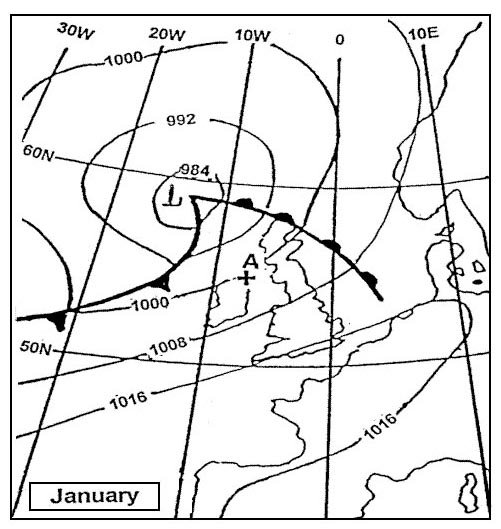
Flight visibility from the cockpit during approach in a tropical downpour can ? [ Certification weather ]
Question 149-1 : Tens of metres about 1000 metres about 200 metres about 500 metres
Which of the following factors have the greatest effect on the formation of the ?
Question 149-2 : Cloud temperature and droplet size aircraft speed and size of cloud droplets aircraft speed and curvature of the airfoil relative humidity inside the cloud
 Cloud temperature and droplet size
Cloud temperature and droplet size Hoar frost is most likely to form when ?
Question 149-3 : Taking off from an airfield with a significant ground inversion sky clear flying inside convective clouds flying inside stratiform clouds flying in supercooled drizzle
 Taking off from an airfield with a significant ground inversion (sky clear).
Taking off from an airfield with a significant ground inversion (sky clear). Two aircraft one with a sharp wing profile s and the other with a thick ?
Question 149-4 : Aircraft s experiences more icing than t aircraft t experiences more icing than s aircraft s and t experience the same amount of icing neither of the aircraft accumulate ice due to the small size of droplets
 Aircraft s experiences more icing than t.
Aircraft s experiences more icing than t. While descending through a cloud cover at high level a small amount of a white ?
Question 149-5 : Rime ice clear ice mixed ice frost
 Rime ice.
Rime ice. A small supercooled cloud droplet that collides with an airfoil will most likely ?
Question 149-6 : Freeze immediately and create rime ice travel back over the wing creating clear ice travel back over the wing creating rime ice freeze immediately and create clear ice
 Freeze immediately and create rime ice.
Freeze immediately and create rime ice. A flight is to depart from an airport with runways 09 and 27 surface wind is ?
Question 149-7 : Depart on runway 09 with a tailwind take off is not possible under these conditions depart runway 27 with as steep an ascent as possible depart runway 27 with maximum throttle during the passage through the inversion
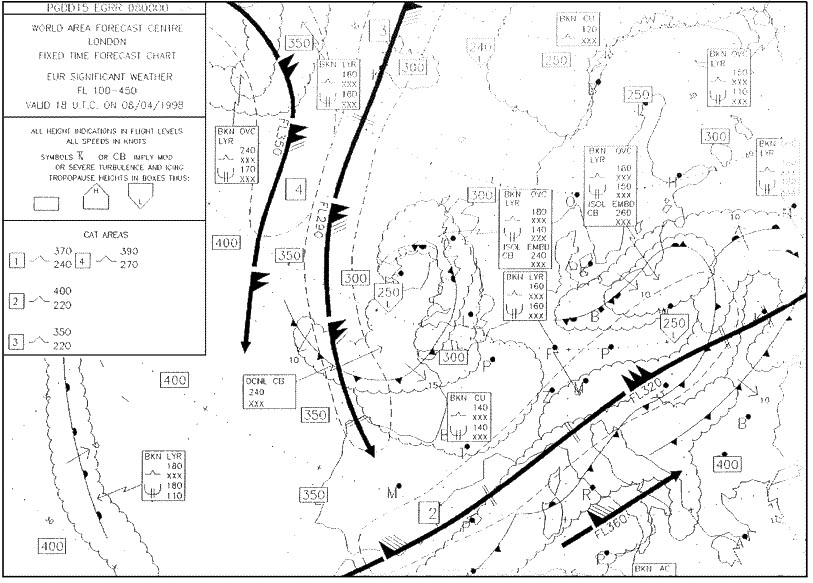 Depart on runway 09 with a tailwind.
Depart on runway 09 with a tailwind. The turbulence which occurs at high flight levels above fl 250 is mainly of the ?
