A stormscope is ?
Question 151-37 : An instrument on board an aircraft to detect electrical discharges an instrument to detect wind shear by means of the doppler effect during flight the technical term jargon for a radar scope showing thunderstorms an instrument to measure wind velocity
 An instrument on board an aircraft to detect electrical discharges.
An instrument on board an aircraft to detect electrical discharges. Most tornadoes have a speed of movement that usually ranges from ?
Question 151-38 : 20 to 40 knots 100 to 140 knots 30 to 70 knots 120 to 180 knots
 20 to 40 knots.
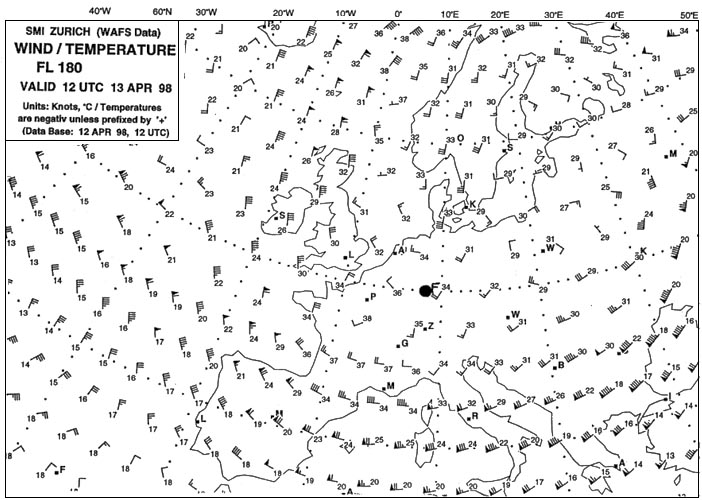
20 to 40 knots. Which of the following statements regarding the development of valley ?
Question 151-39 : Valley inversions often are a result of radiation cooling in combination with gravity both affecting the air at the surface of a mountain slope usually a valley inversion is initiated by radiation cooling and anabatic winds which are due to orographic conditions the most important prerequisite for the development of valley inversions is warm air ascending along the mountain slope thus leaving cooler air behind in the bottom of the valley the predominant factor in the development process of valley inversions is the non uniformity of incident solar radiation due to orographic conditions in combination with density variations within the air
 Valley inversions often are a result of radiation cooling in combination with gravity, both affecting the air at the surface of a mountain slope.
Valley inversions often are a result of radiation cooling in combination with gravity, both affecting the air at the surface of a mountain slope. During the preparation for approach to zurich airport 1416 ft/amsl a pilot ?
Question 151-40 : For wind shear just above the inversion for freezing precipitation below the inversion for fog below the inversion that the performance of the engine will be reduced from inversion level down to ground
 For wind shear just above the inversion.
For wind shear just above the inversion. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5999 Free Training Exam
