Which of the following changes of state is known as freezing ? [ Revision flight ]
Question 135-1 : Liquid to solid gas to solid liquid to gas solid to liquid
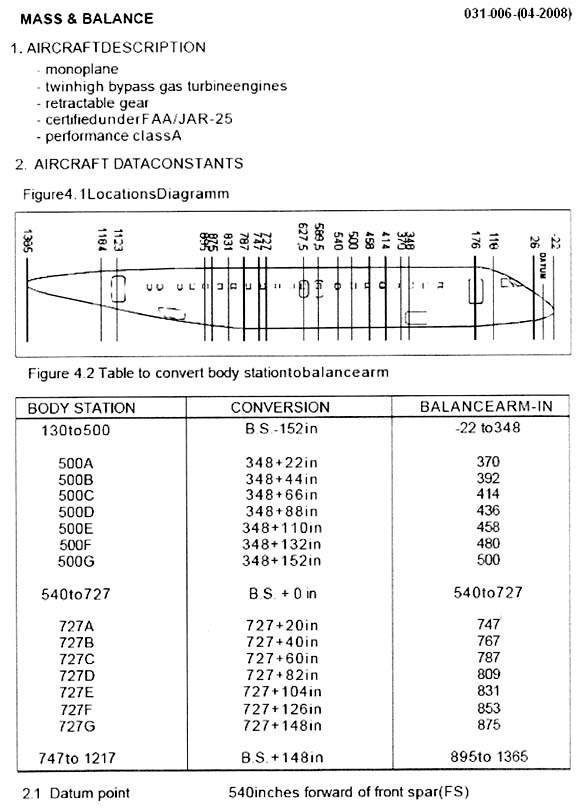 Liquid to solid.
Liquid to solid. Consider a parcel of air which is moved upwards in the surrounding air by an ?
Question 135-2 : Tends to gain altitude after being released tends to maintain its new altitude after being released tends to return to its original altitude when it is released tends to descend when it is released it will move to and maintain an altitude below its original altitude
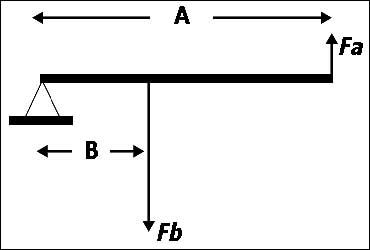 Tends to gain altitude after being released.
Tends to gain altitude after being released. In which of the following changes of state is latent heat absorbed ?
Question 135-3 : Liquid to gas liquid to solid gas to solid gas to liquid
In which of the following changes of state is latent heat released ?
Question 135-4 : Gas to solid solid to liquid solid to gas liquid to gas
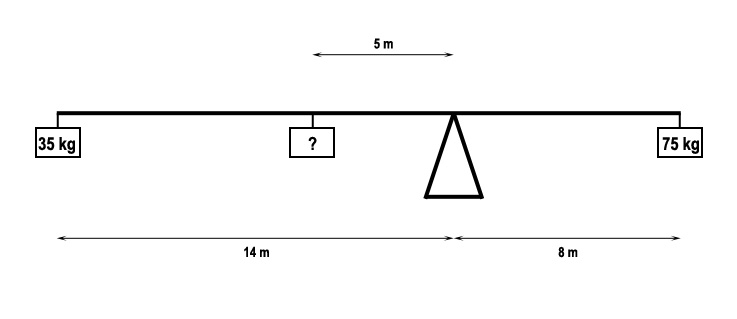 Gas to solid.
Gas to solid. What is foehn wind ?
Question 135-5 : It is an adiabatically heated wind blowing down a mountain side the temperature on the lee side is normally higher than on the windward side of the mountain at the same level it is a flow of warm air up a slope of a hill caused by surface heating it is a warm and moist anabatic wind that usually carries precipitation it is an adiabatically heated wind blowing down a mountain side the temperature on the lee side is normally lower than on the windward side of the mountain at the same level
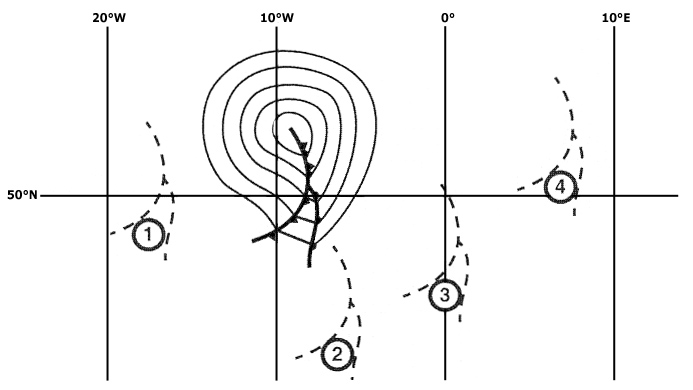 It is an adiabatically heated wind blowing down a mountain side. the temperature on the lee side is normally higher than on the windward side of the mountain at the same level.