Question 149-8 : The turbulence is a small scale one and can cause damage the manoeuvring of the aircraft will be made more difficult or even impossible for the passengers the flight will be unpleasant the turbulence is a large scale one waving so that the aircraft will be difficult to manoeuvre the passengers will feel some discomfort the turbulence can be resembled with the roughness of a washing board small scale and will not have influence on the aircraft and its solidity but will make flight a little more difficult the passengers will seldom notice anything of this turbulence the turbulence is wave like which makes the flight unpleasant for the passengers but the manoeuvring will not be affected essentially
 The turbulence is a small scale one and can cause damage. the manoeuvring of the aircraft will be made more difficult or even impossible. for the passengers the flight will be unpleasant.
The turbulence is a small scale one and can cause damage. the manoeuvring of the aircraft will be made more difficult or even impossible. for the passengers the flight will be unpleasant. Aircraft struck by lightning may sometimes get considerable damage and at least ?
Question 149-9 : Aircraft made by composite material may get severe damage the crew may be blinded and temporarily lose the hearing an aircraft made by metal has a certain capacity to attract a lightning but the lightning will follow the surface and therefore no damage will be caused an aircraft has in the atmosphere the same qualities as a 'faradays cage' which means that struck of lightning seldom occurs but if it happens the result will be an occasional engine failure the crew may get a shock aircraft made by composite material can't conduct a lightning and will therefore very seldom be struck
 Aircraft made by composite material may get severe damage, the crew may be blinded and temporarily lose the hearing.
Aircraft made by composite material may get severe damage, the crew may be blinded and temporarily lose the hearing. The most dangerous icing conditions are encountered in ?
Question 149-10 : Supercooled precipitation unstable clouds at medium levels zones where the air temperature is below 15°c icy clouds at high levels
 Supercooled precipitation.
Supercooled precipitation. After a prolonged vmc descent in very cold air you penetrate a humid air mass ?
Question 149-11 : Hoar frost rime ice clear ice smooth icing
 Hoar frost.
Hoar frost. An aircraft flies into supercooled rain in an area with a temperature below ?
Question 149-12 : Clear ice hoar frost rime ice granular frost
 Clear ice.
Clear ice. An aircraft flying at fl 45 oat 6°c obtains a reading of 1860 ft on its radio ?
Question 149-13 : 1030 hpa 996 hpa 1013 hpa 1042 hpa
 1030 hpa.
1030 hpa. Assuming that an initial 'trigger' force is present the conditions most likely ?
Question 149-14 : High relative humidity and instability throughout a deep layer high surface temperature low dew point and high dry adiabatic lapse rate rapid orographic cooling of cloud containing ice crystals intense surface heating anticyclonic pressure system and relatively high freezing level
 High relative humidity and instability throughout a deep layer.
High relative humidity and instability throughout a deep layer. Convective weather phenomena include ?
Question 149-15 : Thunderstorms hail tornadoes wind gusts heavy showers lightning strikes thunderstorms tornadoes hail haze wind gusts advection fog heavy showers lightning strikes hail mist squalls light rain over a large area hail lightning strikes wind lulls squalls stratocumulus low level wind maximum
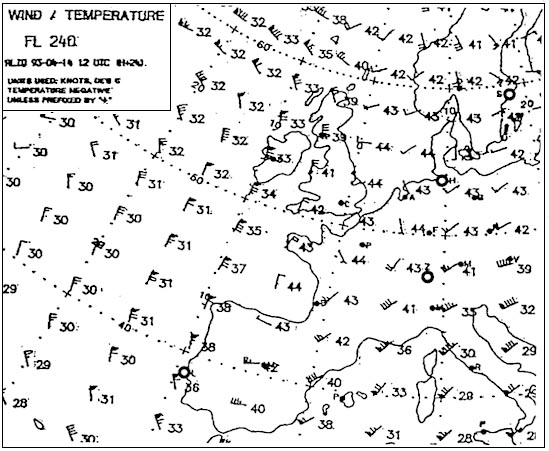 Thunderstorms, hail, tornadoes, wind gusts, heavy showers, lightning strikes
Thunderstorms, hail, tornadoes, wind gusts, heavy showers, lightning strikes For a vfr aircraft the conditions in which it could encounter severe airframe ?
