The environmental lapse rate in an actual atmosphere ? [ Revision flight ]
Question 133-1 : Varies with time has a fixed value of 1°c/100m has a fixed value of 0 65°c/100m has a fixed value of 2°c/1000 ft
 Varies with time.
Varies with time. The dry adiabatic lapse rate has a value of ?
Question 133-2 : 1°c/100 m 2°c/1000 ft 0 65°c/100 m 0 5°c/100 m
 1°c/100 m.
1°c/100 m. The dry adiabatic lapse rate ?
Question 133-3 : Has a constant fixed value is greater in summer than in winter is greater during the night than during the day has a variable value
An air mass is called stable when ?
Question 133-4 : The vertical motion of rising air tends to become weaker and disappears the temperature in a given air mass decreases rapidly with height the pressure in a given area is constant the environmental lapse rate is high with little vertical motion of air currents
 The vertical motion of rising air tends to become weaker and disappears
The vertical motion of rising air tends to become weaker and disappears Advection is ?
Question 133-5 : Horizontal motion of air vertical motion of air the same as subsidence the same as convection
Subsidence is ?
Question 133-6 : Vertically downwards motion of air horizontal motion of air vertically upwards motion of air the same as convection
 Vertically downwards motion of air.
Vertically downwards motion of air. Rising air cools because ?
Question 133-7 : It expands surrounding air is cooler at higher levels it becomes more moist it contracts
 It expands.
It expands. A layer can be ?
Question 133-8 : Stable for unsaturated air and unstable for saturated air stable for saturated air and unstable for unsaturated air unstable for unsaturated air and neutral for saturated air unstable for unsaturated air and conditionally unstable
 Stable for unsaturated air and unstable for saturated air.
Stable for unsaturated air and unstable for saturated air. In a layer of air the decrease in temperature per 100 metres increase in height ?
Question 133-9 : Absolutely unstable absolutely stable conditionally unstable conditionally stable
 Absolutely unstable.
Absolutely unstable. Which statement is true for a conditionally unstable layer ?
Question 133-10 : The environmental lapse rate is less than 1°c/100 m the environmental lapse rate is less than 0 65°c/100 m the layer is unstable for unsaturated air the wet adiabatic lapse rate is 0 65°c/100 m
 The environmental lapse rate is less than 1°c/100 m.
The environmental lapse rate is less than 1°c/100 m. The stability in a layer is increasing if ?
Question 133-11 : Warm air is advected in the upper part and cold air in the lower part warm air is advected in the lower part and cold air in the upper part warm and moist air is advected in the lower part cold and dry air is advected in the upper part
 Warm air is advected in the upper part and cold air in the lower part.
Warm air is advected in the upper part and cold air in the lower part. Which of the following statements concerning the lifting of a parcel of air is ?
Question 133-12 : Unsaturated parcels cool more rapidly than saturated parcels unsaturated parcels cool less rapidly than saturated parcels unsaturated parcels cool at a rate of 0 65°c per 100 m saturated parcels always cool at a rate of 0 65°c per 100 m
 Unsaturated parcels cool more rapidly than saturated parcels.
Unsaturated parcels cool more rapidly than saturated parcels. When in the upper part of a layer warm air is advected the ?
Question 133-13 : Stability increases in the layer stability decreases in the layer wind will back with increasing height in the northern hemisphere wind speed will always decrease with increasing height in the northern hemisphere
 Stability increases in the layer.
Stability increases in the layer. The dew point temperature ?
Question 133-14 : Can be equal to the air temperature is always lower than the air temperature is always higher than the air temperature can not be equal to the air temperature
 Can be equal to the air temperature.
Can be equal to the air temperature. Relative humidity depends on ?
Question 133-15 : Moisture content and temperature of the air moisture content and pressure of the air moisture content of the air only temperature of the air only
 Moisture content and temperature of the air
Moisture content and temperature of the air When water evaporates into unsaturated air ?
Question 133-16 : Heat is absorbed heat is released relative humidity is not changed relative humidity is decreased
 Heat is absorbed.
Heat is absorbed. A moist but unsaturated parcel of air becomes saturated by ?
Question 133-17 : Lifting the parcel to a higher level lowering the parcel to a lower level moving the parcel to an area with lower pressure and equal temperature moving the parcel to an area with higher pressure and equal temperature
 Lifting the parcel to a higher level.
Lifting the parcel to a higher level. A sample of moist but unsaturated air may become saturated by ?
Question 133-18 : Expanding it adiabatically raising the temperature lowering the pressure keeping temperature constant compressing it adiabatically
 Expanding it adiabatically.
