Which fl corresponds with the 200 hpa pressure level ? [ Revision flight ]
Question 137-1 : Fl 390 fl 300 fl 50 fl 100
 Fl 390.
Fl 390. What is the approximate vertical interval which is equal to a pressure change ?
Question 137-2 : 15 m 50 ft 8 m 27 ft 32 m 105 ft 64 m 210 ft
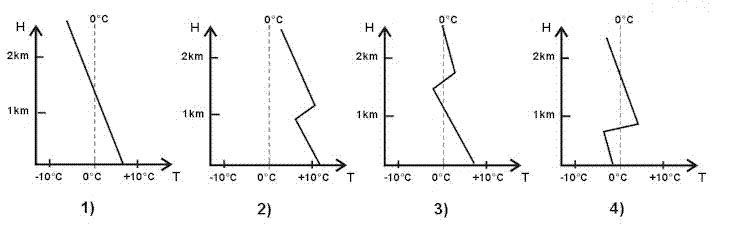
The temperature at fl 140 is 12°c what will the temperature be at fl 110 if ?
Question 137-3 : 6°c 18°c 9°c 15°c
 -6°c.
-6°c. If atmospheric conditions exist such that the temperature deviation is isa ?
Question 137-4 : 6240 ft 6000 ft 5900 ft 5760 ft
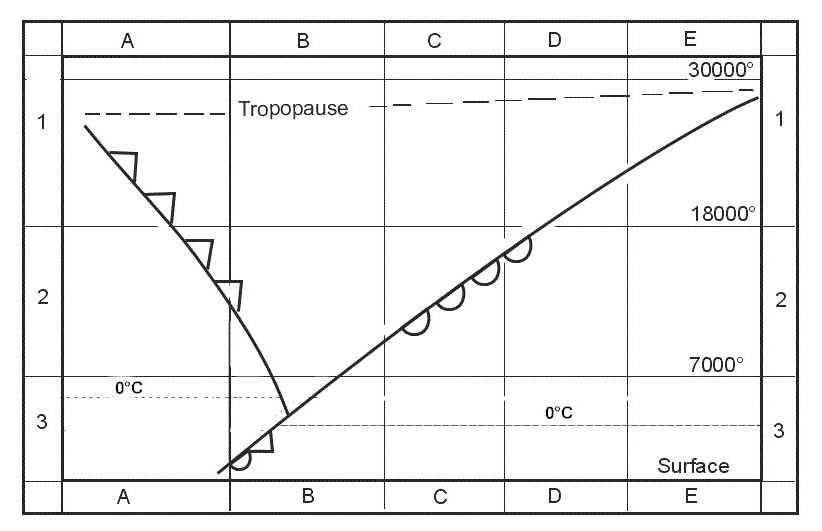
How does the height of the tropopause normally vary with latitude in the ?
Question 137-5 : It decreases from south to north it remains constant from north to south it remains constant throughout the year it increases from south to north
 It decreases from south to north.
It decreases from south to north. What approximately is the average height of the tropopause over the equator ?
Question 137-6 : 16 km 40 km 8 km 11 km
 16 km.
16 km. In which layer is most of the atmospheric humidity concentrated ?
Question 137-7 : Troposphere tropopause stratopause stratosphere
 Troposphere.
Troposphere. Under what condition does pressure altitude have the same value as density ?
Question 137-8 : At standard temperature when the altimeter has no position error at sea level when the temperature is 0°c when the altimeter setting is 1013 2 hpa
 At standard temperature.
At standard temperature. In the troposphere the decrease of pressure per 100 m increase in height ?
Question 137-9 : Is smaller at higher levels than at lower levels remains constant at all levels is greater at higher levels than at lower levels is in the order of 27 hpa near msl
 Is smaller at higher levels than at lower levels.
Is smaller at higher levels than at lower levels. In a situation with a weak pressure gradient and no thunderstorms around what ?
Question 137-10 : Apparently nothing because any changes would be small increase rapidly show strong fluctuations decrease rapidly
 Apparently nothing, because any changes would be small.
