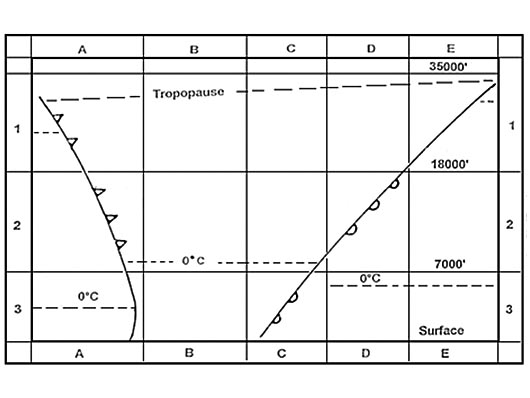
An aircraft is flying through the polar front jet stream from south to north ? [ Preparation civilian ]
Question 129-1 : It decreases it increases it first increases then decreases it remains constant
 It decreases.
It decreases. What is the average height of the arctic jet stream core ?
Question 129-2 : 20000 ft 30000 ft 40000 ft 50000 ft
 20000 ft .
20000 ft . What is the approximate ratio between height and width for a jet stream cross ?
Question 129-3 : Ratio is 1/100 ratio is 1/1 ratio is 1/10 ratio is 1/1000
 Ratio is 1/100.
Ratio is 1/100. Which jet stream blows all year round over the northern hemisphere ?
Question 129-4 : The subtropical jet stream the polar night jet stream the equatorial jet stream the arctic jet stream
What is the average height of the jet core within a polar front jet stream ?
Question 129-5 : 30000 ft 40000 ft 50000 ft 20000 ft
 30000 ft.
30000 ft. An aircraft is flying from south to north above the polar front jet stream at ?
Question 129-6 : It decreases it increases it stays the same it decreases and then increases
A wind speed of 350 kt within a jet stream core should be world wide regarded as ?
Question 129-7 : Possible but a very rare phenomenon not unusual in polar regions a common occurrence not possible
 Possible but a very rare phenomenon.
Possible but a very rare phenomenon. An aircraft over western europe is crossing a jet stream 2500 ft below its core ?
Question 129-8 : From the right from the left tailwind headwind
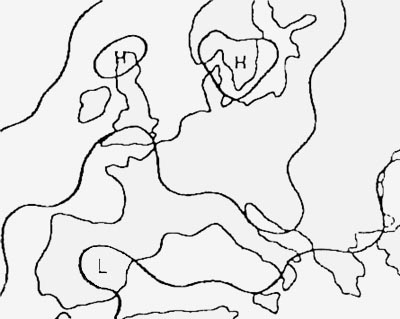 From the right.
From the right. What is the main cause for the formation of a polar front jet stream ?
Question 129-9 : The north south horizontal temperature gradient at the polar front the pressure difference close to the ground between a high over the azores and a low over iceland strong winds in the upper atmosphere the varied elevations of the tropopause in the polar front region
 The north-south horizontal temperature gradient at the polar front.
The north-south horizontal temperature gradient at the polar front. Which jet stream is connected with a surface front system ?
Question 129-10 : The polar front jet stream the easterly jet stream the subtropical jet stream the equatorial jet stream
 The polar front jet stream.
The polar front jet stream. At approximately what flight level is the subtropical jet stream found ?
Question 129-11 : Fl 400 fl 150 fl 200 fl 500
 Fl 400.
Fl 400. Flight zurich to rome etd 1600 utc eta 1800 utc at what flight level would you ?
Question 129-12 : Fl 220 fl 160 fl 320 fl 140
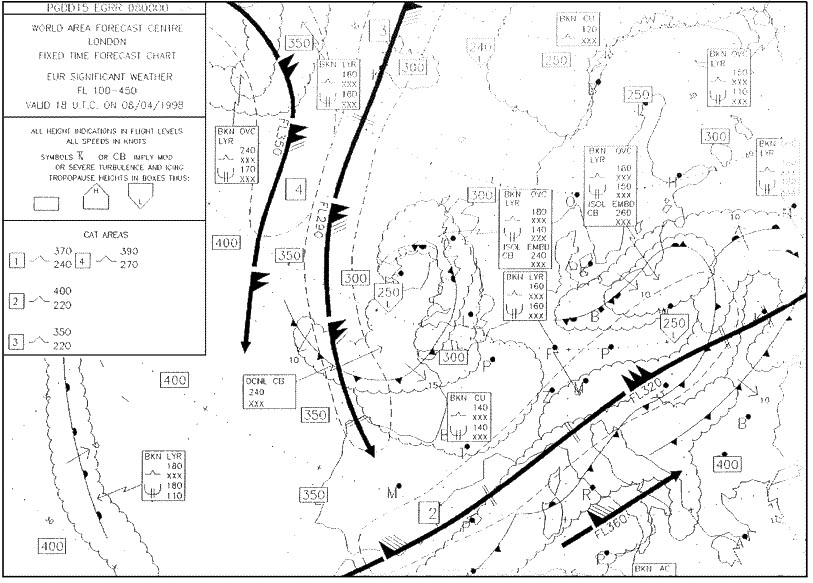 Fl 220.