Question 149-16 : Flight into freezing rain resulting in clear ice formation flight into supercooled rain resulting in rime ice formation flight into an area outside of clouds where the temperature is below 0°c resulting in rime ice formation flight between two cloud layers without precipitation resulting in clear ice formation
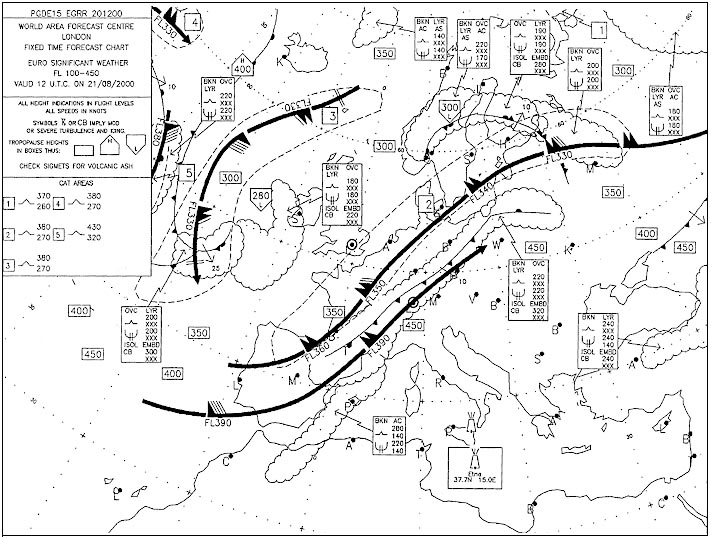 Flight into freezing rain, resulting in clear ice formation
Flight into freezing rain, resulting in clear ice formation Hazardous hailstones reaching the ground are most likely to be experienced ?
Question 149-17 : In continental interiors in middle latitudes over the sea near the equator in continental interiors near the equator over the sea in middle latitudes
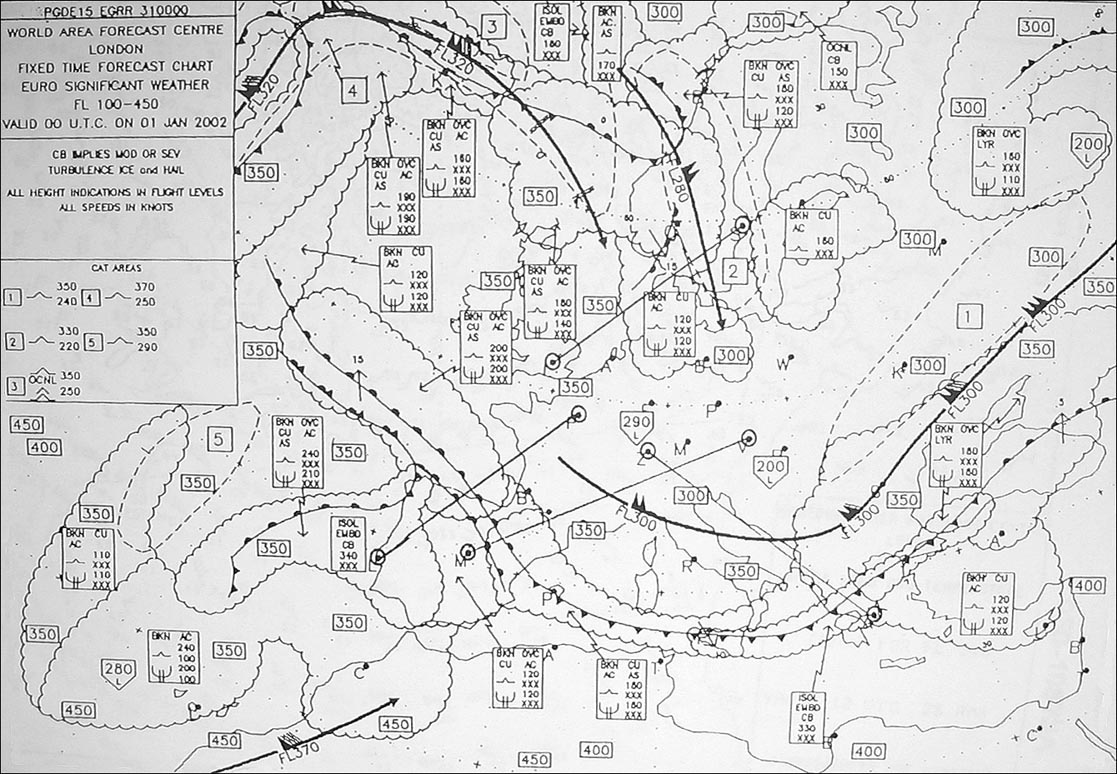 In continental interiors in middle latitudes.
