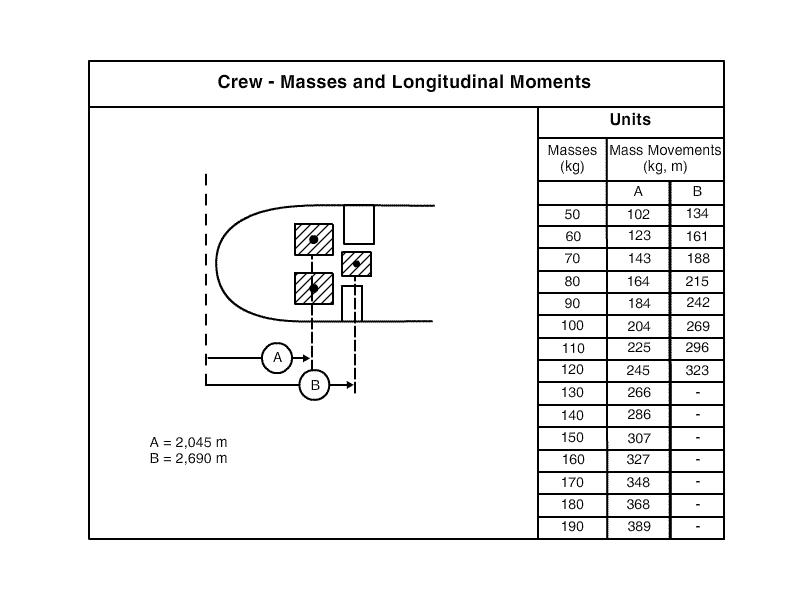
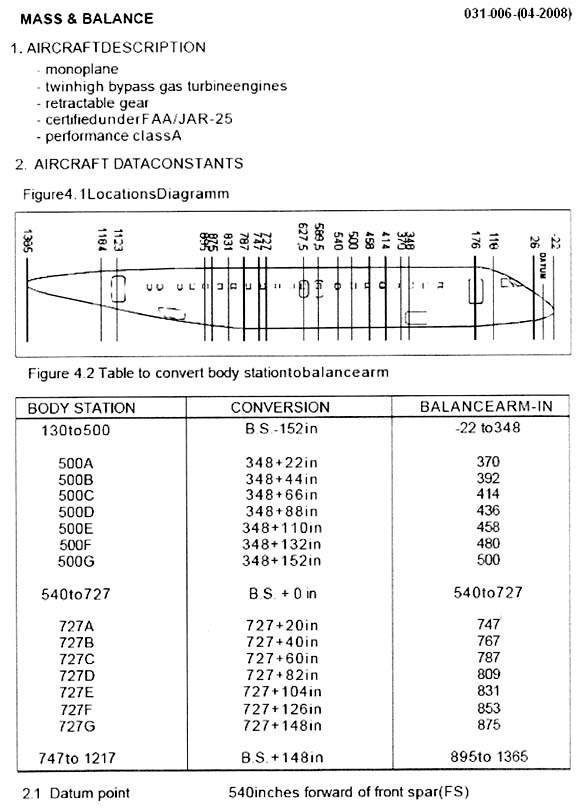
With all other quantities being constant the density of the atmosphere ? [ Preparation civilian ]
Question 127-1 : Air pressure relative humidity stability temperature
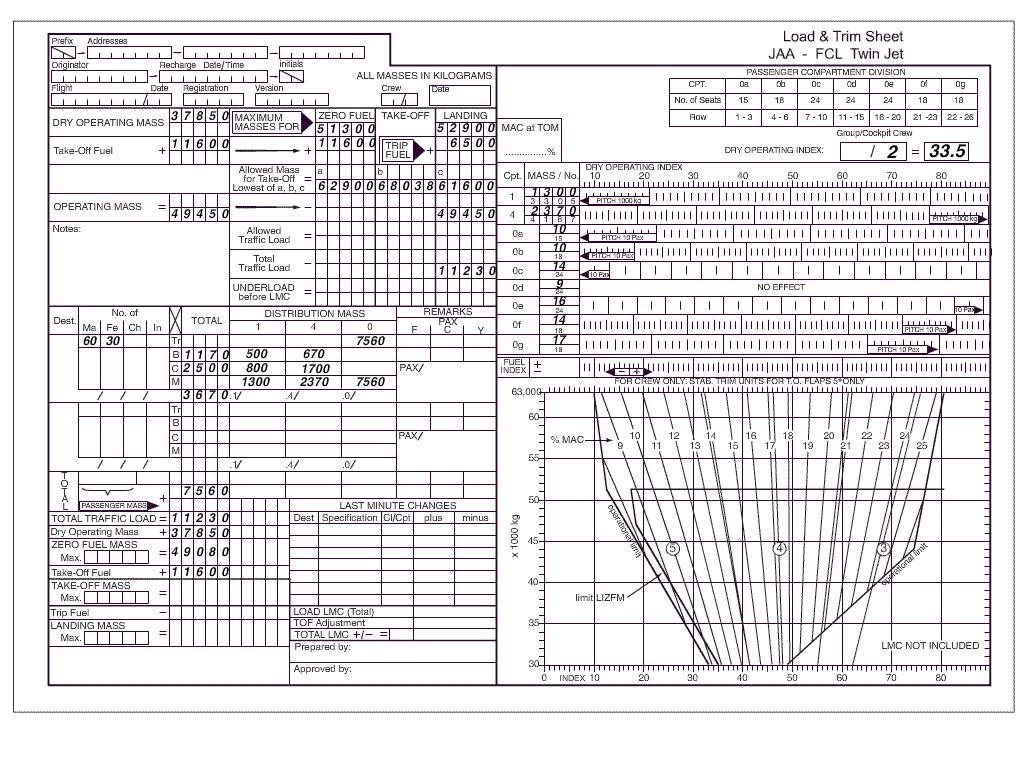 Air pressure.
Air pressure. You are flying over the sea at fl 250 and measure an outside temperature of ?
Question 127-2 : 23770 ft/amsl 26230 ft/amsl 26770 ft/amsl 23230 ft/amsl
 23770 ft/amsl.
23770 ft/amsl. You are flying at fl 200 .outside air temperature is 40°c and the pressure at ?
Question 127-3 : 19310 ft 20630 ft 21770 ft 18290 ft
 19310 ft.
19310 ft. You are flying at fl 160 .outside air temperature is 27°c and the pressure at ?
Question 127-4 : 15100 ft 15620 ft 16360 ft 16920 ft
 15100 ft.
15100 ft. Which statement concerning the tropopause is correct ?