Apparently nothing, because any changes would be small. What pressure is defined as qfe ?
Question 137-11 : The pressure at field elevation the pressure of the altimeter the pressure reduced to sea level using actual temperatures the pressure reduced to sea level using isa temperatures
 The pressure at field elevation
The pressure at field elevation What is the approximate composition of the dry air by volume in the troposphere ?
Question 137-12 : 21% oxygen 78% nitrogen and the rest other gasses 10% oxygen 89% nitrogen and the rest other gasses 88% oxygen 9% nitrogen and the rest other gasses 50% oxygen 40% nitrogen and the rest other gasses
 21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen, and the rest other gasses.
21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen, and the rest other gasses. How does temperature vary with increasing altitude in the icao standard ?
Question 137-13 : Decreases increases at first it increases and higher up it decreases remains constant
 Decreases
Decreases What is the boundary layer between troposphere and stratosphere called ?
Question 137-14 : Tropopause ionosphere stratosphere atmosphere
 Tropopause.
Tropopause. An outside air temperature of 35°c is measured while cruising at fl 200 what ?
Question 137-15 : 10°c colder than isa 10°c warmer than isa 5°c warmer than isa 5°c colder than isa
 10°c colder than isa.
10°c colder than isa. The qnh of an airport at sea level is 983 hpa and the temperature deviation ?
Question 137-16 : 8640 ft 10160 ft 9740 ft 11460 ft
 8640 ft.
8640 ft. What information is required to convert a minimum safe altitude into a lowest ?
Question 137-17 : Lowest value of qnh and the highest negative temperature deviation from isa highest value of qnh and the highest negative temperature deviation from isa highest value of qnh and the highest positive temperature deviation from isa lowest value of qnh and the lowest negative temperature deviation from isa
 Lowest value of qnh and the highest negative temperature deviation from isa.
Lowest value of qnh and the highest negative temperature deviation from isa. What is the relationship if any between qfe and qnh at an airport situated 50 ?
Question 137-18 : Qfe is greater than qnh qfe is smaller than qnh qfe equals qnh no clear relationship exists
 Qfe is greater than qnh.
Qfe is greater than qnh. You plan a flight over a mountain range at a true altitude of 15000 ft/amsl the ?
Question 137-19 : 16230 ft 15690 ft 14370 ft 13830 ft
 16230 ft.
16230 ft. During a flight at fl 100 from marseille qnh 1012 hpa to palma de mallorca qnh ?
Question 137-20 : The air at marseille is warmer than that at palma de mallorca the altimeters are erroneous and need to be tested the air at marseille is colder than that at palma de mallorca one of the two qnh values may be incorrect
 The air at marseille is warmer than that at palma de mallorca.
The air at marseille is warmer than that at palma de mallorca. An aircraft lands at an airport airport elevation 1240 ft qnh 1008 hpa the ?
Question 137-21 : 1375 ft 1200 ft 1105 ft 1280 ft
 1375 ft.
1375 ft. After landing at an aerodrome aerodrome elevation 1715 ft the altimeter ?
Question 137-22 : 1028 hpa 1015 hpa 1013 hpa 998 hpa
 1028 hpa.
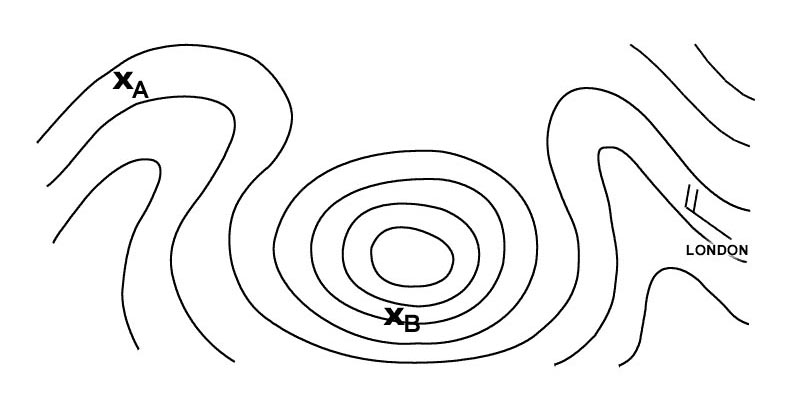
1028 hpa. You intend to overfly a mountain range the recommended minimum flight altitude ?