In continental interiors in middle latitudes. Ice accretion to the airframe is likely to be most hazardous at temperatures ?
Question 149-18 : Between 0°c and 23°c in large cu between 0°c and 17°c in as between 0°c and 17°c in st below 40°c in cb
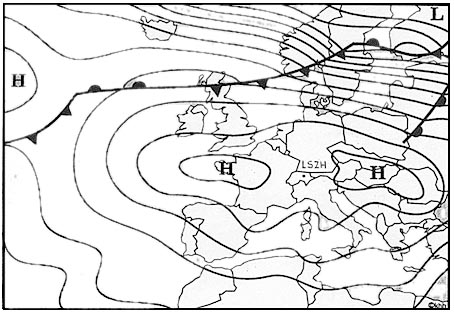 Between 0°c and -23°c in large cu.
Between 0°c and -23°c in large cu. In a mountainous area the most hazardous flying conditions associated with ?
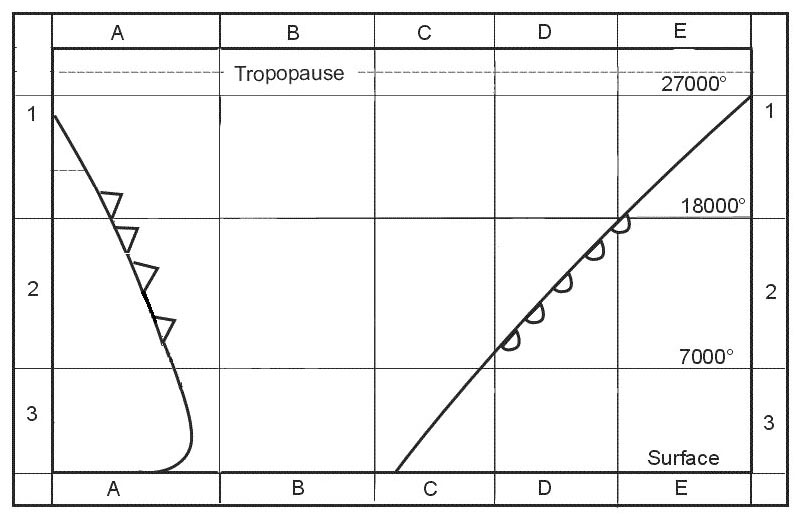
Question 149-19 : In the vicinity of the 'roll' cloud or rotor zone beneath the first wave on the leeward side on the windward side of the mountain just above the 'cap' cloud just above the lenticular cloud on the windward side between the troughs of the waves particularly 30 nm to 50 nm downwind and close to the tropopause
 In the vicinity of the 'roll' cloud or rotor zone beneath the first wave on the leeward side
In the vicinity of the 'roll' cloud or rotor zone beneath the first wave on the leeward side In addition to a stable layer of air over a substantial mountain range the ?
Question 149-20 : Wind speed excess of 20 kt at the surface and increasing with height wind direction perpendicular to the general direction of the range steep dry adiabatic lapse rate wind speed increasing and changing direction rapidly with increase in height conditional instability wind speed constant from a direction parallel to the mountain range significant moisture loss due to precipitation rapid lowering of the tropopause in the area of the mountain range
 Wind speed excess of 20 kt at the surface and increasing with height, wind direction perpendicular to the general direction of the range.
Wind speed excess of 20 kt at the surface and increasing with height, wind direction perpendicular to the general direction of the range. Mountain waves should be expected ?
Question 149-21 : On the downwind side of the mountain chain when instability is high directly over the mountain chain on the upwind side of the mountain chain
 On the downwind side of the mountain chain.
On the downwind side of the mountain chain. The conditions most favourable to the formation of mountain waves are ?
Question 149-22 : Wind direction approximately at right angles to the mountain range wind speed 30 kt and steadily increasing with height an inversion just above the crest level with less stable air above and below wind direction parallel to the general alignment of the mountain range wind speed increasing with height intense surface heating wind speed less than 15 kt and wind direction at right angles to mountains intense radiation cooling at night particularly at the higher levels wind direction parallel to the mountain range wind speed increasing with height extensive isothermal layer between mountain crests and the tropopause
 Wind direction approximately at right angles to the mountain range - wind speed 30 kt and steadily increasing with height - an inversion just above the crest level with less stable air above and below.
