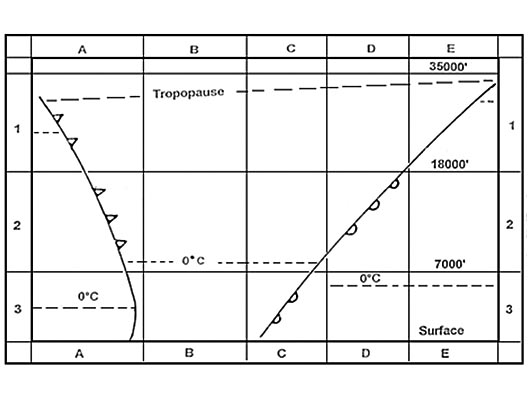
Atmospheric soundings give the following temperature profile .3000 ft ? [ Revision flight ]
Question 138-1 : Fl 150 fl 220 fl 80 fl 180
 Fl 150.
Fl 150. Half the mass of the atmosphere is found in the first ?
Question 138-2 : 5 km 11 km 3 km 8 km
The thickness of the troposphere varies with ?
Question 138-3 : Latitude longitude rotation of the earth the wind
 Latitude.
Latitude. In the lower part of the stratosphere the temperature ?
Question 138-4 : Is almost constant decreases with altitude increases with altitude increases at first and decreases afterward
 Is almost constant.
Is almost constant. Which of the following conditions would cause the altimeter to indicate a lower ?
Question 138-5 : Air temperature higher than standard atmospheric pressure lower than standard pressure altitude the same as indicated altitude air temperature lower than standard
 Air temperature higher than standard.
Air temperature higher than standard. The qff at an airfield located 400 metres above sea level is 1016 hpa the air ?
Question 138-6 : Less than 1016 hpa 1016 hpa more than 1016 hpa it is not possible to give a definitive answer
 Less than 1016 hpa.
Less than 1016 hpa. The qnh at an airfield located 200 metres above sea level is 1009 hpa the air ?
Question 138-7 : More than 1009 hpa 1009 hpa less than 1009 hpa it is not possible to give a definitive answer
 More than 1009 hpa.
More than 1009 hpa. The qnh at an airfield located 200 metres above sea level is 1022 hpa the air ?
Question 138-8 : It is not possible to give a definitive answer more than 1022 hpa 1022 hpa less than 1022 hpa
 It is not possible to give a definitive answer.
It is not possible to give a definitive answer. The qnh at an airfield located 0 metres above sea level is 1022 hpa the air ?
Question 138-9 : 1022 hpa less than 1022 hpa more than 1022 hpa it is not possible to give a definitive answer
 1022 hpa.
1022 hpa. The qnh at an airfield in california located 69 metres below sea level is 1018 ?
Question 138-10 : More than 1018 hpa 1018 hpa it is not possible to give a definitive answer less than 1018 hpa
 More than 1018 hpa.
More than 1018 hpa. The qff at an airfield in california located 69 metres below sea level is 1030 ?
Question 138-11 : More than 1030 hpa less than 1030 hpa 1030 hpa it is not possible to give a definitive answer
 More than 1030 hpa
More than 1030 hpa If the qfe at locarno 200 metres above sea level is 980 hpa what is the ?
Question 138-12 : 1005 hpa 1000 hpa 1015 hpa 1010 hpa
 1005 hpa.
1005 hpa. If the qfe at locarno 200 metres above sea level is 1000 hpa what is the ?
Question 138-13 : 1025 hpa 985 hpa 990 hpa 1035 hpa
 1025 hpa.
1025 hpa. If the qnh at locarno 200 metres above sea level is 1015 hpa what is the ?
Question 138-14 : 990 hpa 995 hpa 1000 hpa 1005 hpa
 990 hpa.
990 hpa. If the qnh at locarno 200 metres above sea level is 1025 hpa what is the ?
Question 138-15 : 1000 hpa 995 hpa 1005 hpa 1025 hpa
 1000 hpa.
1000 hpa. If you are flying at fl 300 in an air mass that is 15°c warmer than a standard ?
Question 138-16 : 30°c 45°c 60°c 15°c
 -30°c.
-30°c. If you are flying at fl 100 in an air mass that is 10°c warmer than a standard ?
Question 138-17 : +5°c +15°c 10°c 15°c
 +5°c.
+5°c. If you are flying at fl 120 and the outside temperature is 2°c at what ?
Question 138-18 : Fl 110 fl 130 fl 150 fl 90
 Fl 110.
Fl 110. An aircraft flying at fl 100 from marseille qnh 1012 hpa to palma de mallorca ?
Question 138-19 : The air at palma de mallorca is warmer than that at marseille the air at palma de mallorca is colder than that at marseille the altimeters are erroneous and need to be tested one of the two qnh values may be incorrect
 The air at palma de mallorca is warmer than that at marseille.
The air at palma de mallorca is warmer than that at marseille. During a flight over the sea at fl 100 from marseille qnh 1012 hpa to palma de ?
Question 138-20 : None the reason for the change is that the air around palma is warmer than the air around marseille have your altimeter checked because its readings are obviously wrong recheck the qnh because one of the qnh values must be wrong compensate by heading further to the left
 None, the reason for the change is that the air around palma is warmer than the air around marseille
None, the reason for the change is that the air around palma is warmer than the air around marseille During a flight over the sea at fl 100 from marseille qnh 1016 hpa to palma de ?