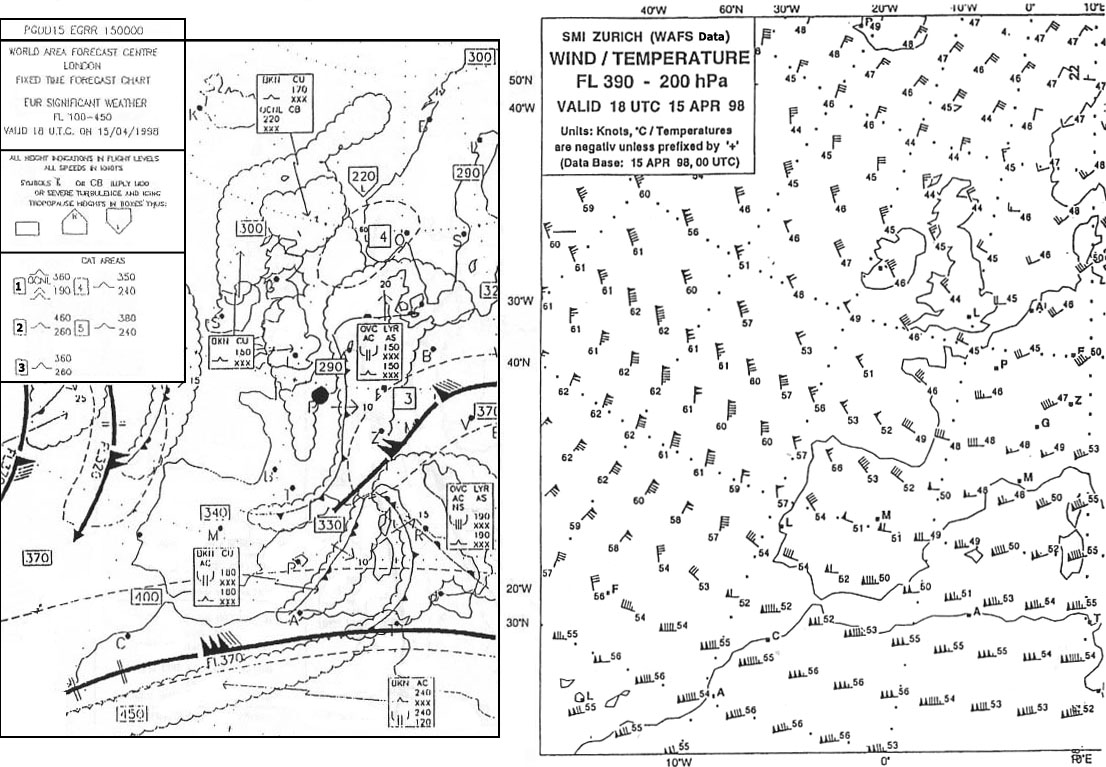
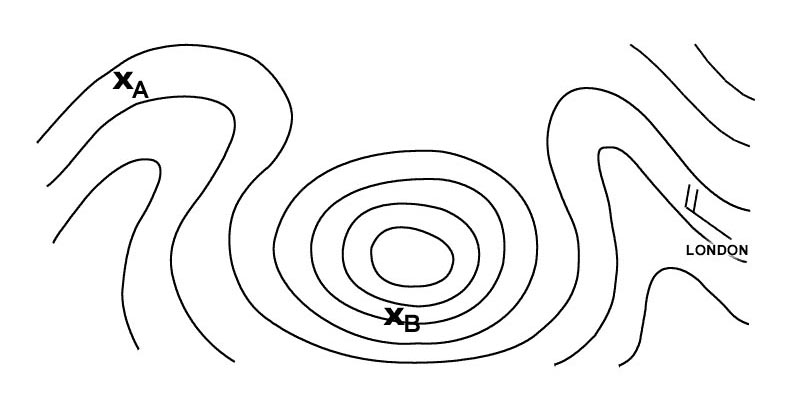
Fl 220. At what flight level is the jet stream core that is situated over northern ?
