In the icao standard atmosphere which of the following alternatives indicates ? [ Preparation civilian ]
Question 128-1 : 15°c at mean sea level decreasing at 0 65°c per 100 metres 13°c at mean sea level decreasing at 2°c per 1000 feet 15°c at mean sea level decreasing at 0 65°c per 100 feet 15 2°c at mean sea level decreasing at 0 65°c per 100 metres
 15°c at mean sea level, decreasing at 0,65°c per 100 metres.
15°c at mean sea level, decreasing at 0,65°c per 100 metres. An aircraft is flying from point a to point b at the flight level corresponding ?
Question 128-2 : Wind speed over a is higher than over b the true altitude will be higher over a than over b wind speed over b is higher than over a the true altitude will be higher over a than over madrid
 Wind speed over a is higher than over b.
Wind speed over a is higher than over b. Which constant pressure chart is standard for fl 450 ?
Question 128-3 : 150 hpa 200 hpa 250 hpa 300 hpa
 150 hpa.
150 hpa. What is meant by the term 'altitude' ?
Question 128-4 : The vertical distance of a level or a point measured from mean sea level the vertical distance of a level or a point measured from the earth's surface altimeter indication when altimeter subscale is set to present qfe the vertical distance of a level or a point measured from the aerodrome reference point
 The vertical distance of a level or a point measured from mean sea level.
The vertical distance of a level or a point measured from mean sea level. Which fl corresponds with the 250 hpa pressure level ?
Question 128-5 : Fl 340 fl 390 fl 450 fl 300
 Fl 340.
Fl 340. An aircraft flies at flight level 40 elevation of the aerodrome 990 ft qnh 976 ?
Question 128-6 : Only a small change of altitude is necessary the aircraft has to descend about 2000 ft the aircraft has to climb about 1000 ft the aircraft has to descend about 1000 ft
 Only a small change of altitude is necessary.
Only a small change of altitude is necessary. A surface based inversion is a characteristic of ?
Question 128-7 : Nocturnal radiation during clear nights cumulus clouds hill fog the passage of cold front
 Nocturnal radiation during clear nights.
Nocturnal radiation during clear nights. Flight from lisbon to kingston .considering the route segment between 30°w and ?
Question 128-8 : 56°c 59°c 52°c 61°c
 -56°c.
-56°c. What is the approximate value of atmospheric pressure at 11000 m amsl in ?
Question 128-9 : One fourth one half one eights the same
 One-fourth.
One-fourth. Which type of inversion can lead to fog formation due to the temperature of air ?
Question 128-10 : Ground inversion frontal inversion turbulence inversion subsidence inversion
 Ground inversion
Ground inversion You are flying at fl 300 where the outside air temperature is 57 5°c and the ?
Question 128-11 : 28500 ft 30000 ft 25000 ft 31500 ft
 28500 ft.
28500 ft. At what flight level is the zero degree isotherm at the equator ?
Question 128-12 : Fl 180 fl 150 fl 200 fl 250
 Fl 180.
Fl 180. Why are polar regions colder than equatorial regions ?
Question 128-13 : Because the angle of incidence of the solar radiation is very small in polar regions because the angle of incidence of the solar radiation is very large in polar regions the sky in the polar regions is cloud covered almost all the year the polar regions stay in the dark almost all the year
 Because the angle of incidence of the solar radiation is very small in polar regions.
Because the angle of incidence of the solar radiation is very small in polar regions. Which of the following is true concerning atmospheric pressure ?
Question 128-14 : It decreases with height it is higher in winter than in summer it is higher at night than during the day it always decreases with height at a rate of 1 hpa per 8m
 It decreases with height.
It decreases with height. The vertical temperature gradient lapse rate in the international standard ?
Question 128-15 : 6 5°c per 1000 m 2°c per 1000 m 3°c per 1000 m 4 5°c per 1000 m
 6.5°c per 1000 m.
6.5°c per 1000 m. What is the approximate height of the tropopause between keflavik and helsinki ?
Question 128-16 : Fl 320 fl 300 fl 360 fl 350
 Fl 320.
Fl 320. For a flight from the azores to the bermudas the tropical tropopause is to be ?
Question 128-17 : 51000 ft 12000 metres 60 000 ft 14000 metres 39 000 ft 9000 metres 33 000 ft 8000 metres
 51000 ft (12000 metres).
51000 ft (12000 metres). Tropopause altitude at 38°n 19°w is . 410 ?
Question 128-18 : Fl 320 fl 360 fl 420 fl 400
 Fl 320.
