A state shall provide assistance to an aircraft subjected to an act of unlawful ? [ Training professional ]
Question 1-1 : Provision of navigation aids air traffic services and permission to land provision of navigation aids air traffic services permission to land and refuelling provision of navigation aids air traffic services permission to land and catering for passengers only permission to land
Security .a state shall take adequate measures for the safety of passengers and ?
Question 1-2 : Until their journey can be continued during a period of investigation and arrange for them to return to their country of origin if is requested by an individual passenger
The international civil aviation convention annex defining the maximum noise ?
Question 1-3 : Annex 16 annex 4 annex 9 annex 11
 Annex 16.
Annex 16. Annex 17 of the convention on international civil aviation chicago deals with ?
Question 1-4 : Security navigation aids aerodrome design and operations airworthiness of aircraft
 Security.
Security. Which of the following icao documents contain international standards and ?
Question 1-5 : Annexes to the convention on international civil aviation procedures for air navigation service pans regional supplementary procedures supps icao technical manuals
Any person who suffers damage on the surface shall upon proof only that damage ?
Question 1-6 : The rome convention the warsaw convention the chicago convention the montreal convention
 The rome convention.
The rome convention. Chicago convention obligation to inform .contracting states have the ?
Question 1-7 : Differences or non compliance with standards in any of the annexes to the convention changes in the national regulations new licenses and ratings for flight crew and ground personnel and any suspended validity of such licenses the pricing policy and agreements for passenger tickets and and freight in international air transport
 Differences or non-compliance with standards in any of the annexes to the convention.
Differences or non-compliance with standards in any of the annexes to the convention. Deleted 1 ?
Question 1-8 : Deleted 1 deleted deleted deleted
 Deleted_1
Deleted_1 Each member state should designate an appropriate authority with its istration ?
Question 1-9 : To all international civil air transport including aircraft engaged solely in the carriage of cargo and yet to domestic flights at the discretion of each member state only to passengers and aircrew in international civil transport flights only to passengers and aircrew in international civil transport flights and domestic flights only to all international civil transport including aircraft engaged solely in the carriage of cargo
 To all international civil air transport including aircraft engaged solely in the carriage of cargo and yet to domestic flights at the discretion of each member state.
To all international civil air transport including aircraft engaged solely in the carriage of cargo and yet to domestic flights at the discretion of each member state. One of the main objectives of icao is to ?
Question 1-10 : Develop principles and technique for international aviation approve new international airlines with jet aircraft approve the ticket prices set by international airline companies approve new international airlines
 Develop principles and technique for international aviation.
Develop principles and technique for international aviation. Which of the following frequencies is not an international emergency frequency ?
Question 1-11 : 2430 khz 121 5 mhz 243 0 mhz 2182 khz
 2430 khz.
2430 khz. The convention of rome 1933/1952 for the unification of certain rules relating ?
Question 1-12 : To third parties on the surface to other aircraft in case of a midair collision caused by dangerous goods that have been carried by an aircraft to other aircraft while operating on ground
 To third parties on the surface.
To third parties on the surface. The convention on offences and certain acts committed on board aircraft is ?
Question 1-13 : The convention of tokyo the convention of paris the convention of chicago the convention of rome
 The convention of tokyo.
The convention of tokyo. The convention signed by the states and moved by a desire to ensure adequate ?
Question 1-14 : The rome convention the warsaw convention the paris convention the tokyo convention
 The rome convention.
The rome convention. The convention which deals with offences against penal law is ?
Question 1-15 : The convention of tokyo the convention of madrid the convention of rome the convention of warsaw
 The convention of tokyo.
The convention of tokyo. The first freedom of the air is ?
Question 1-16 : The right to overfly another state without landing the right to land for a technical stop the opportunity to operate a commercial flight with passengers on board between two states the right to board passengers from the state where the aircraft is registered and to fly to an other state
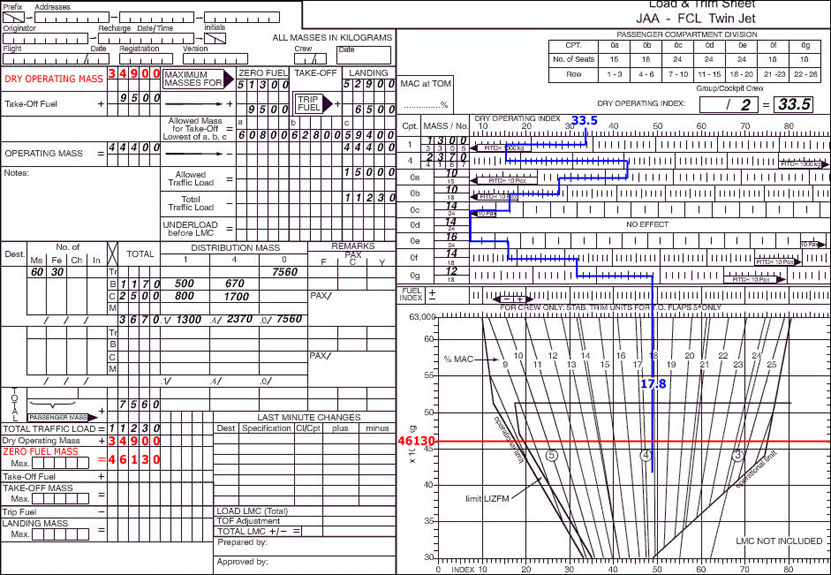 The right to overfly another state without landing.