Question 129-13 : Fl 280 fl 330 fl 360 fl 300
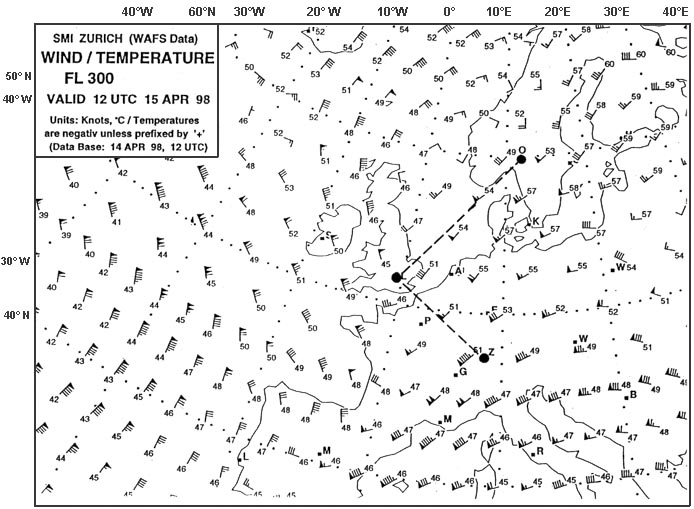 Fl 280.
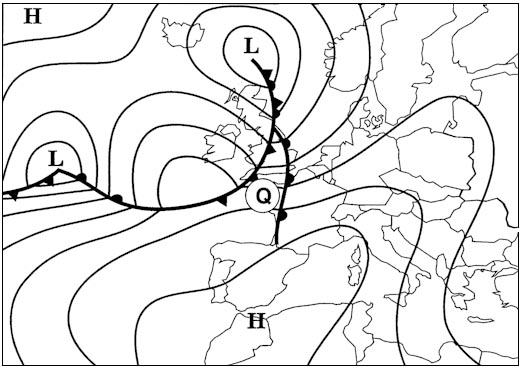
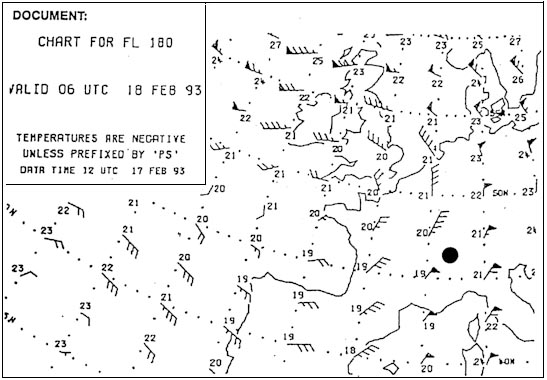
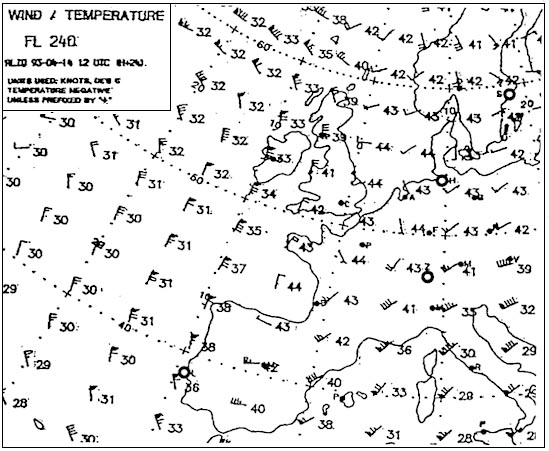
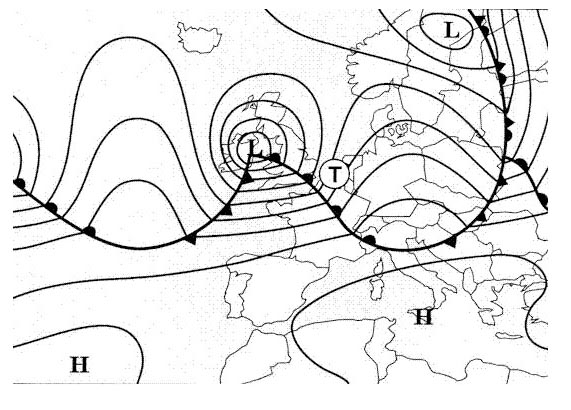
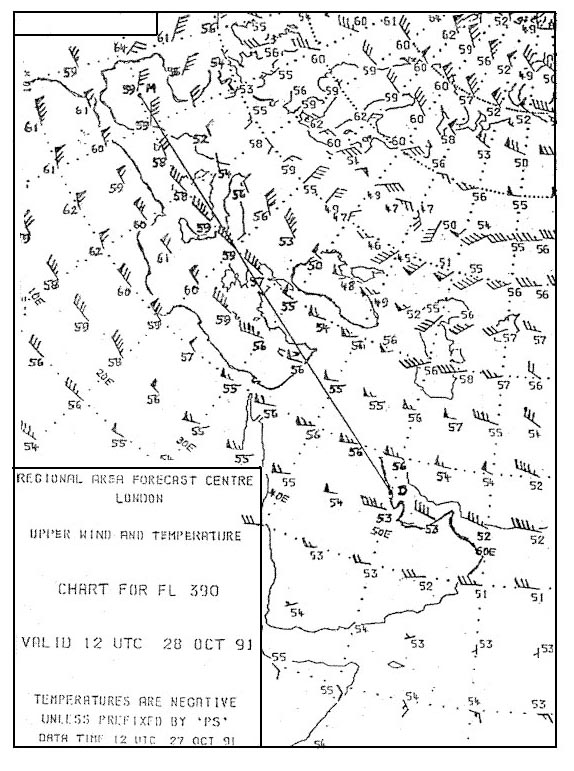
Fl 280. Select from the map the wind for the route zurich london at fl 280 . 277 ?