Wind direction approximately at right angles to the mountain range - wind speed 30 kt and steadily increasing with height - an inversion just above the crest level with less stable air above and below. The formation of clear ice on the leading edges of an aircraft is most likely ?
Question 149-23 : Relatively slow freezing of large supercooled water droplets instantaneous freezing of small supercooled water droplets instantaneous freezing of large supercooled water droplets and snow crystals relatively slow freezing of small supercooled water droplets and ice crystals
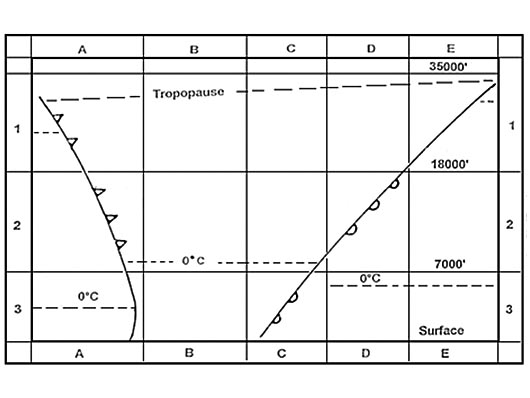 Relatively slow freezing of large supercooled water droplets.
Relatively slow freezing of large supercooled water droplets. Thunderstorms are often preceded by ?
Question 149-24 : Altocumulus castellanus nimbostratus altostratus altocumulus lenticularis
 Altocumulus castellanus.
Altocumulus castellanus. Thunderstorms reach their greatest intensity during the ?
Question 149-25 : Mature stage cumulus stage dissipating stage period in which precipitation is not falling
 Mature stage.
Mature stage. What intensity and type of airframe icing is most likely to occur when aircraft ?
Question 149-26 : Light or moderate hoar frost moderate opaque rime nil ice light opaque rime and light clear ice
 Light or moderate hoar frost.
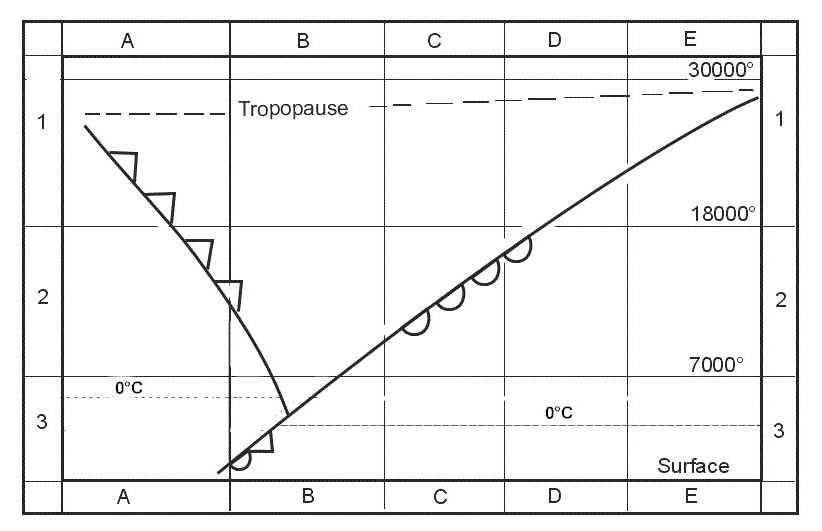
Light or moderate hoar frost. What intensity and type of airframe icing is most likely to occur when flying ?
Question 149-27 : Light rime severe clear moderate hoar frost moderate clear
 Light - rime.
Light - rime. What is a microburst downburst ?
Question 149-28 : A concentrated downdraft with high speeds and a lower temperature than the surrounding air a concentrated downdraft with high speeds and a higher temperature than the surrounding air an extremely strong wind gust in a tropical revolving storm a small low pressure system where the wind circulates with very high speeds
 A concentrated downdraft with high speeds and a lower temperature than the surrounding air.
A concentrated downdraft with high speeds and a lower temperature than the surrounding air. What visibility is most likely to be experienced at 1400 utc .eddf 272200z ?
