If in a 100 m thick layer the temperature at the bottom of the layer is 10°c ? [ Revision flight ]
Question 134-1 : Absolutely unstable absolutely stable conditionally unstable neutral
 Absolutely unstable.
Absolutely unstable. A wide body takes off on a clear night in dhahran saudi arabia shortly after ?
Question 134-2 : A very strong temperature inversion sand/dust in the engines very pronounced downdrafts low relative humidity
 A very strong temperature inversion.
A very strong temperature inversion. The value of the saturated adiabatic lapse rate is closest to that of the dry ?
Question 134-3 : Cirrus freezing fog stratus cumulonimbus
Dew point is defined as ?
Question 134-4 : The temperature to which moist air must be cooled to become saturated at a given pressure the lowest temperature at which evaporation will occur for a given pressure the lowest temperature to which air must be cooled in order to reduce the relative humidity the temperature below which the change of state in a given volume of air will result in the absorption of latent heat
 The temperature to which moist air must be cooled to become saturated at a given pressure
The temperature to which moist air must be cooled to become saturated at a given pressure The process by which water vapour is transformed directly into ice is known as ?
Question 134-5 : Sublimation supercooling supersaturation radiation cooling
 Sublimation.
Sublimation. A foehn wind occurs on the ?
Question 134-6 : Leeward side of a mountain range and is caused by significant moisture loss by precipitation from cloud windward side of a mountain range and is caused by surface heating windward side of a mountain range and is caused by surface cooling and reverse air flow leeward side of a mountain range and is caused by the condensation level being lower on the leeward side than on the windward side
 Leeward side of a mountain range and is caused by significant moisture loss by precipitation from cloud
Leeward side of a mountain range and is caused by significant moisture loss by precipitation from cloud Relative humidity at a given temperature is the relation between ?
Question 134-7 : Actual water vapour content and saturated water vapour content water vapour weight and dry air weight water vapour weight and humid air volume dew point and air temperature
 Actual water vapour content and saturated water vapour content
Actual water vapour content and saturated water vapour content A parcel of unsaturated air is forced to rise through an isothermal layer so ?
Question 134-8 : Decreases 1°c per 100 m remains constant decreases 0 65°c per 100 m becomes equal to the temperature of the isothermal layer
 Decreases 1°c per 100 m.
Decreases 1°c per 100 m. Absolute instability in the atmosphere will occur when the environmental lapse ?
Question 134-9 : Greater than both saturated adiabatic lapse rate and dry adiabatic lapse rate less than saturated adiabatic lapse rate less than both saturated adiabatic lapse rate and dry adiabatic lapse rate greater than saturated adiabatic lapse rate but less than dry adiabatic lapse rate
 Greater than both saturated adiabatic lapse rate and dry adiabatic lapse rate
Greater than both saturated adiabatic lapse rate and dry adiabatic lapse rate For both saturated and unsaturated air instability will occur when the ?
Question 134-10 : Environmental lapse rate is greater than both dry adiabatic lapse rate and saturated adiabatic lapse rate environmental lapse rate is greater than saturated adiabatic lapse rate but less than dry adiabatic lapse rate environmental lapse rate is less than both dry adiabatic lapse rate and saturated adiabatic lapse rate dry adiabatic lapse rate is less than saturated adiabatic lapse rate but greater than environmental lapse rate
 Environmental lapse rate is greater than both dry adiabatic lapse rate and saturated adiabatic lapse rate
Environmental lapse rate is greater than both dry adiabatic lapse rate and saturated adiabatic lapse rate In the lower levels of the atmosphere when the environmental lapse rate is ?
Question 134-11 : Conditionally unstable stable unstable absolutely unstable
 Conditionally unstable.
Conditionally unstable. Surface temperature inversions are frequently generated by ?
Question 134-12 : Terrestrial radiation on a calm clear night an unstable air mass causing convection currents and mixing of the atmosphere at lower levels gusting winds increasing surface friction during the day with consequent mixing at the lower levels compression causing the release of latent heat in a layer of stratiform cloud
 Terrestrial radiation on a calm clear night.
Terrestrial radiation on a calm clear night. Surface based temperature inversions are common during ?
Question 134-13 : Cloud free nights in winter when the ground is dry cloud free days in summer when the ground is dry cloudy days in summer when the ground is wet cloudy days in winter when the ground is wet
 Cloud-free nights in winter when the ground is dry.
Cloud-free nights in winter when the ground is dry. The maximum vapour pressure over a flat supercooled water surface and the ?
Question 134-14 : Greater over the water surface smaller over the water surface equal over both surfaces the same over both surfaces if the air pressure is the same
 Greater over the water surface.
Greater over the water surface. The stability in a layer increases by advection of ?