Question 129-14 : 220/60 250/80 040/60 160/90
 220/60.
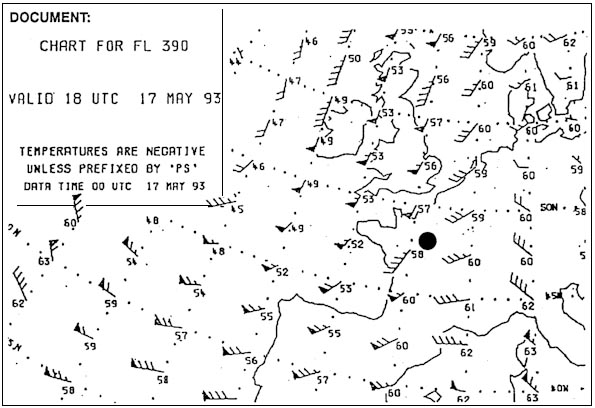
220/60. What name is given to the jet stream lying over north africa b . 280 ?
Question 129-15 : Sub tropical jet stream equatorial jet stream polar front jet stream arctic jet stream
 Sub-tropical jet stream.
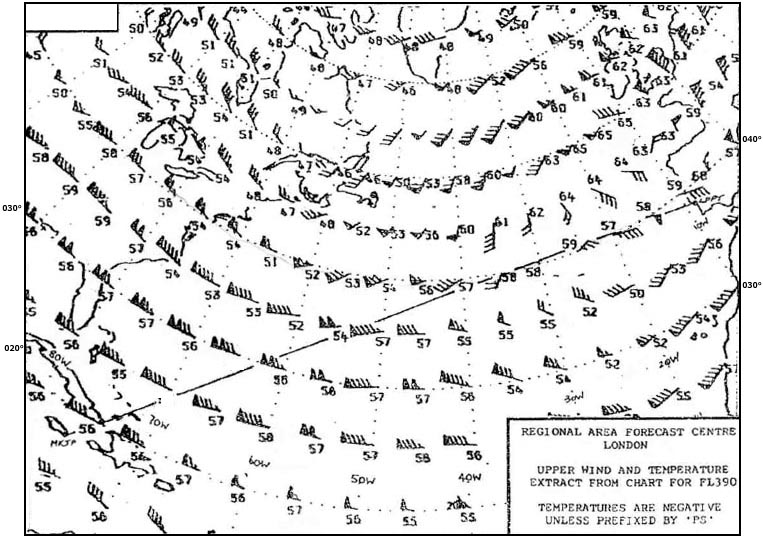
Sub-tropical jet stream. What wind is forecast at fl 390 over paris . 281 ?
Question 129-16 : 210°/40 kt 240°/20 kt 030°/40 kt 190°/40 kt
 210°/40 kt.