Expanding it adiabatically. The maximum amount of water vapour that the air can contain depends on the ?
Question 133-19 : Air temperature relative humidity stability of the air dewpoint
 Air temperature.
Air temperature. Convective clouds are formed ?
Question 133-20 : In unstable atmosphere in stable atmosphere in summer during the day only in mid latitudes only
 In unstable atmosphere.
In unstable atmosphere. The most effective way to dissipate cloud is by ?
Question 133-21 : Subsidence convection a decrease in temperature a decrease in pressure
 Subsidence.
Subsidence. Areas of sinking air are generally cloudless because as air sinks it ?
Question 133-22 : Is heated by compression reaches warmer layers is heated by expansion loses water vapour
 Is heated by compression.
Is heated by compression. The main factor which contributes to the formation of very low clouds ahead of ?
Question 133-23 : Saturation of the cold air by rain falling into it and evaporating saturation of the warm air by rain falling into it and evaporating reduction of outgoing radiation due to clouds warm air moving over a cold surface
 Saturation of the cold air by rain falling into it and evaporating.
Saturation of the cold air by rain falling into it and evaporating. In an unstable layer there are cumuliform clouds the vertical extent of these ?
Question 133-24 : Thickness of the unstable layer wind direction air pressure at the surface pressure at different levels
 Thickness of the unstable layer
Thickness of the unstable layer Which of the following phenomena are formed when a moist stable layer of air is ?
Question 133-25 : Stratified clouds inversions showers and thunderstorms areas of severe turbulence
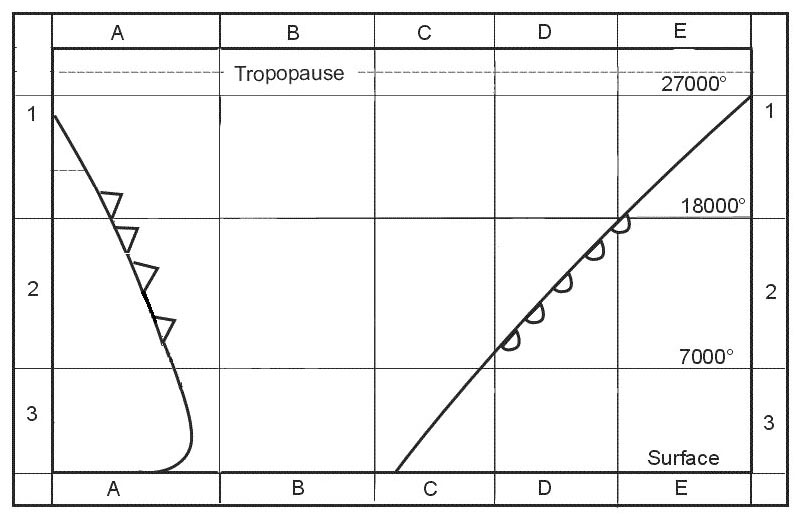 Stratified clouds.
Stratified clouds. The height of the lifting condensation level is determined by ?
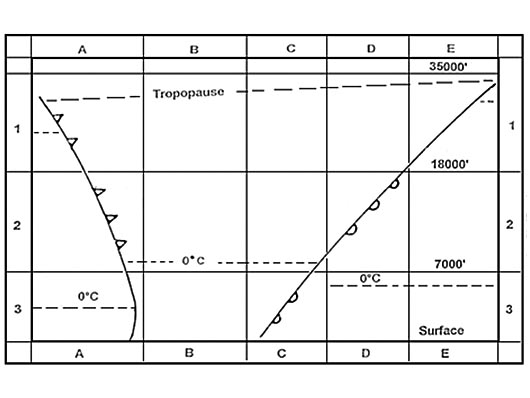
Question 133-26 : Temperature and dewpoint at the surface temperature at surface and air pressure wind and dewpoint at the surface wet adiabatic lapse rate and dewpoint at the surface
 Temperature and dewpoint at the surface.
Temperature and dewpoint at the surface. During an adiabatic process heat is ?
Question 133-27 : Neither added nor lost added lost added but the result is an overall loss
 Neither added nor lost.
Neither added nor lost. The decrease in temperature per 100 metres in an unsaturated rising parcel of ?
Question 133-28 : 1°c 2°c 0 65°c 0 5°c
 1°c.
1°c. The decrease in temperature per 100 metres in a saturated rising parcel of air ?
Question 133-29 : 0 6°c 1°c 1 5°c 0 35°c
 0.6°c.