Question 149-29 : 9000 metres 4000 metres 1000 metres 1600 metres
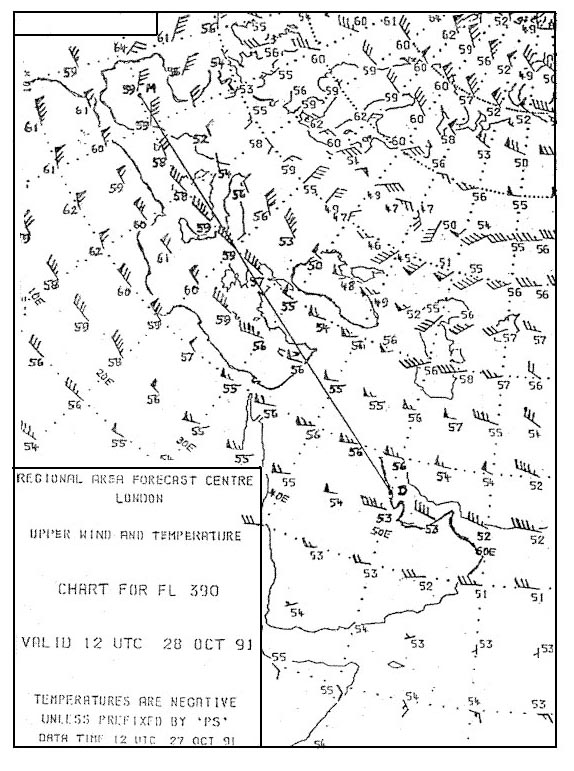 9000 metres
9000 metres Which statement is correct concerning a mountain ridge where a marked mountain ?
Question 149-30 : Ragged altocumulus lenticularis is an indication for the presence of moderate/severe turbulence at the level of these clouds the atmosphere is unstable at the level of the mountain tops there are always rotor clouds the axis of a rotor is horizontal and perpendicular to the mountains
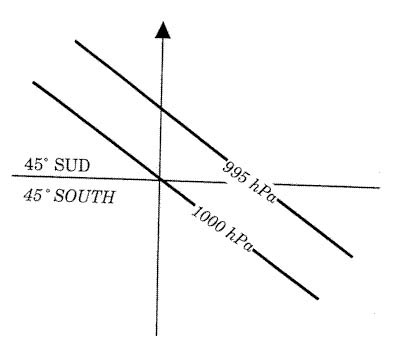 Ragged altocumulus lenticularis is an indication for the presence of moderate/severe turbulence at the level of these clouds
Ragged altocumulus lenticularis is an indication for the presence of moderate/severe turbulence at the level of these clouds Which thunderstorms move forward the fastest ?
Question 149-31 : Frontal thunderstorms orographic thunderstorms thermal thunderstorms thunderstorms formed by lifting processes
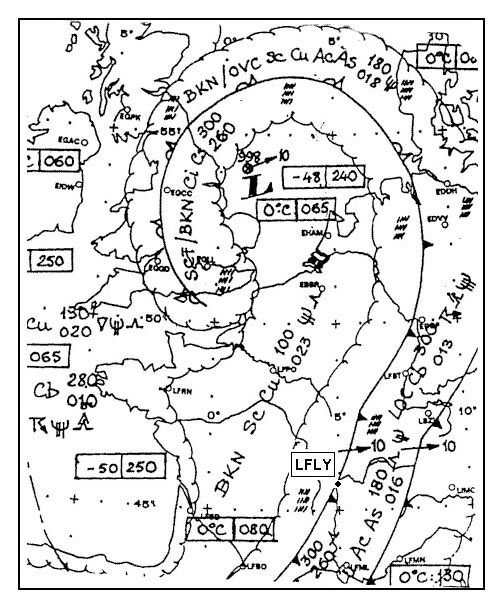 Frontal thunderstorms.
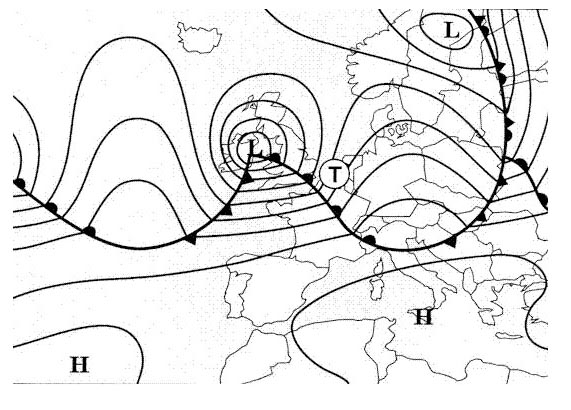
Frontal thunderstorms. Which weather chart gives information about icing ?
Question 149-32 : Significant weather chart 500 hpa chart surface chart 700 hpa chart
 Significant weather chart.
Significant weather chart. Lenticular clouds in mountainous areas indicate ?