The right to overfly another state without landing. The international civil aviation convention annex containing standards and ?
Question 1-17 : Annex 1 annex 2 annex 11 annex 12
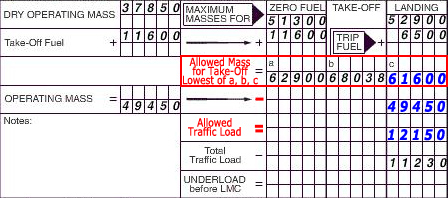 Annex 1.
Annex 1. The international civil aviation organisation icao was established by the ?
Question 1-18 : Chicago warsaw the hague montreal
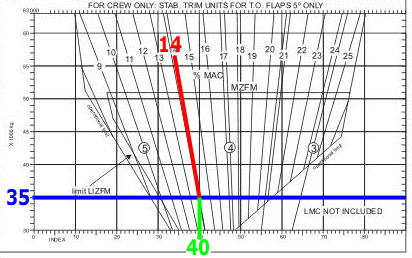 Chicago.
Chicago. The international civil aviation organisation icao establishes ?
Question 1-19 : Standards and recommended international practices for contracting member states aeronautical standards adopted by all states standards and recommended practices applied without exception by all states signatory to the chicago convention proposals for aeronautical regulations in the form of 19 annexes
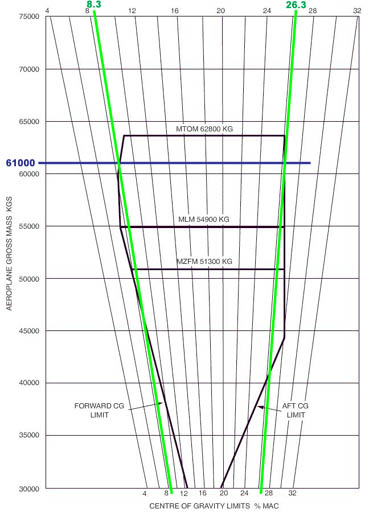 Standards and recommended international practices for contracting member states.
Standards and recommended international practices for contracting member states. The international convention defining rules relative to the responsibilities of ?
Question 1-20 : Montreal convention tokyo convention hague convention chicago convention
 Montreal convention.
Montreal convention. Icao .the objectives of icao was ratified by the ?
Question 1-21 : Chicago convention 1944 geneva convention 1936 geneva convention 1948 warsaw convention 1929
The obligation of a carrier to transport any person away from the territory of ?
Question 1-22 : This statement is correct the operator has no obligation the obligation is for the contracting state of the operator the obligation of the operator terminates as soon as the person leaves the aeroplane
 This statement is correct.
This statement is correct. The rome convention and later amendments deals with ?
Question 1-23 : Damage caused by foreign aircraft to third parties on the surface offences and certain other acts committed on board aircraft damage caused by any aircraft to third parties on the surface regulation of transportation of dangerous goods
The second freedom of the air is the ?
Question 1-24 : Right to land for a technical stop right to overfly without landing right to operate a commercial passenger flight with passengers on board between two states right to 'cabotage' traffic trans border traffic
 Right to land for a technical stop.
Right to land for a technical stop. Icao publications .the 'standards' contained in the annexes to the chicago ?
Question 1-25 : Binding for the member states that have not notified icao about a national difference binding for all member states binding for all air line companies with international traffic advice and guidance material to be included into the national aviation legislation of a contracting state
 Binding for the member states that have not notified icao about a national difference.
Binding for the member states that have not notified icao about a national difference. The montreal convention and later amendments deals with ?
Question 1-26 : Limitation of the operator's liability for damage caused to passengers and goods transported the regulation of transportation of dangerous goods operators licence for international scheduled aviation the security system at airports
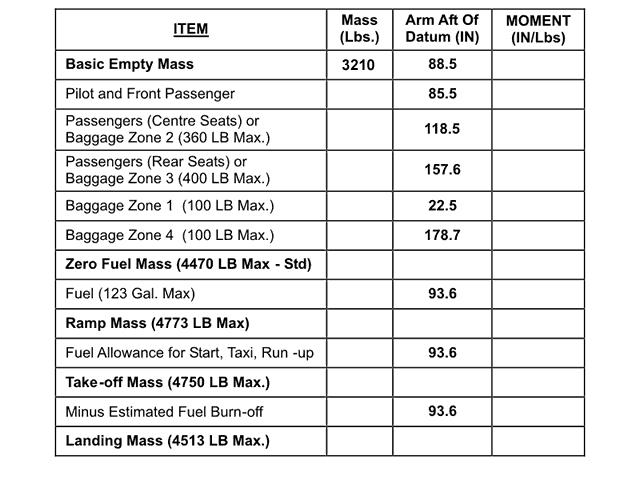 Limitation of the operator's liability for damage caused to passengers and goods transported.