Question 127-5 : The layer just above the tropopause is absolutely stable above the tropopause no clear air turbulence occurs in the icao standard atmosphere the tropopause lies lower over the poles than over the equator the temperature at the tropopause is approximately 80°c over the poles and 40°c over the equator
Pressure altitude is obtained by ?
Question 127-6 : Setting the altimeter to standard sea level pressure correcting the altimeter for temperature deviation from isa setting the altimeter to a station pressure which has been corrected to sea level setting the altimeter to qff pressure
 Setting the altimeter to standard sea level pressure.
Setting the altimeter to standard sea level pressure. What is approximately the temperature at 20000 ft in the icao standard ?
Question 127-7 : 25°c 15°c 20°c 30°c
 -25°c.
-25°c. What is the most probable temperature at the tropical tropopause ?
Question 127-8 : 75°c 55°c 35°c 25°c
 -75°c.
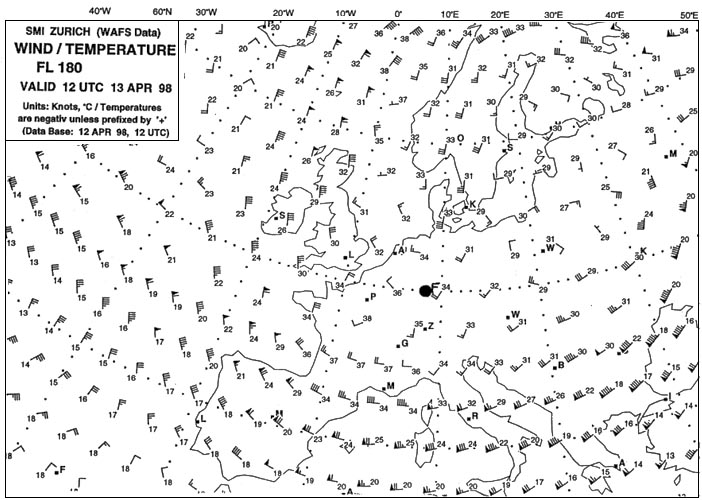
-75°c. What is the average temperature difference from isa at fl 300 between edinburgh ?