Question 149-33 : Turbulence unstable air an inversion light variable winds
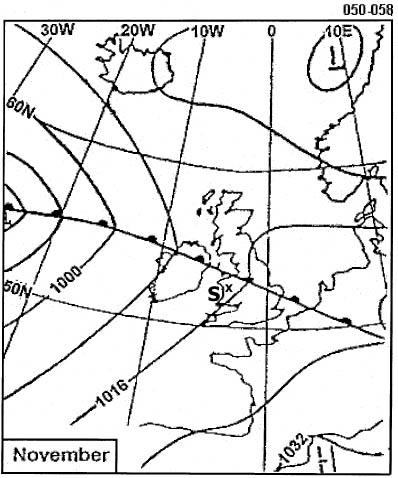 Turbulence.
Turbulence. Which of the following statements about lightnings and lightning strikes is ?
Question 149-34 : The aircraft is temporarily part of the lightning trajectory spherical lightnings often penetrate into aircraft compasses and electronics are always affected lightning strikes always cause heavy damage
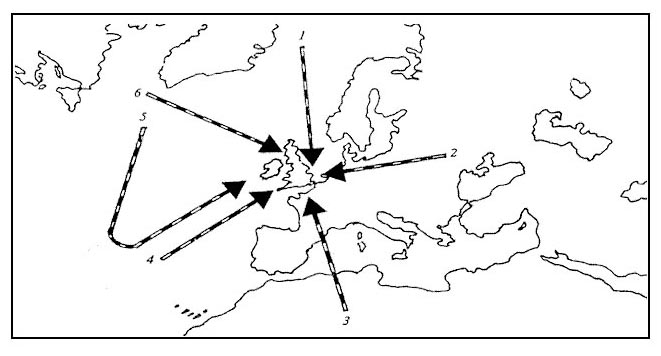 The aircraft is temporarily part of the lightning trajectory.
The aircraft is temporarily part of the lightning trajectory. Which of the following situations favours the formation of heavy thunderstorms ?
Question 149-35 : A cold front approaching a mountain range in the evening the passage of a warm front in the morning a cold front on the leeward side of a mountain range a warm sector moving over a snow covered ground
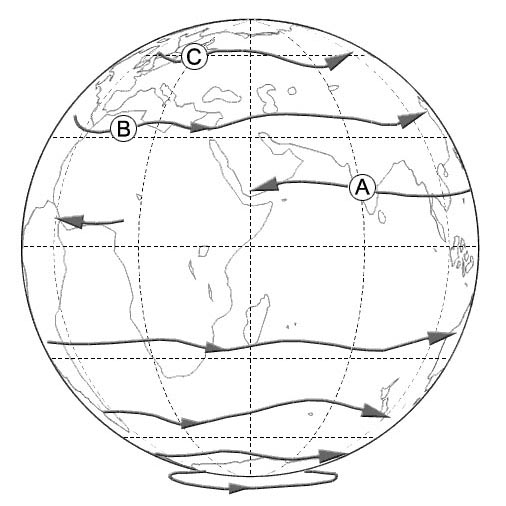 A cold front approaching a mountain range in the evening.
A cold front approaching a mountain range in the evening. With the development of a thunderstorm at what stage will there be only ?
Question 149-36 : Initial stage mature stage anvil stage dissipating stage
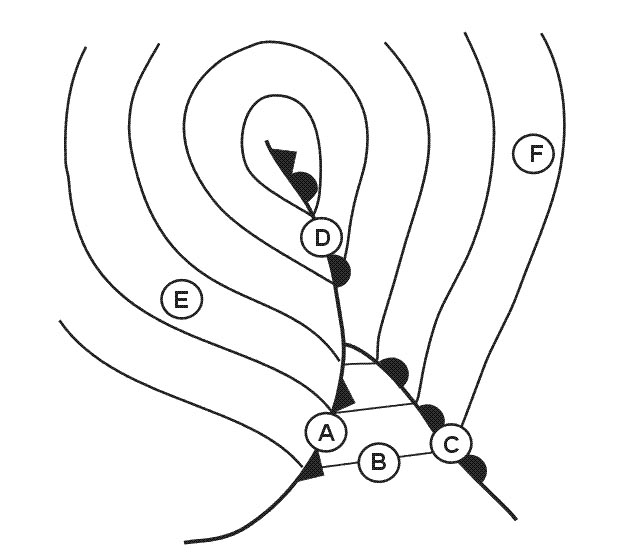 Initial stage.
Initial stage. Where does wind shear occur ?