It is an adiabatically heated wind blowing down a mountain side. the temperature on the lee side is normally higher than on the windward side of the mountain at the same level. What is 'mixing ratio' ?
Question 135-6 : The number of grammes of water vapour per kilogramme of dry air the percentage of water drops per volume unit of dry air the volume of water vapour which is mixed with each volume unit of dry air the ratio between actual water vapour content and saturated water vapour content
 The number of grammes of water vapour per kilogramme of dry air.
The number of grammes of water vapour per kilogramme of dry air. A night in january has been cold and clear in the forenoon of the next day an ?
Question 135-7 : The aircraft suffers reduced lift and thrust due to a temperature inversion at the top of the fog the additional weight gained by water which has been gathered on wings and fuselage during flight through the fog reduces the lift the water which has been gathered during flight through the fog modifies the aerodynamic properties of the aircraft thus reducing lift the aircraft is under influence of a mountain breeze descending air from the surrounding hills due to the incident sunshine
 The aircraft suffers reduced lift and thrust due to a temperature inversion at the top of the fog.
The aircraft suffers reduced lift and thrust due to a temperature inversion at the top of the fog. Which of the following changes of state is known as melting ?
Question 135-8 : Solid to liquid solid to gas liquid to solid liquid to gas
 Solid to liquid.
Solid to liquid. In which of the following changes of state is latent heat absorbed ?
Question 135-9 : Solid to liquid liquid to solid gas to solid gas to liquid
 Solid to liquid.
Solid to liquid. Which of the following changes of state is known as evaporation ?
Question 135-10 : Liquid to gas liquid to solid gas to solid solid to liquid
 Liquid to gas.
Liquid to gas. Which of the following changes of state is known as condensation ?
Question 135-11 : Gas to liquid gas to solid liquid to gas liquid to solid
 Gas to liquid.
Gas to liquid. Check the correctness of the following statements .1 the maximum water vapor ?
Question 135-12 : 1 is incorrect and 2 is correct 1 and 2 are incorrect 1 is correct and 2 is incorrect 1 and 2 are correct
 1 is incorrect and 2 is correct.
1 is incorrect and 2 is correct. In an isothermal layer the state of the atmosphere is ?
Question 135-13 : Absolutely stable absolutely unstable neutral conditionally unstable
 Absolutely stable.
Absolutely stable. In which of the following changes of state is latent heat absorbed ?
Question 135-14 : Solid to gas liquid to solid gas to solid gas to liquid
 Solid to gas.
Solid to gas. Given the following information what is the approximate relative humidity of ?
Question 135-15 : 75% 50% 55% 95%
 75%.
75%. As regards water which state change process delivers the main part of the ?
Question 135-16 : Condensation freezing evaporation sublimation
 Condensation.
Condensation. Several physical processes contribute to atmospheric warming which of the ?
Question 135-17 : Convection and condensation solar radiation and conduction absorption and vaporisation absorption and evaporation
 Convection and condensation.
Convection and condensation. What is the mean temperature deviation from isa for the frankfurt roma route . ?
Question 135-18 : 4°c colder than isa 4°c warmer than isa 10°c colder than isa 10°c warmer than isa
 4°c colder than isa.
4°c colder than isa. During a high altitude flight favourable contrail formation conditions are ?
Question 135-19 : High humidity low temperatures and presence of aerosols high humidity low temperatures and absence of aerosols low humidity high temperatures and presence of aerosols high humidity high temperatures and presence of aerosols
 High humidity, low temperatures and presence of aerosols.
High humidity, low temperatures and presence of aerosols. An inversion is a layer of air in which the temperature ?
Question 135-20 : Increases with increasing altitude decreases by more than 1°c per 100 m with altitude decreases by less than 1°c per 100 m with altitude remains unchanged with increasing altitude
 Increases with increasing altitude.