Question 134-15 : Cold air in the lower part warm air in the lower part dry air in the upper part moist air in the lower part
 Cold air in the lower part.
Cold air in the lower part. The temperature at the surface is given as +15°c and at 4000 ft it is +9°c ?
Question 134-16 : Stable conditionally unstable absolutely unstable unstable
 Stable.
Stable. Which of the following phenomena is least likely to lead to the formation of a ?
Question 134-17 : Ground radiation convection convergence orographic lift
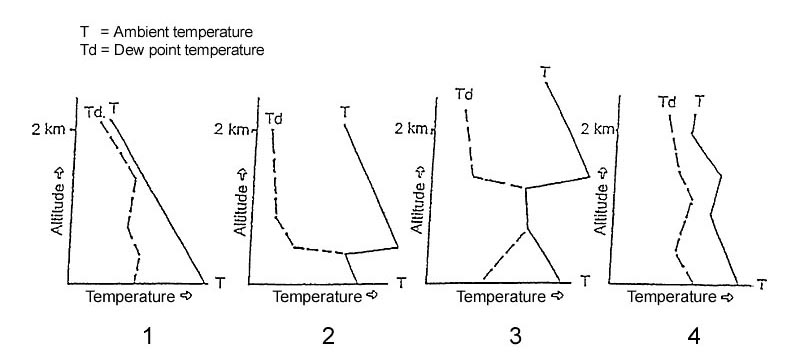 Ground radiation.
Ground radiation. Which of the following sets of conditions are most favourable to the ?
Question 134-18 : Environmental lapse rate greater than saturated adiabatic lapse rate through a great vertical extent high relative humidity and an initial lifting process extensive isothermal layer ice particles and water droplets must exist just below the freezing level and orographic lifting environmental lapse rate less than saturated adiabatic lapse rate with dew point below 0°c and considerable surface heating environmental lapse rate less than dry adiabatic lapse rate with freezing level below the cloud base high relative humidity and strong surface winds
 Environmental lapse rate greater than saturated adiabatic lapse rate through a great vertical extent, high relative humidity and an initial lifting process
Environmental lapse rate greater than saturated adiabatic lapse rate through a great vertical extent, high relative humidity and an initial lifting process Which of the following statements is correct ?
Question 134-19 : The bergeron findeisen process is mainly based on the difference of maximum vapour pressure over water and over ice of the same temperature the principle of the bergeron findeisen process is mainly based on the difference in size of the cloud elements at mid latitudes the coalescense process is usually the initial process in the formation of precipitation in the tropics stratiform precipitation does not occur
 The bergeron-findeisen process is mainly based on the difference of maximum vapour pressure over water and over ice of the same temperature.
The bergeron-findeisen process is mainly based on the difference of maximum vapour pressure over water and over ice of the same temperature. Which of the following statements is true of the dew point of an air mass ?
Question 134-20 : It can only be equal to or lower than the temperature of the air mass it can be higher than the temperature of the air mass it can be used together with the air pressure to estimate the air mass's relative humidity it can be used to estimate the air mass's relative humidity even if the air temperature is unknown
 It can only be equal to, or lower, than the temperature of the air mass.
It can only be equal to, or lower, than the temperature of the air mass. Which one of the following can provide the initial lifting leading to air mass ?
Question 134-21 : Advection of cold air over a warm sea mountain waves advection of warm air over a cold sea low level wind shear
 Advection of cold air over a warm sea.
Advection of cold air over a warm sea. Which of the following quantities remains unchanged if unsaturated air is ?
Question 134-22 : Mixing ratio difference between temperature and dewpoint temperature maximum vapour pressure maximum mixing ratio
 Mixing ratio.
Mixing ratio. Which of the following processes will increase the stability of an air mass ?
Question 134-23 : Cooling by the underlying surface addition of water vapour in the lower layer warming of the air mass from below advection of colder air aloft
 Cooling by the underlying surface.
Cooling by the underlying surface. Which statement is correct for an absolutely unstable atmosphere ?
Question 134-24 : Visibility is good between showers the environmental lapse rate is less than 1°c / 100 m clouds are mainly of the stratiform type the dry adiabatic lapse rate is more than 1°c / 100 m
 Visibility is good between showers.
Visibility is good between showers. Relative humidity ?
Question 134-25 : Increases if the air is cooled whilst maintaining the vapour pressure constant is higher in warm air than in cool air is higher in cool air than in warm air decreases if the air is cooled whilst maintaining the vapour pressure constant
 Increases if the air is cooled whilst maintaining the vapour pressure constant.
Increases if the air is cooled whilst maintaining the vapour pressure constant. What is true for the water vapour distribution in the layer between the surface ?