Question 149-37 : At any level in the atmosphere if associated with either a change of wind direction and/or wind speed wind shear of any significance occurs only in connection with jetstreams wind shear occurs primarily at lower altitudes in the vicinity of mountain waves wind shear occurs only when there is a strong temperature inversion or when the jetstream is associated with a strong depression
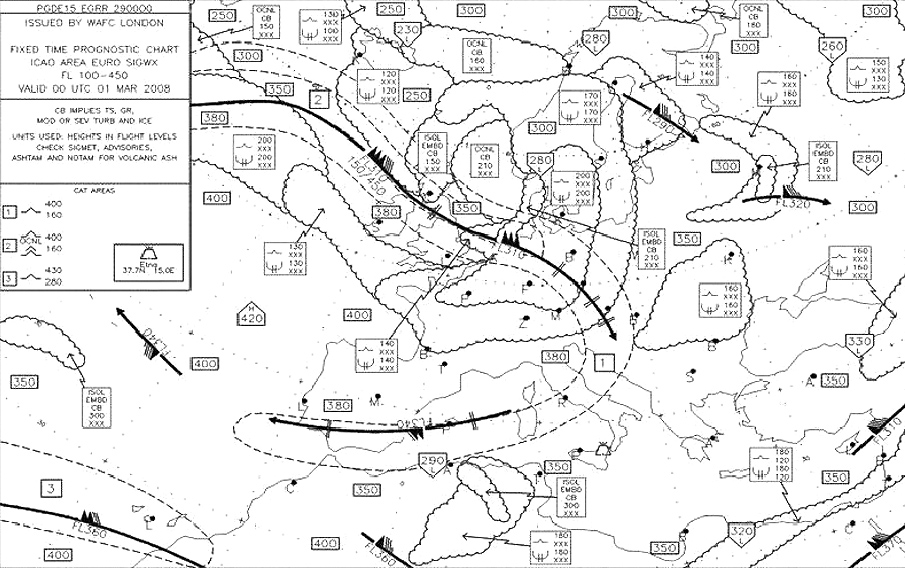 At any level in the atmosphere if associated with either a change of wind direction and/or wind speed.
At any level in the atmosphere if associated with either a change of wind direction and/or wind speed. When severe mountain waves are present where would the area of most severe ?
Question 149-38 : In the rotor zone just above the cap cloud on the windward side of the mountain range just below the tropopause
 In the rotor zone.
In the rotor zone. Taf lszh 250600z 250716 00000kt 0100 fg vv001 becmg 0810 0800 vv002 becmg 1012 ?
Question 149-39 : Visibility 2 5 kilometres mist cloud base 500 feet wind speed 5 knots visibility 800 metres fog wind from 230° cloud base 500 feet visibility 800 metres fog vertical visibility 200 feet calm visibility 6 kilometres cloud base 500 feet wind speed 5 knots
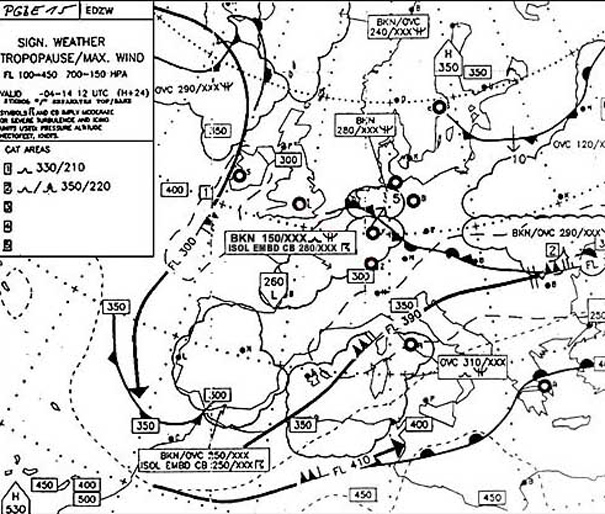 Visibility 2,5 kilometres, mist, cloud base 500 feet, wind speed 5 knots
Visibility 2,5 kilometres, mist, cloud base 500 feet, wind speed 5 knots Which statement is correct for microbursts ?
Question 149-40 : The diameter of the affected area on the surface does not exceed 4 km they only develop below convective clouds with heavy rain they occur in the tropics only their downdraft is warmer than the surroundings
 The diameter of the affected area on the surface does not exceed 4 km.
The diameter of the affected area on the surface does not exceed 4 km. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5919 Free Training Exam