Increases with increasing altitude. In which of these cloud types can icing be virtually ruled out ?
Question 135-21 : Cirrus ci stratocumulus sc nimbostratus ns cumulus cu
 Cirrus (ci).
Cirrus (ci). The most likely reason for radiation fog to dissipate or become low stratus is ?
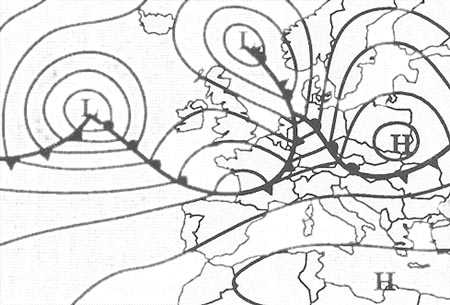
Question 135-22 : Increasing surface wind speed an increasingly stable atmosphere surface cooling a low level temperature inversion
 Increasing surface wind speed.
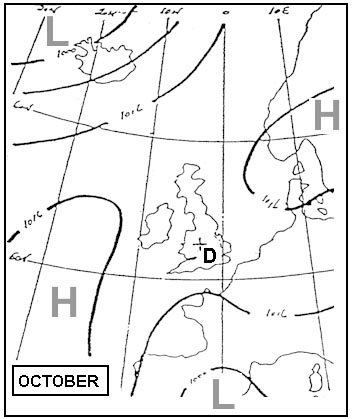
Increasing surface wind speed. What conditions are most likely to lead to the formation of hill fog ?
Question 135-23 : Humid stable air mass wind blowing towards the hills high relative humidity wind blowing parallel in range and an unstable air mass clear skies calm or light winds with relatively low humidity precipitation which is lifted by the action of moderate winds striking the range
 Humid stable air mass, wind blowing towards the hills.
Humid stable air mass, wind blowing towards the hills. Clouds fog or dew will always be formed when ?
Question 135-24 : Water vapour condenses water vapour is present relative humidity reaches 98% temperature and dew point are nearly equal
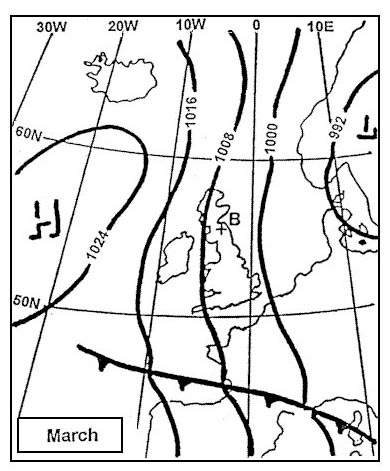 Water vapour condenses.
Water vapour condenses. Which of the following is a cause of stratus forming over flat land ?
Question 135-25 : Radiation during the night from the earth surface in moderate wind unstable air convection during the day the release of latent heat
 Radiation during the night from the earth surface in moderate wind.
Radiation during the night from the earth surface in moderate wind. Which of the following processes within a layer of air may lead to the building ?
Question 135-26 : Convection radiation subsidence frontal lifting within stable layers
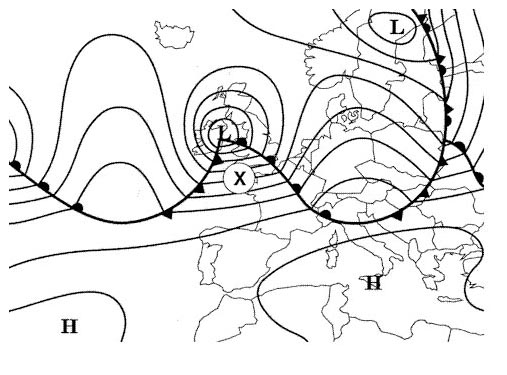 Convection.
Convection. What are the characteristics of cumuliform clouds ?
Question 135-27 : Large water droplets instability turbulence showers and mainly clear ice small water droplets stability no turbulence and extensive areas of rain large water droplets stability no turbulence showers and mainly rime ice small water droplets instability turbulence extensive areas of rain and rime ice
 Large water droplets, instability, turbulence, showers and mainly clear ice.
Large water droplets, instability, turbulence, showers and mainly clear ice. Which of the following clouds are classified as medium level clouds in ?