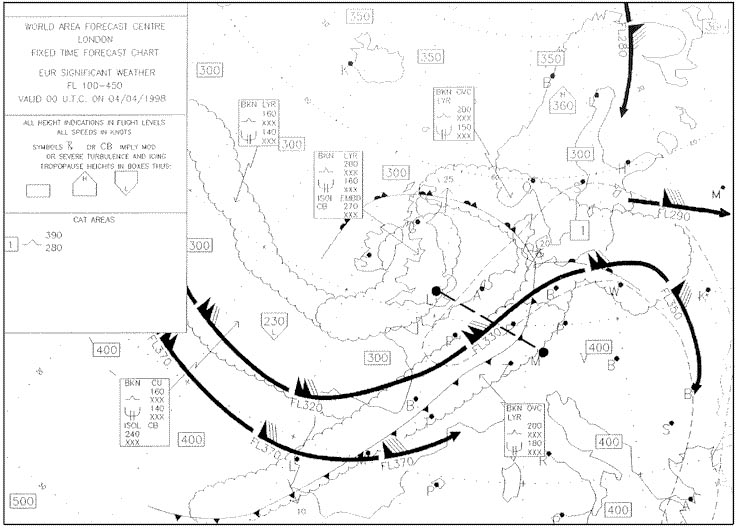
210°/40 kt. What is the direction and maximum speed of the jet stream affecting the route ?
Question 129-17 : 220° / 120 kt 050° / 120 km/h 050° / 120 kt 230° / 120 m/sec
 220° / 120 kt.
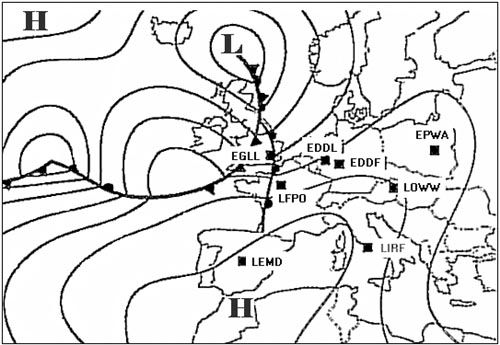
220° / 120 kt. Flight from bordeaux to amsterdam eta 2100 utc at eta amsterdam what surface ?
Question 129-18 : 120° / 15 kt gusts 25 kt 250° / 20 kt 140° / 10 kt 300° / 15 kt maximum wind 25 kt
 120° / 15 kt gusts 25 kt.
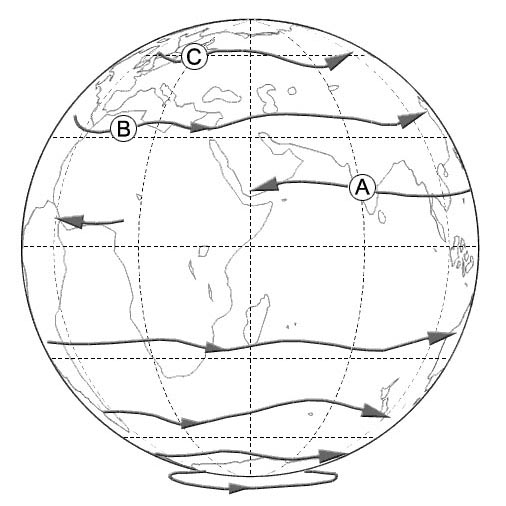
120° / 15 kt gusts 25 kt. The equatorial easterly jet is a jet stream that occurs ?
Question 129-19 : Only in the summer of the northern hemisphere at approximately 45 000 ft only in the winter of the northern hemisphere at approximately 30 000 ft during the whole year in the southern hemisphere during the whole year in the northern hemisphere
 Only in the summer of the northern hemisphere at approximately 45 000 ft.
Only in the summer of the northern hemisphere at approximately 45 000 ft. In which zone of a polar front jet stream is the strongest cat to be expected ?
Question 129-20 : On the polar air side of the core on the tropical air side of the core exactly in the centre of the core about 12000 ft above the core
 On the polar air side of the core.
On the polar air side of the core. What is the minimum speed for a wind to be classified as a jet stream ?
Question 129-21 : 80 kt 50 kt 70 kt 100 kt
 80 kt.
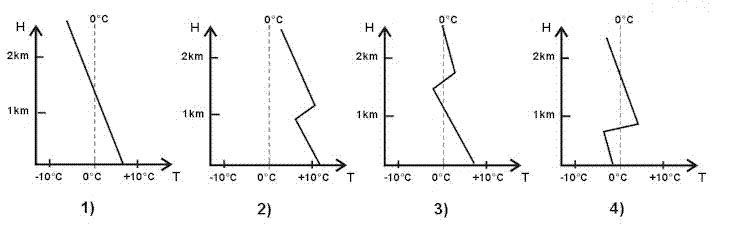
80 kt. A wind sounding in the region of a polar front jet stream gives the following ?
Question 129-22 : With a warm front with a cold front with a itcz with an easterly wave
 With a warm front.
With a warm front. What is the most significant difference between an equatorial jet stream and ?