Question 127-9 : 2°c +12°c +2°c 12°c
 -2°c.
-2°c. Considering the route between valencia and charleston at fl 340 the forecast ?
Question 127-10 : 50°c 45°c 55°c 40°c
 -50°c
-50°c The temperature lapse rate of the standard atmosphere in the troposphere is ?
Question 127-11 : 2°c/1000 ft 3°c/1000 ft 6 5°c/1000 ft 2 5°c/1000 ft
 2°c/1000 ft.
2°c/1000 ft. The radiosonde can directly measure ?
Question 127-12 : Atmospheric pressure air temperature humidity air temperature humidity wind humidity wind atmospheric pressure wind atmospheric pressure air temperature
 Atmospheric pressure, air temperature, humidity.
Atmospheric pressure, air temperature, humidity. Flight from lisbon lppt to kingston mkjp at 40°n 20°w the temperature ?
Question 127-13 : 0°c +6°c +2°c 2°c
 0°c.
0°c. At which pressure and temperature conditions may you safely assume that the ?
Question 127-14 : At a temperature greater than or equal to that of the isa and where the qnh is greater than or equal to 1013 25 hpa in a cold low pressure region at a temperature less than or equal to that of the isa and where the qnh is less than 1013 25 hpa in a very cold area with a qnh of 1015 hpa
 At a temperature greater than or equal to that of the isa and where the qnh is greater than or equal to 1013.25 hpa.
At a temperature greater than or equal to that of the isa and where the qnh is greater than or equal to 1013.25 hpa. Given .altimeter setting 1013 2 hpa.altimeter reading 5000 ft.outside air ?
Question 127-15 : 3515 ft 4190 ft 4325 ft 4865 ft
 3515 ft.
3515 ft. At fl 180 the air temperature is 35°c the air density at this level is ?
Question 127-16 : Greater than the density of the isa at fl 180 less than the density of the isa at fl 180 equal to the density of the isa at fl 180 unable to be determined without knowing the qnh
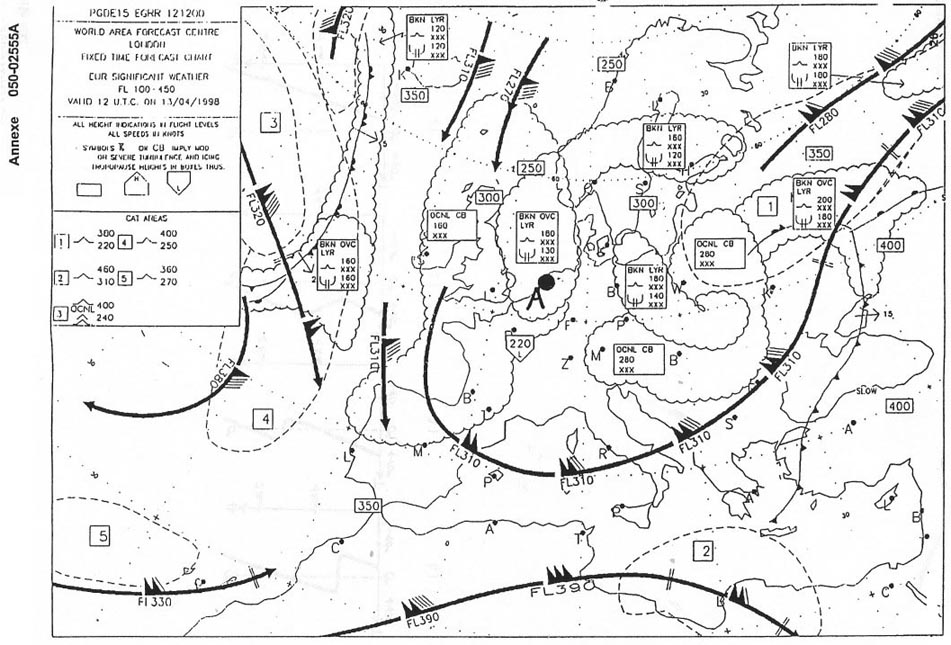 Greater than the density of the isa at fl 180.