Question 138-21 : The air at marseille is warmer than that at palma de mallorca one of the qnh values must be wrong the altimeter is faulty the air at palma de mallorca is warmer than that at marseille
 The air at marseille is warmer than that at palma de mallorca.
The air at marseille is warmer than that at palma de mallorca. During a flight over the sea at fl 135 the true altitude is 13500 feet local ?
Question 138-22 : It is colder than isa its average temperature is the same as isa it is warmer than isa there is insufficient information to make any assumption
 It is colder than isa.
It is colder than isa. An aircraft is flying over the sea at fl 90 the true altitude is 9100 feet ?
Question 138-23 : There is insufficient information to make any assumption it is colder than isa it is warmer than isa its average temperature is the same as isa
 There is insufficient information to make any assumption.
There is insufficient information to make any assumption. An aircraft is flying over the sea at fl 120 with a true altitude of 12000 feet ?
Question 138-24 : Its average temperature is the same as isa it is colder than isa it is warmer than isa there is insufficient information to come to any conclusion
 Its average temperature is the same as isa.
Its average temperature is the same as isa. An aircraft is flying over the sea at fl 100 with a true altitude of 10000 feet ?
Question 138-25 : It is warmer than isa its average temperature is about isa it is colder than isa there is insufficient information to come to any conclusion
 It is warmer than isa.
It is warmer than isa. Which layer of the atmosphere contains more than 90 per cent of all water vapour ?
Question 138-26 : Troposphere lower stratosphere upper stratosphere ozone layer
 Troposphere.
Troposphere. The temperature at fl 80 is +6°c what will the temperature be at fl 130 if the ?
Question 138-27 : 4°c 6°c 0°c +2°c
 -4°c.
-4°c. The temperature at fl 110 is 5°c what will the temperature be at fl 50 if the ?
Question 138-28 : +7°c +3°c 3°c 0°c
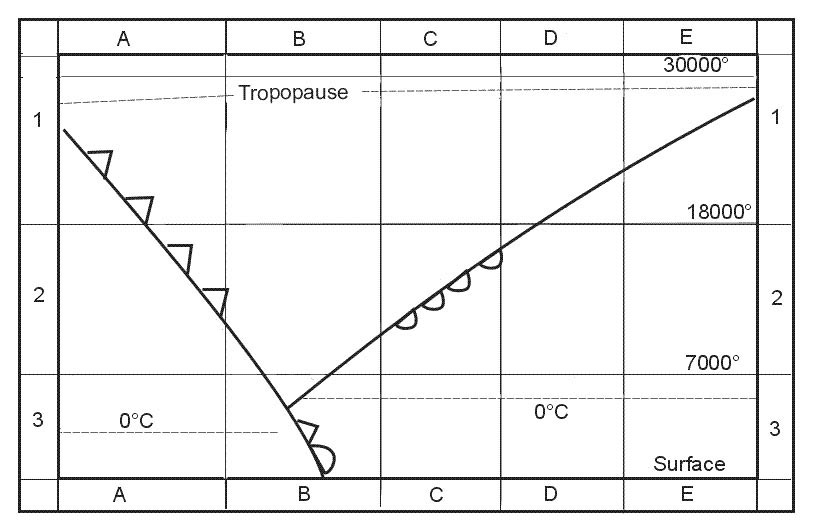 +7°c.
+7°c. The temperature at fl 160 is 22°c what will the temperature be at fl 90 if the ?
Question 138-29 : 8°c 4°c 0°c +4°c
 -8°c.
-8°c. A temperature of +15°c is recorded at an altitude of 500 metres above sea ?
Question 138-30 : +2°c +4°c 0°c 2°c
 +2°c.
+2°c. How would you characterise an air temperature of 15°c at the 700 hpa level ?
Question 138-31 : Low high within +/ 5°c of isa 20°c below standard
 Low.
Low. An air temperature of 30°c at the 300 hpa level over central europe in summer ?
Question 138-32 : High low very low within +/ 5°c of isa
 High.
High. How would you characterise an air temperature of 55°c at the 200 hpa level ?
Question 138-33 : Within +/ 5°c of isa high low very high
 Within +/-5°c of isa.
Within +/-5°c of isa. What is the technical term for an increase in temperature with altitude ?
Question 138-34 : Inversion subsidence adiabatic advection
 Inversion.
Inversion. The station pressure used in surface weather charts is ?
Question 138-35 : Qff qfe qnh qne
 Qff.
Qff. Which fl corresponds with the 300 hpa pressure level ?
Question 138-36 : Fl 300 fl 50 fl 100 fl 390
 Fl 300
Fl 300 Which fl corresponds with the 500 hpa pressure level ?
Question 138-37 : Fl 180 fl 390 fl 100 fl 160
 Fl 180.
Fl 180. Which fl corresponds with the 700 hpa pressure level ?
Question 138-38 : Fl 100 fl 180 fl 300 fl 390
 Fl 100.
Fl 100. Which fl corresponds with the 850 hpa pressure level ?
Question 138-39 : Fl 50 fl100 fl 300 fl 390
 Fl 50.
Fl 50. The qff at an airfield located 400 metres above sea level is 1016 hpa the air ?
Question 138-40 : More than 1016 hpa 1016 hpa less than 1016 hpa it is not possible to give a definitive answer
 More than 1016 hpa.
More than 1016 hpa. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5479 Free Training Exam
