What process in an air mass leads to the creation of wide spread ns and as ? [ Revision flight ]
Question 136-1 : Lifting sinking convection process radiation
 Lifting.
Lifting. Which of the following cloud is classified as low level cloud ?
Question 136-2 : St cs as cc
 St
St Which of the following is most likely to lead to the dissipation of radiation ?
Question 136-3 : A marked increase in wind velocity near the ground a marked decrease in wind velocity close to the ground ground cooling caused by radiation during the night a build up of a high pressure area resulting in adiabatic warming associated with a sinking air mass
 A marked increase in wind velocity near the ground
A marked increase in wind velocity near the ground Which of the following conditions is most likely to lead to the formation of ?
Question 136-4 : Cold air moving over warm water warm air moving over cold water the sea is warmed by strong radiation from the sun the coastal region of the sea cools at night
 Cold air moving over warm water
Cold air moving over warm water The lowest cloud base forecast at eta zurich 1200 utc is .lszh 061019 ?
Question 136-5 : 1500 ft 1000 ft 2500 ft 5000 ft
 1500 ft.
1500 ft. Extensive cloud and precipitation is often associated with a non frontal ?
Question 136-6 : Surface convergence and upper level divergence causing widespread ascent of air in the depression surface convergence and upper level divergence causing widespread descent of air in the depression surface divergence and upper level convergence causing widespread descent of air in the depression surface divergence and upper level convergence causing widespread ascent of air in the depression
 Surface convergence and upper level divergence causing widespread ascent of air in the depression.
Surface convergence and upper level divergence causing widespread ascent of air in the depression. Which of the following meteorological phenomenon indicates upper level ?
Question 136-7 : Ac castellanus ac lenticularis halo red cirrus
 Ac castellanus.
Ac castellanus. Which type of fog is likely to form when air having temperature of 15°c and ?
Question 136-8 : Advection fog radiation fog steam fog frontal fog
 Advection fog.
Advection fog. What type of fog is most likely to form over flat land during a clear night ?
Question 136-9 : Radiation orographic advection steam
 Radiation.
Radiation. Which types of clouds are typical evidence of stable air conditions ?
Question 136-10 : St as cu cb ns cu cb cc
 St, as
St, as Which one of the displayed cloud forms is representative of altocumulus ?
Question 136-11 : N°2 n°4 n°1 n°3
 N°2.
N°2. Which one of the displayed cloud forms is representative of a cumulonimbus ?
Question 136-12 : N°4 n°3 n°2 n°1
 N°4.
N°4. A plain in western europe with an average height of 500 m 1600 ft above sea ?
Question 136-13 : 1500 7000 ft above ground 100 1500 ft above ground 7000 15000 ft above ground 15000 25000 ft above ground
 1500 - 7000 ft above ground.
1500 - 7000 ft above ground. A plain in western europe with an average height of 500 m 1600 ft above sea ?
Question 136-14 : 15000 35000 ft above the terrain 7000 15000 ft above the terrain 1500 7000 ft above the terrain 100 1500 ft above the terrain
 15000 - 35000 ft above the terrain.
15000 - 35000 ft above the terrain. Which of the following cloud types is found at high levels ?
Question 136-15 : Ci sc as cu
 Ci.
Ci. Which of the following cloud types is a medium level cloud ?
Question 136-16 : As cs st sc
 As.
As. Under which of these conditions is radiation fog most likely to form ?
Question 136-17 : Little or no cloud very dry air strong surface winds very low temperatures
 Little or no cloud.
Little or no cloud. Which of the following is most likely to lead to the formation of radiation fog ?
Question 136-18 : Heat loss from the ground on clear nights dry warm air passing over warm ground the passage of fronts cold air passing over warm ground
 Heat loss from the ground on clear nights
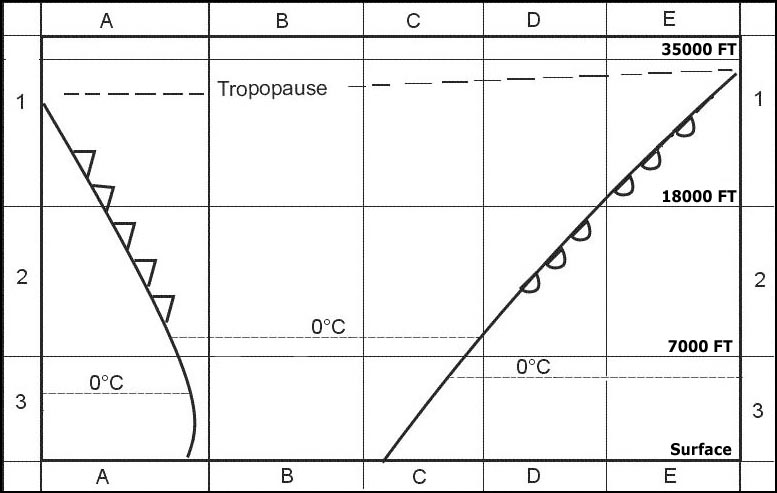
Heat loss from the ground on clear nights Of the four radio soundings select the one that indicates low stratus . 298 ?