Question 135-28 : As ac sc ns ci cc cs st
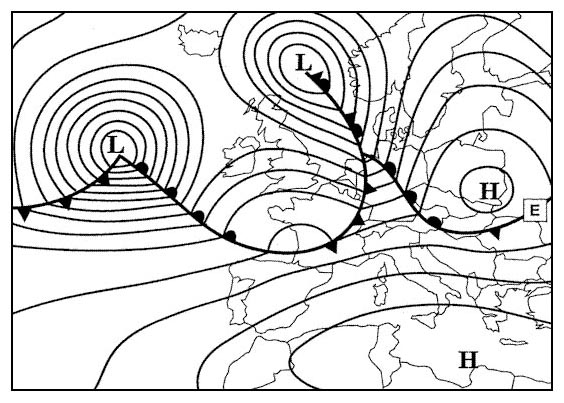 As, ac.
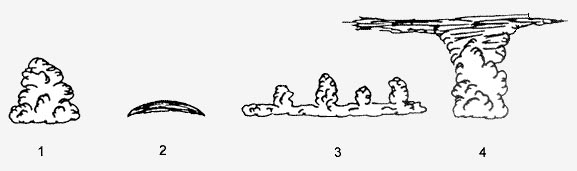
As, ac. Which one of the displayed cloud forms is representative of altocumulus ?
Question 135-29 : N°3 n°1 n°2 n°4
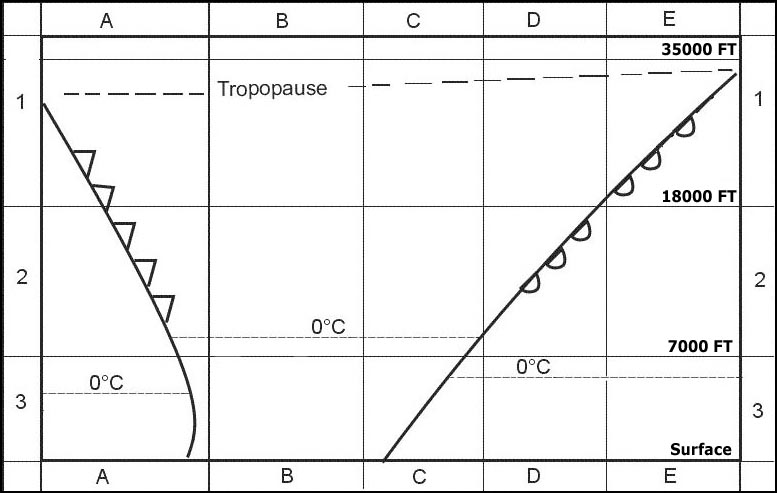 N°3.
N°3. What is the main composition of clouds classified as 'high level clouds' ?
Question 135-30 : Ice crystals supercooled water droplets water droplets water vapour
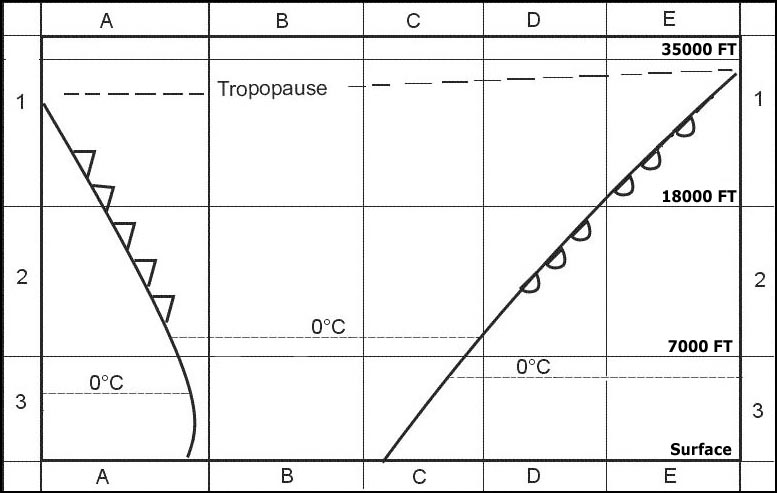 Ice crystals.
Ice crystals. A plain in western europe with an average elevation of 500 m 1600 ft above sea ?