Question 129-23 : Wind direction vertical dimension horizontal dimension wind speed
 Wind direction.
Wind direction. You cross a jet stream in horizontal flight at approximately right angles while ?
Question 129-24 : This phenomenon is absolutely normal as you are crossing the jet core you assume the front associated with the jet stream to be very weak with practically no temperature difference between the two air masses since the result of such readings seems impossible you will have the instruments tested after landing this phenomenon does not surprise you at all since normally no large temperature differences are possible at these heights
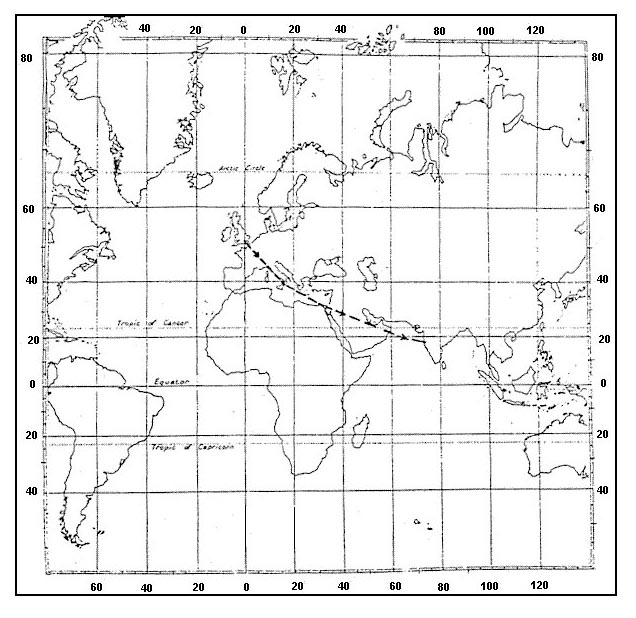 This phenomenon is absolutely normal as you are crossing the jet core.
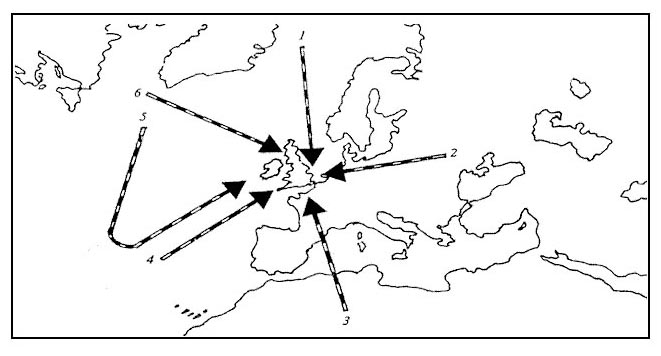
This phenomenon is absolutely normal as you are crossing the jet core. What jet streams are likely to be crossed during a flight from stockholm to rio ?
Question 129-25 : A polar front jet stream followed by one or two subtropical jet streams a subtropical jet stream followed by a polar front jet stream a polar front jet stream followed by a subtropical jet stream and later a second polar front jet stream one subtropical jet stream
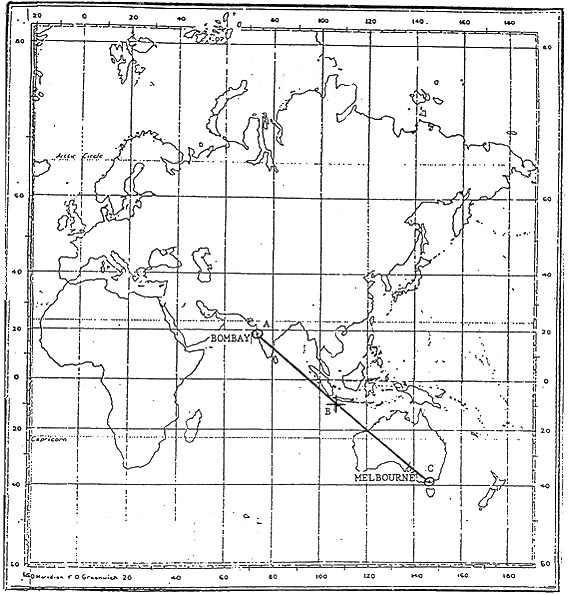 A polar front jet stream followed by one or two subtropical jet streams.
A polar front jet stream followed by one or two subtropical jet streams. While crossing a jet stream at right angles in western europe 3000 ft below its ?