Question 136-19 : N°3 n°1 n°2 n°4
 N°3.
N°3. In which of the following metar reports is the probability of fog formation in ?
Question 136-20 : 201850z 15003kt 6000 sct120 05/04 q1032 becmg 1600 br= 201850z 21003kt 8000 sct250 12/m08 q1028 nosig= 201850z 06018g30kt 5000 ra ovc010 04/01 q1024 nosig= 201850z 25010kt 4000 ra bkn012 ovc030 12/10 q1006 tempo 1500=
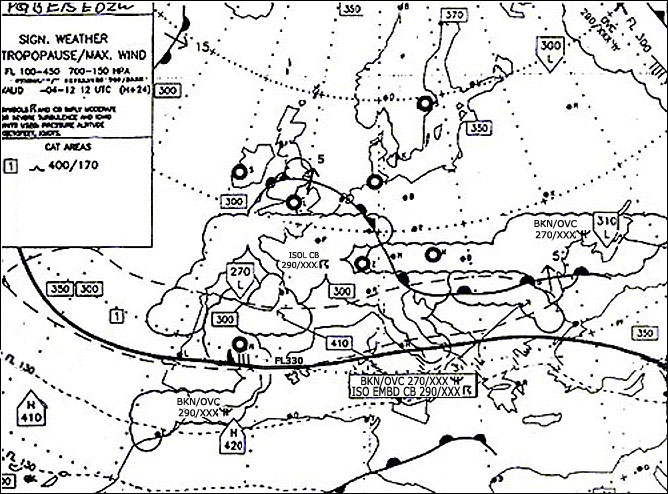 201850z 15003kt 6000 sct120 05/04 q1032 becmg 1600 br=
201850z 15003kt 6000 sct120 05/04 q1032 becmg 1600 br= Which airport is most likely to have fog in the coming night . 302 ?
Question 136-21 : Lszh enfb ekch essa
 Lszh.
Lszh. Which of the following cloud types are most likely to produce light to moderate ?
Question 136-22 : Altocumulus and altostratus stratocumulus and cirrostratus stratus and cumulonimbus altostratus and cirrocumulus
 Altocumulus and altostratus.
Altocumulus and altostratus. Altostratus clouds are classified as ?
Question 136-23 : Medium level clouds low level clouds high level clouds convective clouds
 Medium level clouds
Medium level clouds A cumulonimbus cloud at mid latitudes in summer contains ?
Question 136-24 : Ice crystals water droplets and supercooled water droplets only water droplets only ice crystals ice crystals and water droplets but never supercooled water droplets
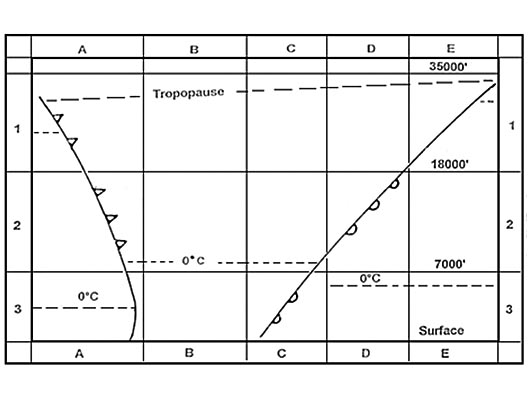 Ice crystals, water droplets and supercooled water droplets
Ice crystals, water droplets and supercooled water droplets Strongly developed cumulus clouds are an indication of ?
Question 136-25 : Instability in the atmosphere the presence of a low level inversion poor surface visibility the presence of warm air aloft
 Instability in the atmosphere.
Instability in the atmosphere. Clouds classified as being low level are considered to have bases from ?
Question 136-26 : The surface to 6500 ft 1000 to 2000 ft 500 to 1000 ft 100 to 200 ft
 The surface to 6500 ft.
The surface to 6500 ft. Which of the following are medium level clouds ?
Question 136-27 : Altostratus and altocumulus cirrocumulus and cirrostratus cumulonimbus all convective clouds
 Altostratus and altocumulus.
Altostratus and altocumulus. Cumulus clouds are an indication for ?