Fl 320. Assuming a normal vertical temperature gradient at what altitude will the ?
Question 128-19 : Fl 60 fl 20 fl 140 fl 120
 Fl 60.
Fl 60. The temperature deviation from isa to the nearest °c overhead charleston at fl ?
Question 128-20 : +5 +3 7 5
 +5.
+5. The maximum possible temperature at north pole is ?
Question 128-21 : Dependent on the seasons 10°c +10°c 20°c
 Dependent on the seasons.
Dependent on the seasons. In the northern hemisphere the force that causes a deviation to the left from ?
Question 128-22 : Frictional force centripetal force pressure gradient coriolis force
 Frictional force.
Frictional force. The wind indicator for a weather observation receives the measured value from ?
Question 128-23 : On a mast 8 10 m above the runway 1 m above the runway close to the station about 2 m above the ground on the roof of the weather station
 On a mast 8-10 m above the runway.
On a mast 8-10 m above the runway. The geostrophic wind is greater than the gradient wind around a low pressure ?
Question 128-24 : Centrifugal force opposes the pressure gradient centrifugal force is added to the pressure gradient coriolis force is added to the pressure gradient coriolis force opposes to the centrifugal force
 Centrifugal force opposes the pressure gradient.
Centrifugal force opposes the pressure gradient. The geostrophic wind is less than the gradient wind around an anticyclone ?
Question 128-25 : Centrifugal force is added to the pressure gradient centrifugal force opposes the pressure gradient effect of coriolis is added to friction coriolis effect opposes the centrifugal force
 Centrifugal force is added to the pressure gradient.
Centrifugal force is added to the pressure gradient. In the lower layers of the atmosphere due to friction the wind changes ?
Question 128-26 : Wind speed decreases and therefore coriolis force decreases the pressure gradient increases turbulence is formed and pressure increases turbulence is formed and pressure decreases
 Wind speed decreases and therefore coriolis force decreases.
Wind speed decreases and therefore coriolis force decreases. The most frequent wind direction in a valley caused by thermal effects is ?
Question 128-27 : Mountain during daylight hours mountain at night valley during daylight hours valley during daylight as much as at night
 Mountain during daylight hours.
Mountain during daylight hours. Convective activity over land in mid latitudes is greatest in ?
Question 128-28 : Summer in the afternoon winter during the night and early morning summer during the night and early morning winter in the afternoon
 Summer in the afternoon.
Summer in the afternoon. Which forces are balanced with geostrophic winds ?
Question 128-29 : Pressure gradient force coriolis force friction force pressure gradient force coriolis force pressure gradient force coriolis force centrifugal force pressure gradient force centrifugal force friction force
 Pressure gradient force, coriolis force.
Pressure gradient force, coriolis force. How does moderate turbulence affect an aircraft ?
Question 128-30 : Changes in altitude or attitude occur but the aircraft remains in positive control at all times rapid and somewhat rhythmic bumpiness is experienced without appreciable changes in altitude or attitude large abrupt changes in altitude or attitude occur but the aircraft may only be out of control momentarily continued flight in this environment will result in structural damage
 Changes in altitude or attitude occur but the aircraft remains in positive control at all times.
Changes in altitude or attitude occur but the aircraft remains in positive control at all times. Which degree of aircraft turbulence is determined by the following icao ?
Question 128-31 : Moderate severe violent light
 Moderate.
Moderate. In a land and sea breeze circulation the land breeze blows ?
Question 128-32 : During the night and is weaker than the sea breeze during the day and is stronger than the sea breeze during the day and is weaker than the sea breeze during the night and is stronger than the sea breeze
 During the night and is weaker than the sea-breeze.
During the night and is weaker than the sea-breeze. A high pressure area slack pressure gradient covers part of the mediterranean ?
Question 128-33 : Sea to land land to sea variable parallel to the coastline
 Sea to land.
Sea to land. A mountain breeze katabatic wind blows ?
Question 128-34 : Down the slope during the night up the slope during the day down the slope during the day up the slope during the night
 Down the slope during the night.
Down the slope during the night. Generally northern hemisphere winds at 5000 ft/agl are south westerly while ?
Question 128-35 : Friction between the wind and the surface a strong pressure gradient at higher altitudes stronger coriolis force at the surface the influence of warm air at the lower altitude
 Friction between the wind and the surface.
Friction between the wind and the surface. Friction between the air and the ground results in the northern hemisphere in ?