Greater than the density of the isa at fl 180. An aircraft flies at flight level 40 elevation of the aerodrome 990 ft and qnh ?
Question 127-17 : Only a small change of altitude is necessary the aircraft has to climb about 1000 ft the aircraft has to descend about 1000 ft the aircraft has to descend about 2000 ft
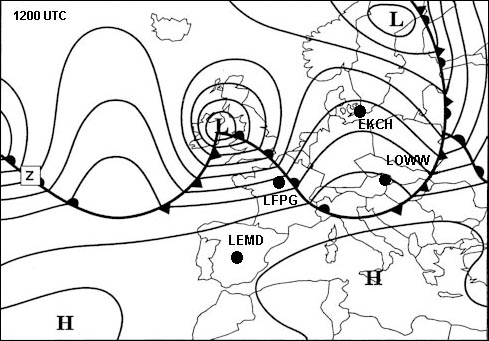 Only a small change of altitude is necessary.
Only a small change of altitude is necessary. The mean temperature that may be expected to affect that segment of the route ?
Question 127-18 : 38°c 34°c 30°c 42°c
 -38°c.
-38°c. Flight from lisbon lppt to kingston mkjp considering the route segment between ?
Question 127-19 : 55°c 52°c 58°c 61°c
 -55°c.
-55°c. What is the average temperature difference from isa at fl 390 between madrid ?
Question 127-20 : 1°c +5°c 5°c +2°c
 -1°c
-1°c The diurnal variation in temperature is largest when ?
Question 127-21 : The sky is clear and the wind is weak the sky is clear and the wind is strong the sky is overcast and the wind is weak the sky is overcast and the wind is strong
 The sky is clear and the wind is weak
The sky is clear and the wind is weak Which of the following statements concerning the tropopause is correct ?
Question 127-22 : The temperature lapse rate changes abruptly at the tropopause the temperature remains constant above and below the tropopause the temperature of the tropopause at the equator is higher than at the poles the temperature of the tropopause at the equator and at the poles is equal
 The temperature lapse rate changes abruptly at the tropopause.
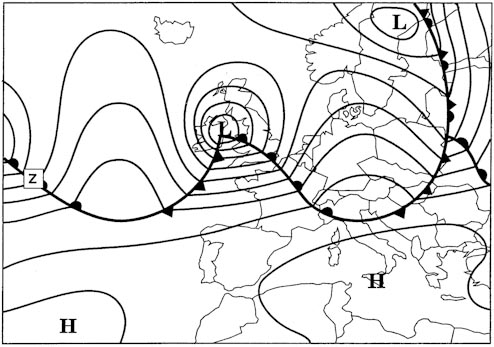
The temperature lapse rate changes abruptly at the tropopause. An aircraft is flying through the alps on a very cold winter's day the regional ?
Question 127-23 : A higher altitude than the elevation of the summit a lower altitude than the elevation of the summit the same altitude as the elevation of the summit there is insufficient information to come to a conclusion
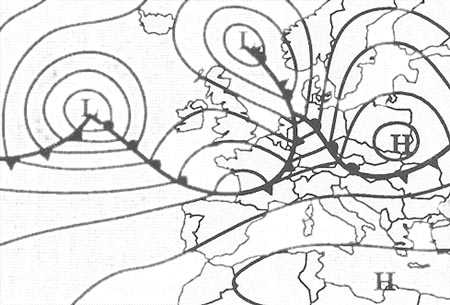 A higher altitude than the elevation of the summit.
A higher altitude than the elevation of the summit. An aircraft is flying through the alps on a warm summer's day the weather is ?