Question 136-28 : Up and downdrafts stability the approach of a cold front the approach of a warm front
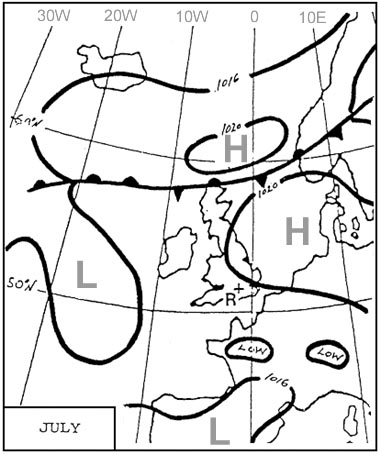 Up and downdrafts.
Up and downdrafts. A generally grey cloud layer with fairly uniform base and uniform appearance ?
Question 136-29 : Stratus altostratus nimbostratus cirrostratus
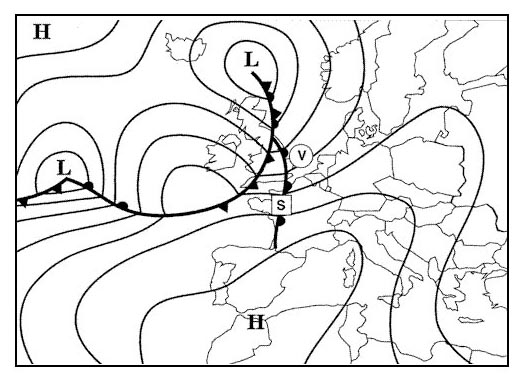 Stratus.
Stratus. The presence of altocumulus castellanus indicates ?
Question 136-30 : Instability in the middle troposphere strong convection at low height stability in the higher troposphere subsidence in a large part of the troposphere
 Instability in the middle troposphere.
Instability in the middle troposphere. In an area of converging air in low level ?
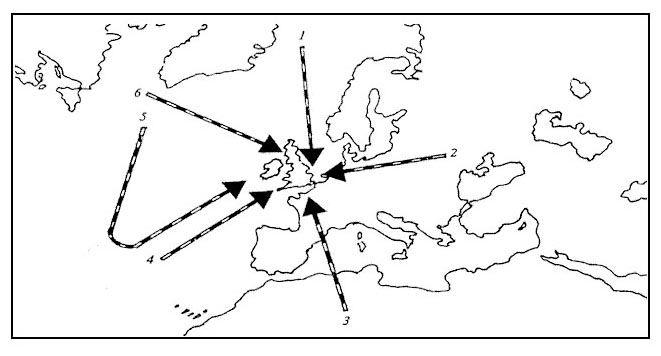
Question 136-31 : Clouds can be formed convective clouds can be dissolved stratified clouds can be dissolved clouds can not be formed
 Clouds can be formed.
Clouds can be formed. When the temperature and dew point are less than one degree apart the weather ?
Question 136-32 : Fog or low cloud clear and cool high scattered clouds unlimited visibility
 Fog or low cloud.
Fog or low cloud. The morning following a clear calm night when the temperature has dropped to ?
Question 136-33 : Radiation fog a cold front advection fog good clear weather
 Radiation fog.
Radiation fog. Advection fog can be formed when ?
Question 136-34 : Warm moist air flows over a colder surface cold moist air flows over a warmer surface warm moist air flows over a warmer surface cold moist air flows over warmer water
 Warm moist air flows over a colder surface.
Warm moist air flows over a colder surface. Steaming fog arctic sea smoke occurs in air ?
Question 136-35 : With cold mass properties with warm mass properties that is absolutely stable that is stable
 With cold mass properties.
With cold mass properties. Frontal fog is most likely to occur ?
Question 136-36 : In advance of a warm front in rear of a warm front in summer in the early morning in winter in the early morning
 In advance of a warm front.
In advance of a warm front. Freezing fog exists if fog droplets ?
Question 136-37 : Are supercooled are frozen are freezing very rapidly freeze when temperature falls below zero
 Are supercooled.
Are supercooled. Which of the following circumstances most favour the development of radiation ?
Question 136-38 : Moist air over land during clear night with little wind warm moist air at the windward side of a mountain maritime tropical air flowing over cold sea advection of very cold air over much warmer sea
 Moist air over land during clear night with little wind
Moist air over land during clear night with little wind Fallstreaks or virga are ?
Question 136-39 : Water or ice particles falling out of a cloud that evaporate before reaching the ground strong downdraughts in the polar jet stream associated with jet streaks gusts associated with a well developed bora strong katabatic winds in mountainous areas and accompanied by heavy precipitation
 Water or ice particles falling out of a cloud that evaporate before reaching the ground.
Water or ice particles falling out of a cloud that evaporate before reaching the ground. The range of wind speed in which radiation fog is most likely to form is ?
Question 136-40 : Below 5 kt between 10 and 15 kt between 5 and 10 kt above 15 kt
 Below 5 kt.
Below 5 kt. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5399 Free Training Exam