Question 128-36 : Backing of the wind and decrease of wind speed at the surface veering of the wind and decrease of wind speed at the surface backing of the wind and increase of wind speed at the surface veering of the wind and increase of wind speed at the surface
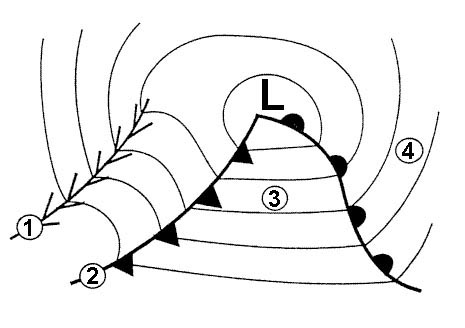
 Backing of the wind and decrease of wind speed at the surface.
Backing of the wind and decrease of wind speed at the surface. What degree of turbulence if any is likely to be encountered while flying ?
Question 128-37 : Severe turbulence in cb cloud moderate turbulence in ns cloud light turbulence in cb cloud light turbulence in st cloud
 Severe turbulence in cb cloud.
Severe turbulence in cb cloud. You are flying at 2500 ft/agl above ground level the wind is 180° and intend ?
Question 128-38 : South southeast south southwest southwest south
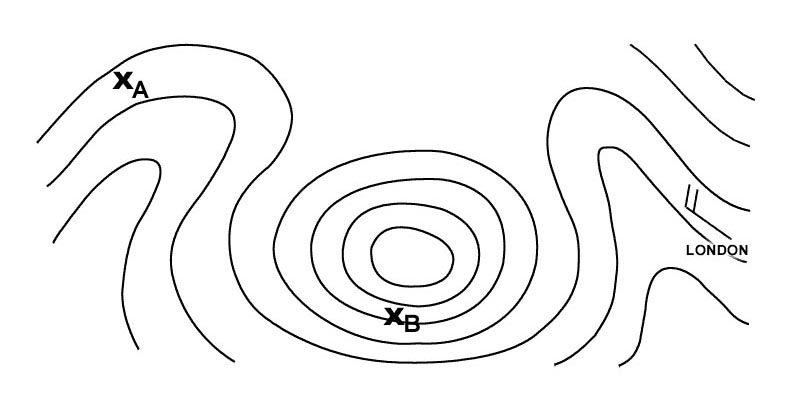 South-southeast.
South-southeast. What units are used to report vertical wind shear ?
Question 128-39 : Kt/100 ft kt m/100 ft m/sec
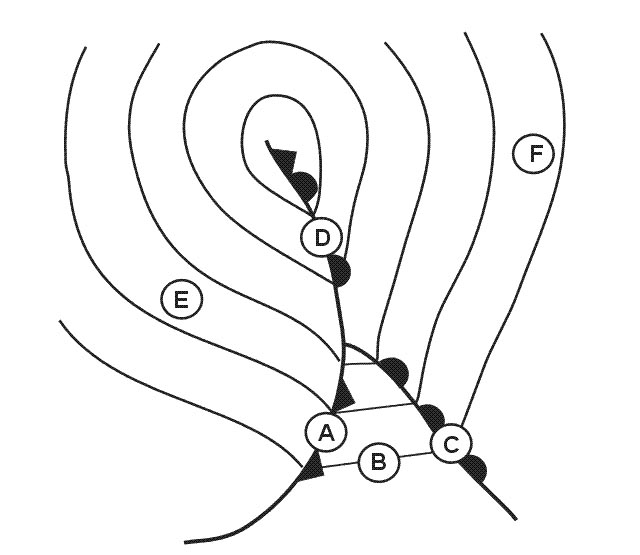 Kt/100 ft.
Kt/100 ft. What name is given to the jet stream lying across india a . 262 ?
Question 128-40 : Tropical jet stream polar front jet stream arctic jet stream sub tropical jet stream
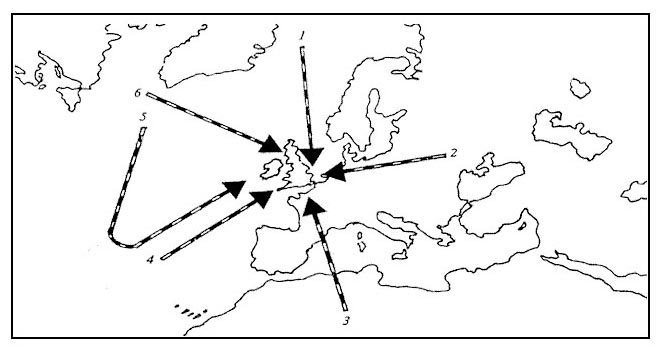 Tropical jet stream.
Tropical jet stream. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5079 Free Training Exam