0.6°c. In unstable air ground visibility is most likely to be restricted by ?
Question 133-30 : Showers of rain or snow haze drizzle low stratus
 Showers of rain or snow.
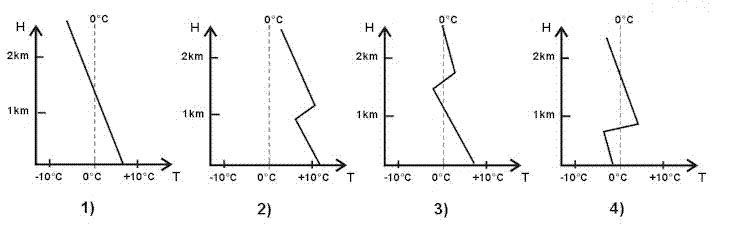
Showers of rain or snow. A vertical temperature profile indicates the possibility of severe icing when ?
Question 133-31 : Intersects the 0°c isotherm twice coincides with a dry adiabatic lapse rate indicates temperatures below 40°c indicates temperatures above 3°c
 Intersects the 0°c isotherm twice.
Intersects the 0°c isotherm twice. The rate of cooling of ascending saturated air is less than the rate of cooling ?
Question 133-32 : Heat is released during the condensation process moist air is heavier than dry air water vapour doesn't cool as rapidly as dry air water vapour absorbs the incoming heat from the sun
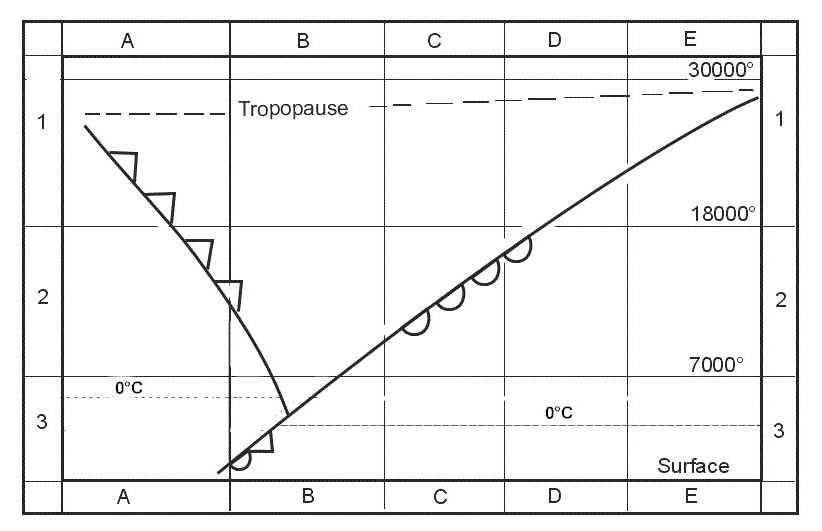 Heat is released during the condensation process.
Heat is released during the condensation process. If the surface temperature is 15°c then the temperature at 10000 ft in a ?
Question 133-33 : 15°c 0°c 5°c 5°c
 -15°c.
-15°c. An inversion is ?
Question 133-34 : An increase of temperature with height an increase of pressure with height a decrease of pressure with height a decrease of temperature with height
 An increase of temperature with height
An increase of temperature with height In still air the temperature decreases at an average of 1 2°c per 100 m ?
Question 133-35 : Dry adiabatic lapse rate saturated adiabatic lapse rate environmental lapse rate normal lapse rate
 Dry adiabatic lapse rate.
Dry adiabatic lapse rate. From which of the following pieces of information can the stability of the ?
Question 133-36 : Environmental lapse rate dry adiabatic lapse rate surface temperature pressure at the surface
 Environmental lapse rate.
Environmental lapse rate. A layer is absolutely unstable if the temperature decrease with height is ?
Question 133-37 : More than 1°c per 100m between 1°c per 100m and 0 65°c per 100m 0 65°c per 100m less than 0 65°c per 100m
 More than 1°c per 100m.
More than 1°c per 100m. A layer in which the temperature remains constant with height is ?
Question 133-38 : Absolutely stable unstable neutral conditionally unstable
 Absolutely stable.
Absolutely stable. A layer in which the temperature increases with height is ?
Question 133-39 : Absolutely stable absolutely unstable conditionally unstable neutral
 Absolutely stable.
Absolutely stable. A layer in which the temperature decreases with 1°c per 100 m increasing ?
Question 133-40 : Neutral for dry air absolutely stable absolutely unstable conditionally unstable
 Neutral for dry air.
Neutral for dry air. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5279 Free Training Exam