Question 137-23 : 14100 ft 13830 ft 14370 ft 15900 ft
 14100 ft.
14100 ft. You are flying at fl 130 and your true altitude is 12000 ft what is the ?
Question 137-24 : Isa 20°c isa +/ 0°c isa +20°c isa +12°c
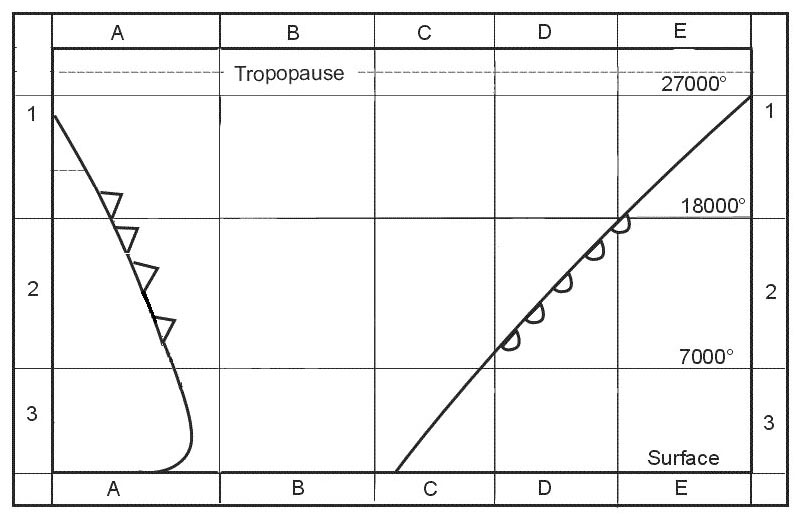 Isa -20°c.
Isa -20°c. Which one of the following statements applies to the tropopause ?
Question 137-25 : It separates the troposphere from the stratosphere it is by definition an isothermal layer it indicates a strong temperature lapse rate it is by definition a temperature inversion
 It separates the troposphere from the stratosphere
It separates the troposphere from the stratosphere The 0° isotherm is forecast to be at fl 50 at what fl would you expect a ?
Question 137-26 : Fl 80 fl 20 fl 100 fl 110
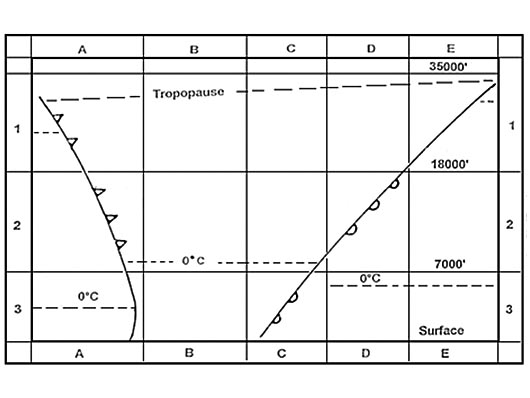 Fl 80.
Fl 80. A vertical spacing of 1000 ft is the standard required separation between two ?
Question 137-27 : Less than 1000 ft it remains 1000 ft more than 1000 ft without qnh information it can not be determined
 Less than 1000 ft.