Question 129-26 : Crosswind from the left crosswind from the right a headwind a tailwind
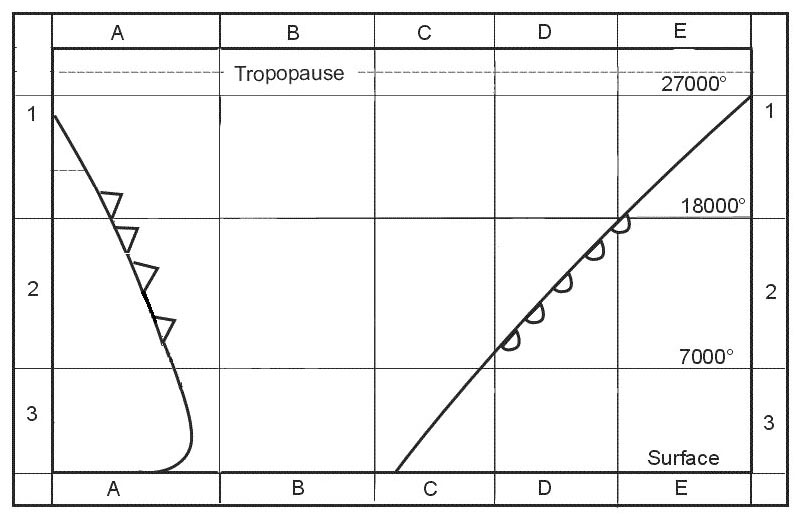 Crosswind from the left.
Crosswind from the left. During the winter months in mid latitudes in the northern hemisphere the polar ?
Question 129-27 : South and speed increases north and speed decreases south and speed decreases north and speed increases
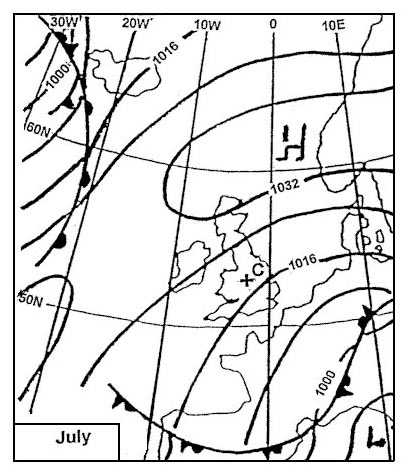 South and speed increases.
South and speed increases. What causes surface winds to flow across the isobars at an angle rather than ?
Question 129-28 : Surface friction coriolis force greater density of the air at the surface greater atmospheric pressure at the surface
 Surface friction.
Surface friction. What prevents air from flowing directly from high pressure areas to low ?
Question 129-29 : Coriolis force surface friction katabatic force the pressure gradient force
 Coriolis force.
Coriolis force. What is the approximate speed of a 25 knot wind expressed in kilometres per hour ?
Question 129-30 : 45 km/h 35 km/h 55 km/h 60 km/h
 45 km/h.
45 km/h. What is the approximate speed of a 90 km/h wind expressed in knots ?
Question 129-31 : 50 kt 55 kt 60 kt 70 kt
 50 kt.
50 kt. What is the approximate speed of a 40 knot wind expressed in m/sec ?
Question 129-32 : 20 m/sec 80 m/sec 72 m/sec 30 m/sec
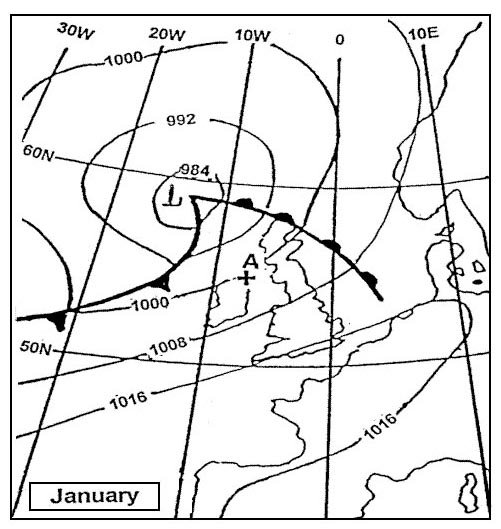 20 m/sec.
20 m/sec. Where in central europe are the highest wind speeds to be found ?