Question 135-31 : 7000 15000 ft above the terrain 100 1500 ft above the terrain 1500 7000 ft above the terrain 15000 25000 ft above the terrain
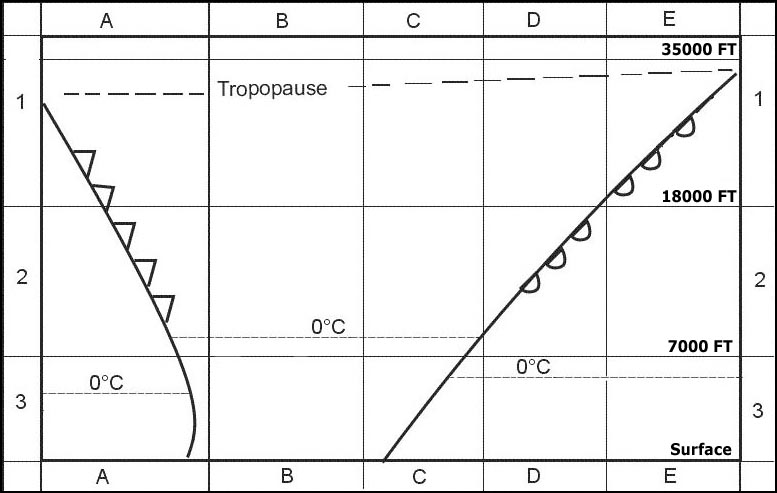 7000 - 15000 ft above the terrain.
7000 - 15000 ft above the terrain. Which of the following clouds may extend into more than one level ?
Question 135-32 : Nimbostratus stratus altocumulus cirrus
 Nimbostratus.
Nimbostratus. Which one of the following types of cloud is most likely to produce heavy ?
Question 135-33 : Ns st cs sc
 Ns.
Ns. With what type of clouds are showers most likely associated ?
Question 135-34 : Cumulonimbus stratocumulus nimbostratus stratus
 Cumulonimbus.
Cumulonimbus. At what time of day or night is radiation fog most likely to occur ?
Question 135-35 : Shortly after sunrise at sunset late evening shortly after midnight
 Shortly after sunrise.
Shortly after sunrise. What is the average vertical extent of radiation fog ?
Question 135-36 : 500 ft 2 000 ft 5 000 ft 10 000 ft
 500 ft.
500 ft. Which of the following weather conditions favour the formation of radiation fog ?
Question 135-37 : Light wind little or no cloud moist air light wind extensive cloud dry air light wind extensive cloud moist air strong wind little or no cloud moist air
 Light wind, little or no cloud, moist air.
Light wind, little or no cloud, moist air. Over central europe what type of cloud cover is typical of the warm sector of a ?
Question 135-38 : St ci cs fair weather cu cu cb
 St.
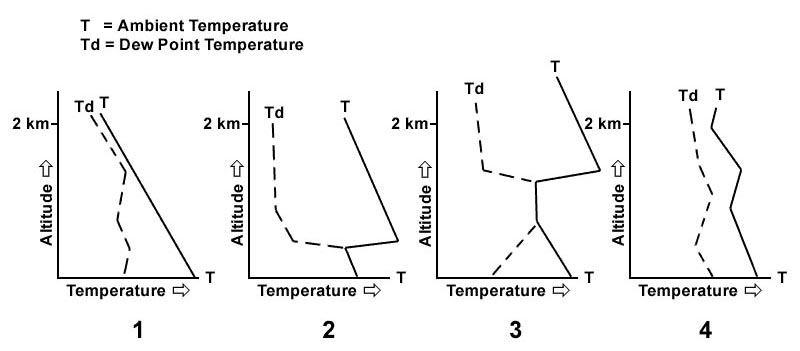
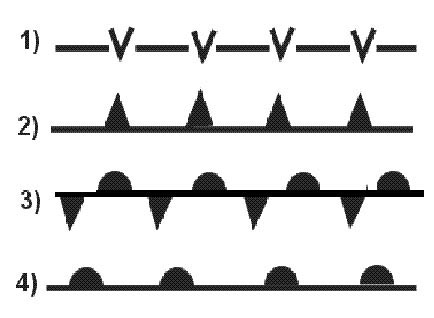
St. Of the four radio soundings select the one that indicates ground fog . 255 ?
Question 135-39 : N°2 n°1 n°3 n°4
 N°2.
N°2. Which of the following cloud types can project up into the stratosphere ?
Question 135-40 : Cumulonimbus cirrostratus altocumulus altostratus
 Cumulonimbus.
Cumulonimbus. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5359 Free Training Exam