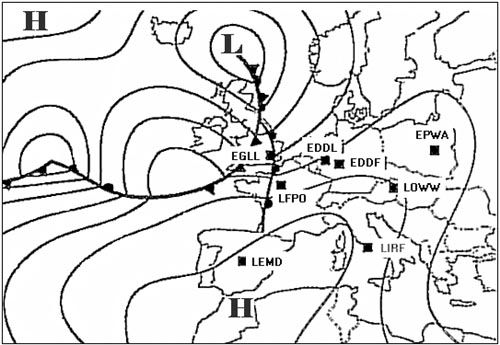
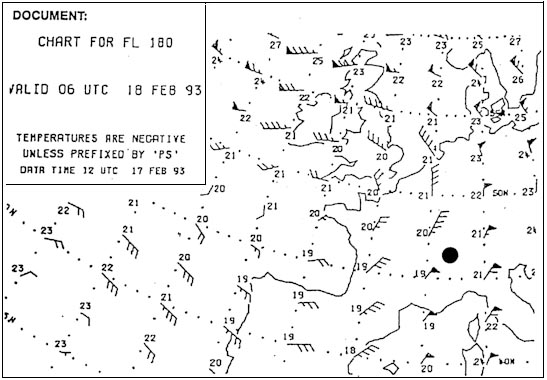
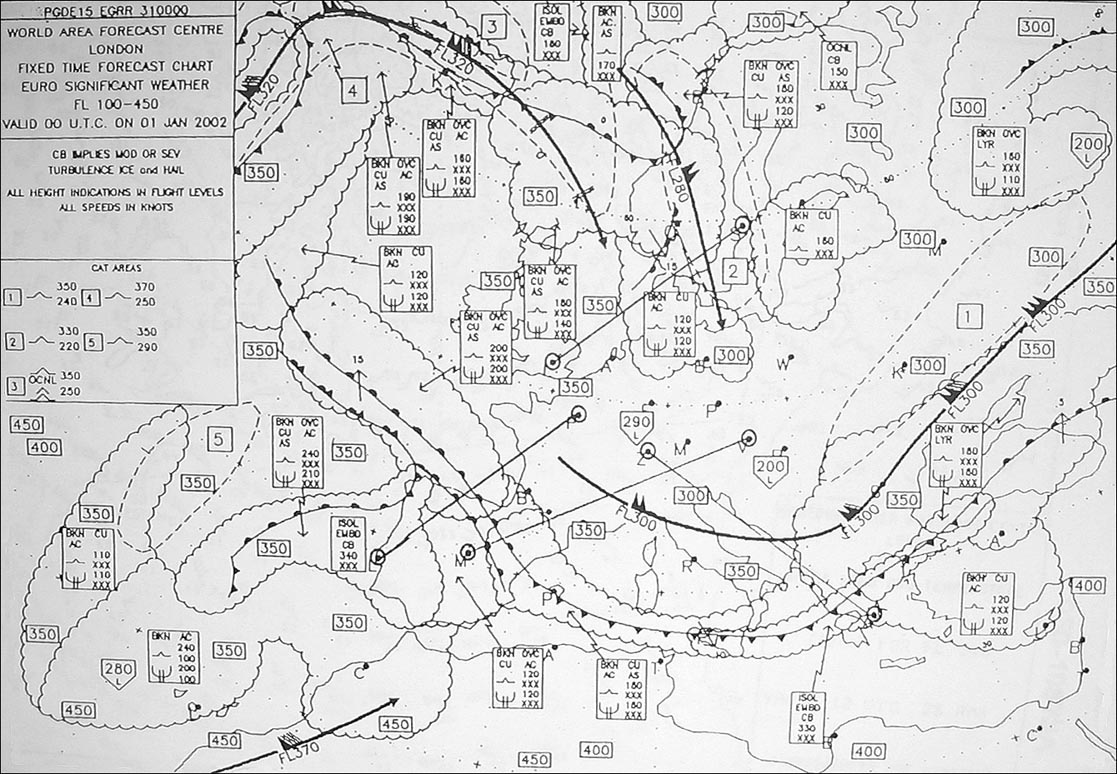
Less than 1000 ft. Over paris at what flight level would you expect to find the tropopause ?