Question 134-26 : The lower part is relatively moist and the upper part is relatively dry the whole layer is relatively dry the whole layer is relatively moist the lower part is relatively dry and the upper part is relatively moist
 The lower part is relatively moist and the upper part is relatively dry.
The lower part is relatively moist and the upper part is relatively dry. What is the dry adiabatic lapse rate ?
Question 134-27 : 3 0°c/1000 ft 2 0°c/1000 ft 1 5°c/1000 ft 3 5°c/1000 ft
 3.0°c/1000 ft
3.0°c/1000 ft What is a characteristic of stable air ?
Question 134-28 : Stratiform clouds unlimited visibility fair weather cumulus clouds temperature decreases rapidly
 Stratiform clouds.
Stratiform clouds. What is a characteristic phenomenon for a stable atmosphere ?
Question 134-29 : Stratified clouds weak wind no precipitation many vertical currents
 Stratified clouds.
Stratified clouds. In an unsaturated layer in the friction layer the air is well mixed by ?
Question 134-30 : Correspond to the dry adiabatic lapse rate at first coincide with the average dry adiabat and then coincide with the average wet adiabat always change toward a more stable position coincide with the average wet adiabat in the layer
 Correspond to the dry adiabatic lapse rate.
Correspond to the dry adiabatic lapse rate. Good visibility in the lower levels may be expected when ?
Question 134-31 : Cool dry air is moving over a warmer surface warm air is moving over a cold surface the atmospheric pressure is low the air temperature is low
 Cool dry air is moving over a warmer surface.
Cool dry air is moving over a warmer surface. A layer of stratus is most likely to be dispersed by ?
Question 134-32 : Insolation resulting in the lifting of the condensation level absorption of longwaved solar radiation in the stratus layer the release of latent heat due to precipitation adiabatic cooling due to subsidence
 Insolation resulting in the lifting of the condensation level.
Insolation resulting in the lifting of the condensation level. After a clear night cumuliform clouds are formed in the morning why can the ?
Question 134-33 : Because the surface temperature increases the wind speed is increasing because the cold air mass changes into a warm air mass because the stability increases because the difference between the temperature and the dewpoint temperature at the initial condensation level becomes smaller
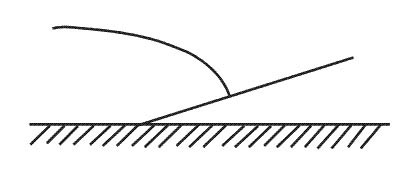 Because the surface temperature increases.
Because the surface temperature increases. Air masses which are being cooled from below are often characterized by ?
Question 134-34 : Fog poor visibility and layered clouds strong winds cumulus clouds good visibility uniform temperature good visibility continuous rain and freezing temperatures
 Fog, poor visibility and layered clouds.
Fog, poor visibility and layered clouds. An inversion is ?
Question 134-35 : An absolutely stable layer a conditionally unstable layer an unstable layer a layer that can be either stable or unstable
 An absolutely stable layer
An absolutely stable layer An unstable air mass is forced to ascend a mountain slope what type of clouds ?
Question 134-36 : Clouds with considerable vertical development and associated turbulence stratiform clouds with considerable turbulence layer like clouds with little vertical development stratiform clouds with a temperature inversion
 Clouds with considerable vertical development and associated turbulence.
Clouds with considerable vertical development and associated turbulence. 8/8 stratus base 200 ft/agl is observed at sunrise at an aerodrome in the north ?
Question 134-37 : Winter ovc base 500 ft/agl summer sct base 3000 ft/agl winter clear sky summer bkn cb base 1500 ft/agl winter bkn base 2500 ft/agl summer bkn base 3500 ft/agl winter sct base 3000 ft/agl summer ovc base 500 ft/agl
 Winter: ovc, base 500 ft/agl, summer: sct, base 3000 ft/agl.
Winter: ovc, base 500 ft/agl, summer: sct, base 3000 ft/agl. The dewpoint temperature ?
Question 134-38 : Can be reached by cooling the air whilst keeping pressure constant can be reached by lowering the pressure whilst keeping temperature constant can not be equal to the air temperature can not be lower than the air temperature
 Can be reached by cooling the air whilst keeping pressure constant
Can be reached by cooling the air whilst keeping pressure constant The amount of water vapour which air can hold largely depends on ?
Question 134-39 : Air temperature stability of air relative humidity the dew point
 Air temperature.
Air temperature. A given mass of air is saturated with water vapour no condensed water .if ?
Question 134-40 : The amount of water vapour remains constant the amount of water vapour decreases relative humidity increases relative humidity remains constant
 The amount of water vapour remains constant.
The amount of water vapour remains constant. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5319 Free Training Exam