Question 127-24 : A lower altitude than the elevation of the summit a higher altitude than the elevation of the summit the same altitude as the elevation of the summit there is insufficient information to come to a conclusion
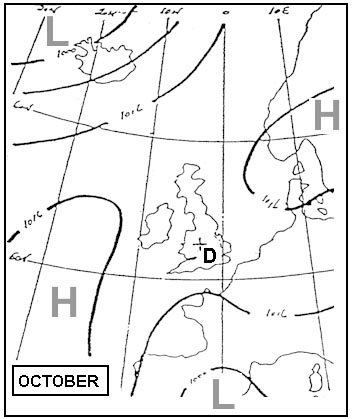 A lower altitude than the elevation of the summit.
A lower altitude than the elevation of the summit. What is the approximate vertical interval which is equal to a pressure change ?
Question 127-25 : 8 m 27 ft 15 m 50 ft 32 m 105 ft 64 m 210 ft
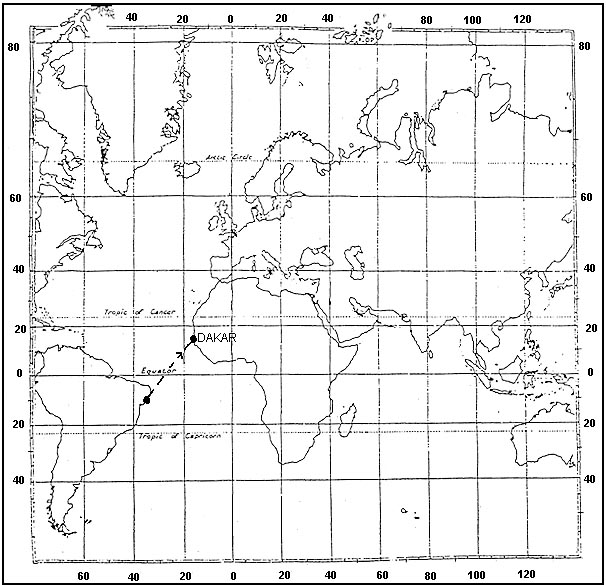 8 m (27 ft).
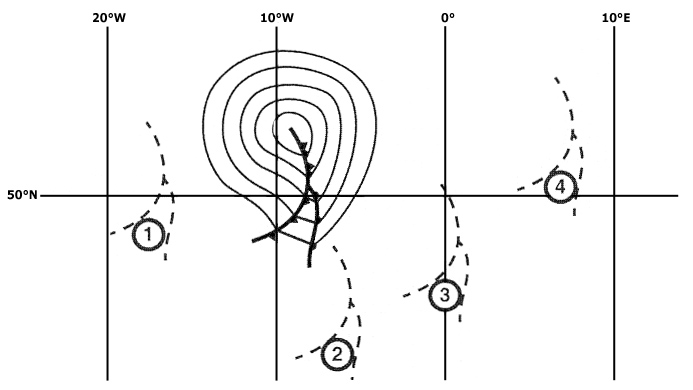
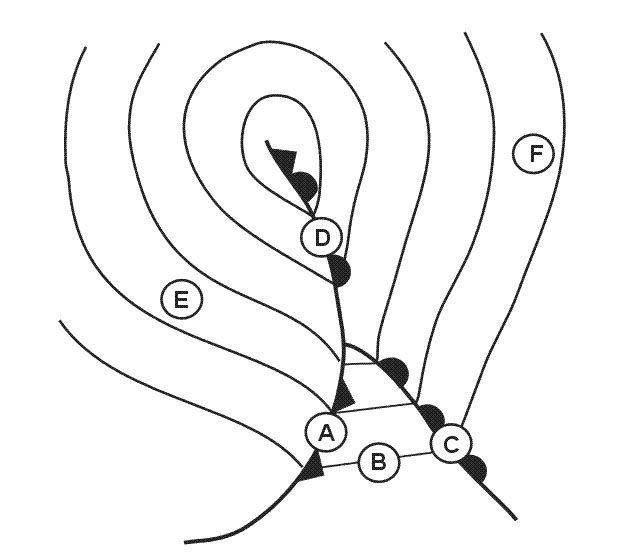
8 m (27 ft). On a route segment from a to b the highest terrain elevation is approximately ?