Question 137-28 : Fl 300 fl 330 fl 150 fl 280
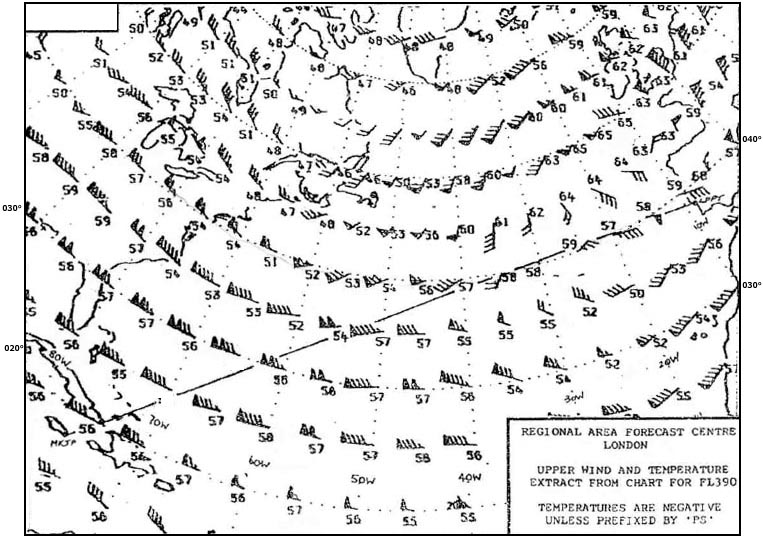 Fl 300.
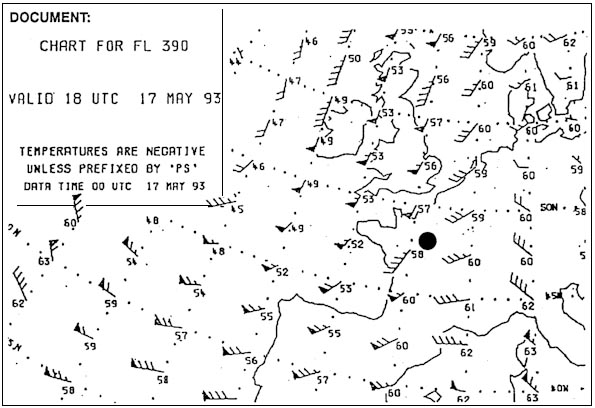
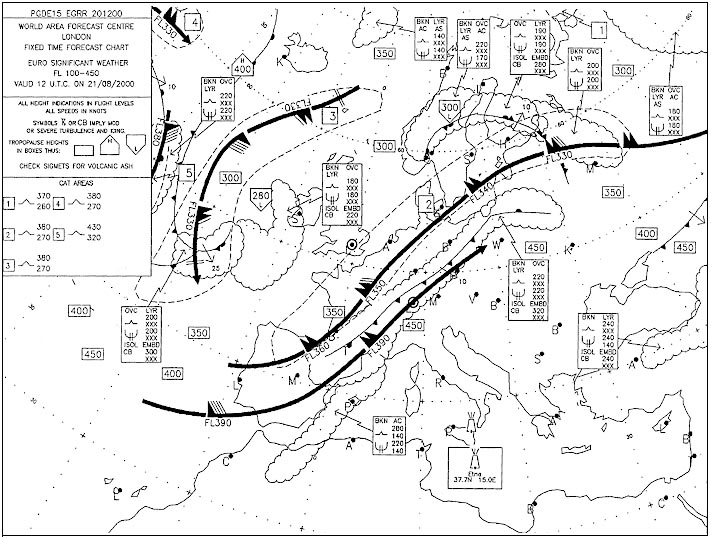
Fl 300. What is the approximate height of the tropopause between munich and helsinki . ?
Question 137-29 : Fl 340 fl 280 fl 300 fl 390
 Fl 340.
Fl 340. At what approximate flight level is the tropopause over frankfurt . 276 ?
Question 137-30 : Fl 330 fl 300 fl 350 fl 240
 Fl 330.