Limitation of the operator's liability for damage caused to passengers and goods transported. When an aircraft has sustained damage the aircraft shall be allowed to resume ?
Question 1-27 : The state of registry considers that the damage sustained is of a nature such that the aircraft is still airworthy the state of manufacture informs the state of registry that the damage sustained is of a nature such that the aircraft is still airworthy the state of registry the state of design and the state of manufacture consider that the aircraft is still airworthy the state of design and the state of manufacture inform the state of registry that the aircraft is still airworthy
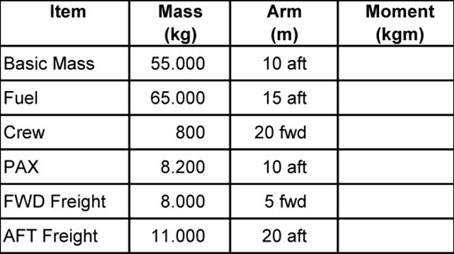 The state of registry considers that the damage sustained is of a nature such that the aircraft is still airworthy.
The state of registry considers that the damage sustained is of a nature such that the aircraft is still airworthy. Which body of icao finalises the standard and recommended practices sarps for ?
Question 1-28 : The air navigation commission the assembly the council the regional air navigation meeting
 The air navigation commission.
The air navigation commission. Which freedom of the air will be exercised by an airline planning a flight that ?
Question 1-29 : 2nd freedom 1st freedom 3rd freedom 4th freedom
 2nd freedom.
2nd freedom. Which of the following annexes to the chicago convention contains international ?
Question 1-30 : Annex 11 annex 14 annex 17 annex 6
 Annex 11.
Annex 11. Which of the following annexes to the chicago convention contains minimum ?
Question 1-31 : Annex 1 annex 2 annex 3 annex 4
 Annex 1.
Annex 1. Which of the following annexes to the chicago convention contains minimum ?
Question 1-32 : Annex 14 annex 6 annex 11 annex 10
 Annex 14.
Annex 14. The requirements for the issue of a medical certificate are contained in the ?
Question 1-33 : Med fcl sera hos
 Med.
Med. The term 'cabotage' refers to ?
Question 1-34 : Domestic services performed by a carrier from another state a flight above territorial waters domestic services performed only by a domestic carriers crop spraying
 Domestic services performed by a carrier from another state.
Domestic services performed by a carrier from another state. Any contracting state may denounce the convention of montreal by written ?
Question 1-35 : 6 months following the date on which notification is received by the depositary governments 3 months following the date on which notification is received by the depositary governments 2 months following the date icao is informed 4 months following the date on which notification is received by the depositary governments
 6 months following the date on which notification is received by the depositary governments.
6 months following the date on which notification is received by the depositary governments. For aircraft flying over the high seas which rules shall be in force ?
Question 1-36 : The rules established under the convention of international civil aviation the rules established by the state s adjacent to the high seas over flown the rules established by the state of registry of the aircraft the rules established by the state of the operator of the aircraft
What is the role and function of iata ?
Question 1-37 : It is an international organisation its mission is to represent lead and serve the airline industry it is a un organization working for development of aviation worldwide it is a multi national which aims to improve the efficiency of air transport it is an international organisation dedicated to improving the efficiency of aeronautical telecommunications
 It is an international organisation, its mission is to represent, lead and serve the airline industry.
It is an international organisation, its mission is to represent, lead and serve the airline industry. In 1957 the treaty of rome was signed and the first step towards eu was taken ?
Question 1-38 : The european economic community the european steel and coal union the united states of europe the council of europe
If a state finds that is impracticable to comply with an international standard ?
Question 1-39 : It shall give immediate notice to icao of the differences between its own practices and the international standard it shall give 60 days notice to icao of the differences between its own practices and the international standard it shall give 90 days notice to icao of the differences between its own practices and the international standard it shall give 45 days notice to icao of the differences between its own practices and the international standard
 It shall give immediate notice to icao of the differences between its own practices and the international standard.
It shall give immediate notice to icao of the differences between its own practices and the international standard. What is the obligation of a state in the event of non compliance with an ?
Question 1-40 : The state has to notify the council of icao and publish such differences in the national aip modifications to international standards shall be published in the national aip only differences to recommended practices have to be notified to icao the state has to notify the assembly of icao only the state has to publish such differences in the national aip only
 The state has to notify the council of icao and publish such differences in the national aip.
The state has to notify the council of icao and publish such differences in the national aip. Try for free without registration.
Then create your account to prepare unlimitedly thanks to our questions, answers, explanations, courses, exams, reports, statistics, technical support ...
Join us and transform the way you learn with our engaging and efficient learning environment.
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 1