Question 129-33 : Just below the tropopause close to the ground at about 5500 metres altitude in the stratosphere
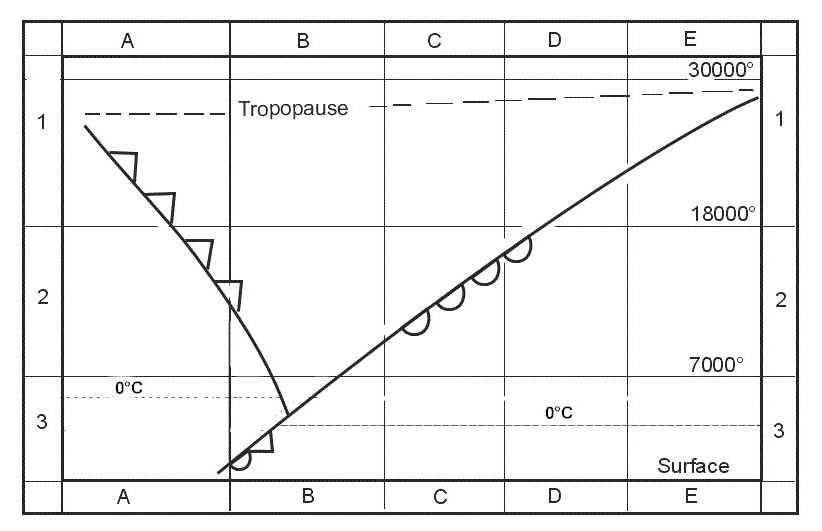 Just below the tropopause.
Just below the tropopause. If paris reports a wind of 19015kt on the metar what wind velocity would you ?
Question 129-34 : 22030 kt 16020 kt 25025 kt 22010 kt
 22030 kt
22030 kt If paris reports a wind of 08010kt on the metar what wind velocity would you ?
Question 129-35 : 11020kt 08015kt 05020kt 08005kt
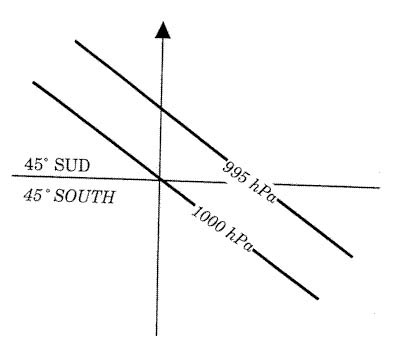 11020kt
11020kt If paris reports a wind of 16020kt on the metar what wind velocity would you ?
Question 129-36 : 19040kt 16030kt 14020kt 17015kt
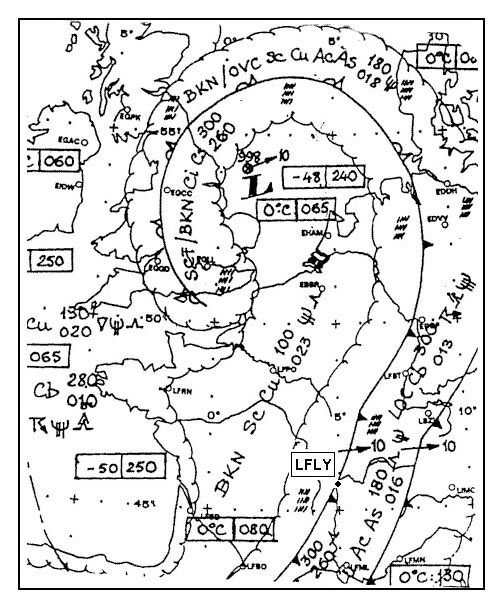 19040kt
19040kt If paris reports a wind of 30012kt on the metar what wind velocity would you ?
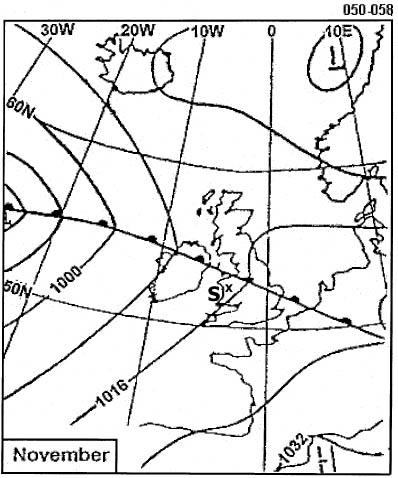
Question 129-37 : 33025kt 23030kt 30025kt 27020kt
 33025kt
33025kt Which of the following is true of a land breeze ?
Question 129-38 : It blows from land to water it blows from water to land it blows by day it blows only at noon
 It blows from land to water.
It blows from land to water. An aircraft is approaching under visual flight rules an airfield whose runway ?
Question 129-39 : Crosswind from the right crosswind from the left tailwind headwind
 Crosswind from the right.
Crosswind from the right. An aircraft is approaching under visual flight rules an airfield northern ?
Question 129-40 : Crosswind from the left headwind tailwind crosswind from the right
 Crosswind from the left.
Crosswind from the left. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5119 Free Training Exam