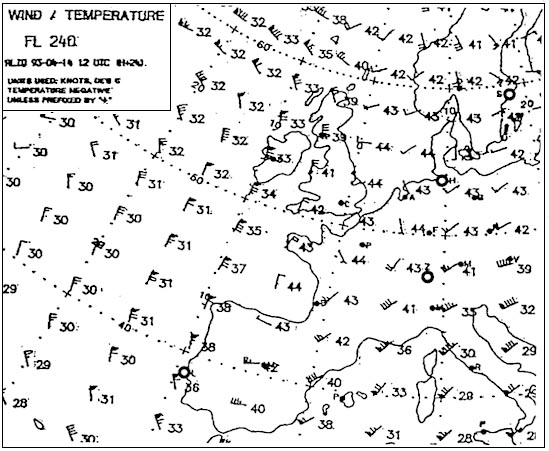
Fl 330. The temperature at fl 330 overhead london will be . 278 ?
Question 137-31 : 45°c 39°c 33°c 57°c
 -45°c.
-45°c. What is the average temperature at fl 160 between oslo and paris . 282 ?
Question 137-32 : 19°c 23°c 15°c 25°c
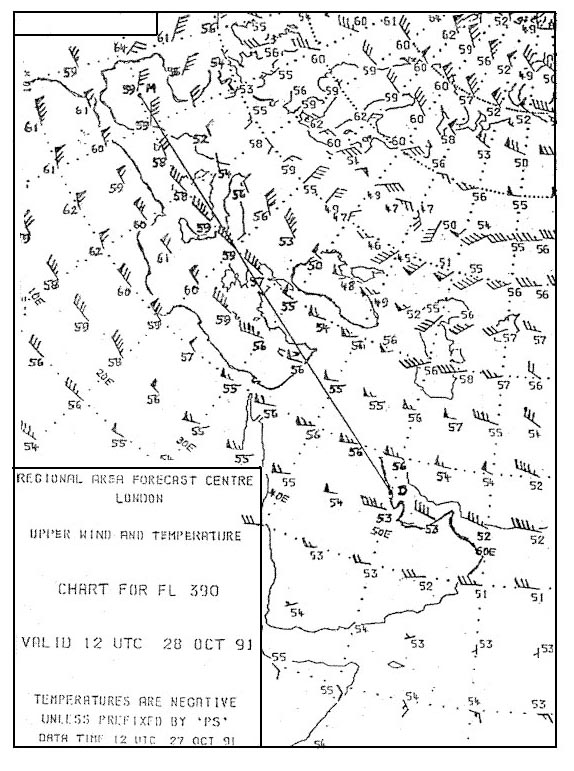 -19°c.
-19°c. What is the temperature deviation in degrees celsius from the icao standard ?
Question 137-33 : Isa 13°c isa 2°c isa +13°c isa +2°c
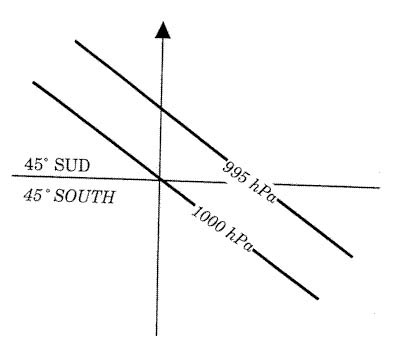 Isa -13°c
Isa -13°c What oat would you expect at fl 200 over geneva . 289 ?
Question 137-34 : 24°c 20°c 16°c 28°c
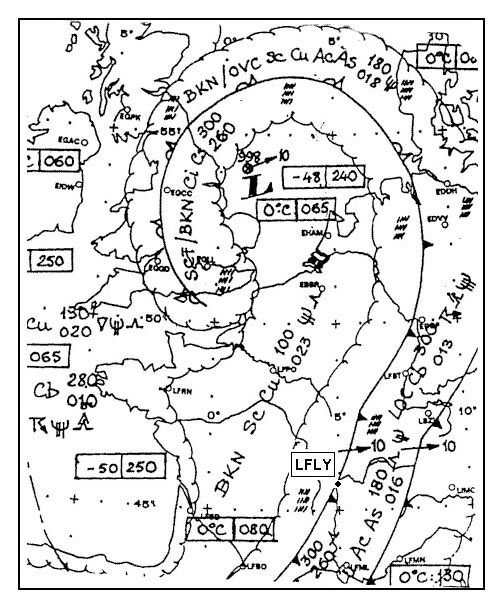 -24°c.
-24°c. An altimeter adjusted to 1013 hpa indicates an altitude of 3600 ft should this ?
Question 137-35 : 3006 ft 2922 ft 4278 ft 4194 ft
 3006 ft.
3006 ft. In geneva the local qnh is 994 hpa the elevation of geneva is 1411 ft the qfe ?
Question 137-36 : 942 hpa 967 hpa 961 hpa 952 hpa
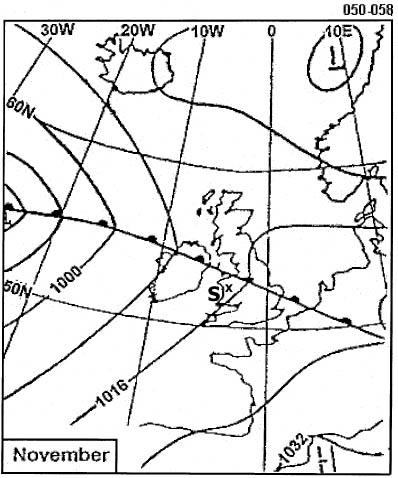 942 hpa.
942 hpa. An aircraft is flying at fl 80 the local qnh is 1000 hpa after the second ?
Question 137-37 : 7650 ft 8600 ft 8350 ft 8000 ft
 7650 ft.
7650 ft. The barometric compensator of an altimeter is locked on reference 1013 2 hpa ?
Question 137-38 : 20 ft 11 ft 10 ft 560 ft
 20 ft.
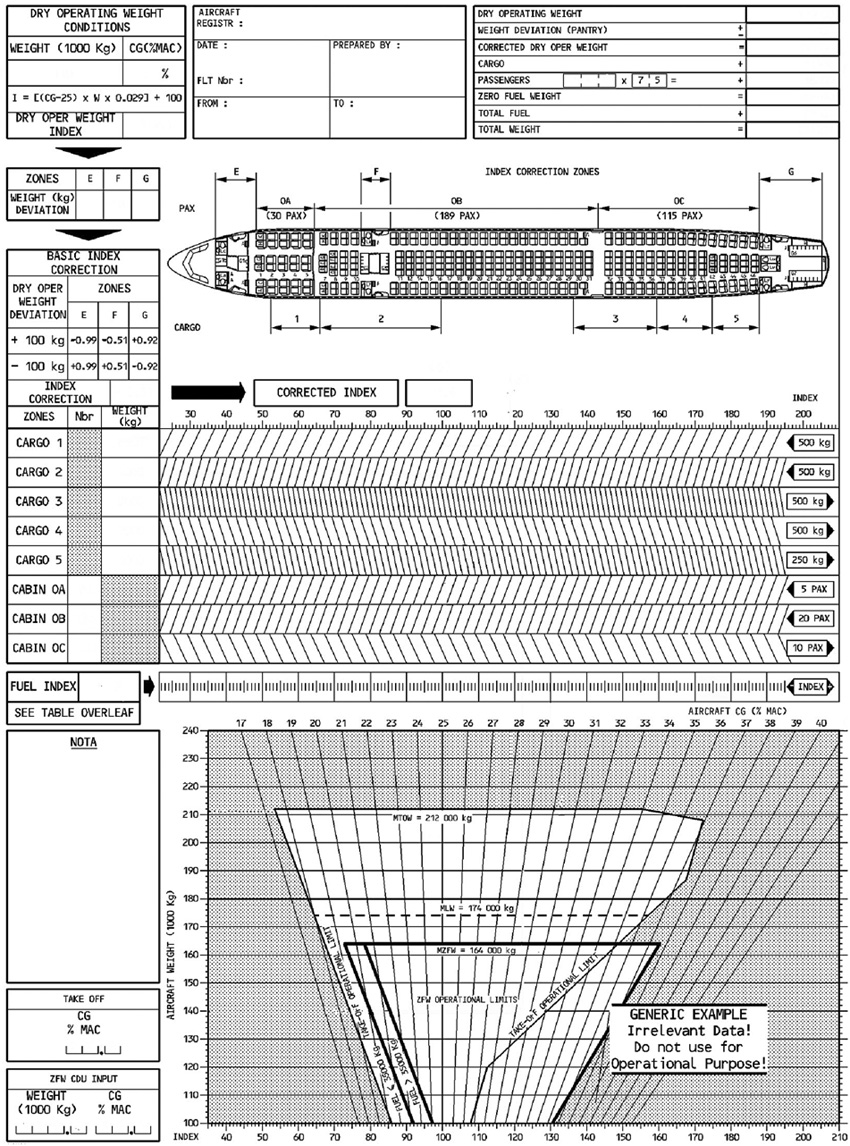
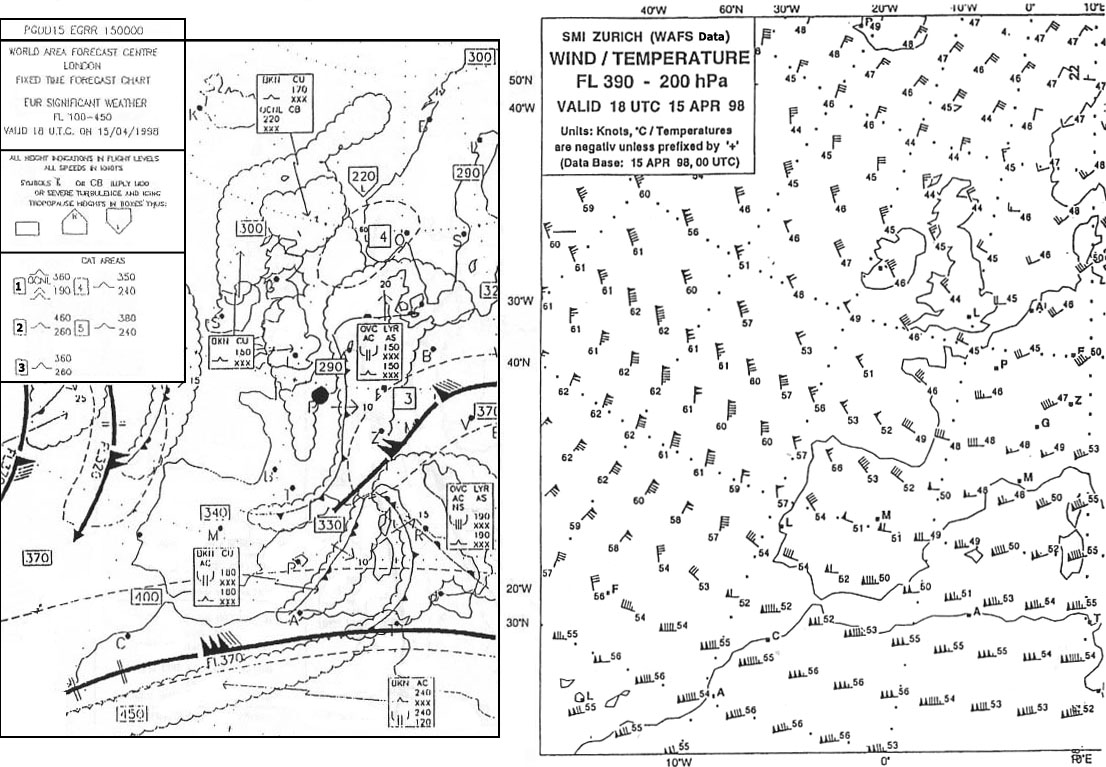
20 ft. The upper wind and temperature chart of 250 hpa corresponds in a standard ?
Question 137-39 : 34 000 ft 39 000 ft 30 000 ft 32 000 ft
 34 000 ft.
34 000 ft. Going from the equator to the north pole the altitude of the tropopause ?
Question 137-40 : Decreases and its temperature increases increases and its temperature increases increases and its temperature decreases decreases and its temperature decreases
 Decreases and its temperature increases.
Decreases and its temperature increases. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5439 Free Training Exam