Question 127-26 : 1300 feet 1400 feet 1100 feet 1000 feet
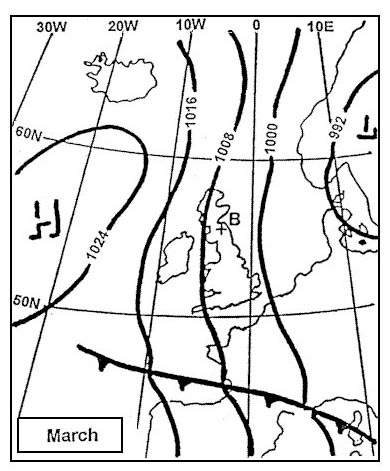 1300 feet.
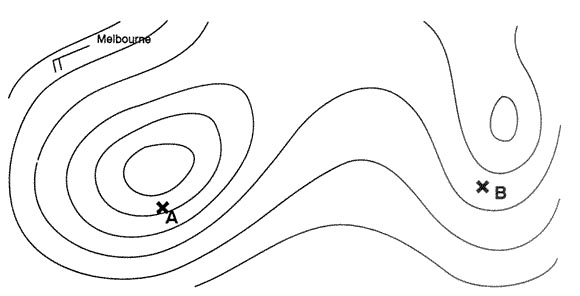
1300 feet. An aircraft is flying from point a to point b at the flight level corresponding ?
Question 127-27 : Wind speed over b is higher than over a the true altitude will be higher over b than over a wind speed over a is higher than over b the true altitude will be higher over b than over london
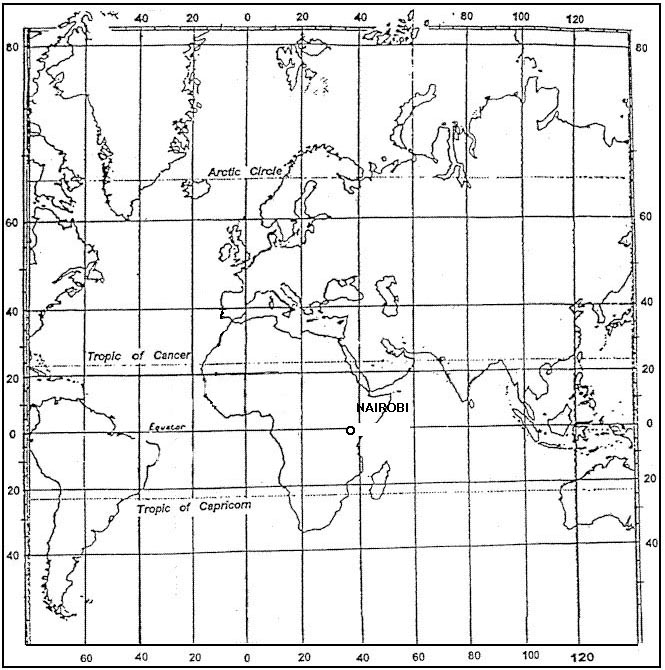 Wind speed over b is higher than over a.
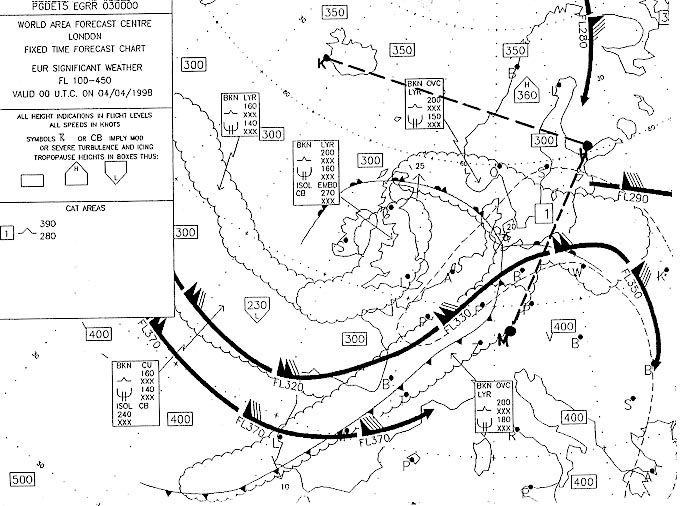
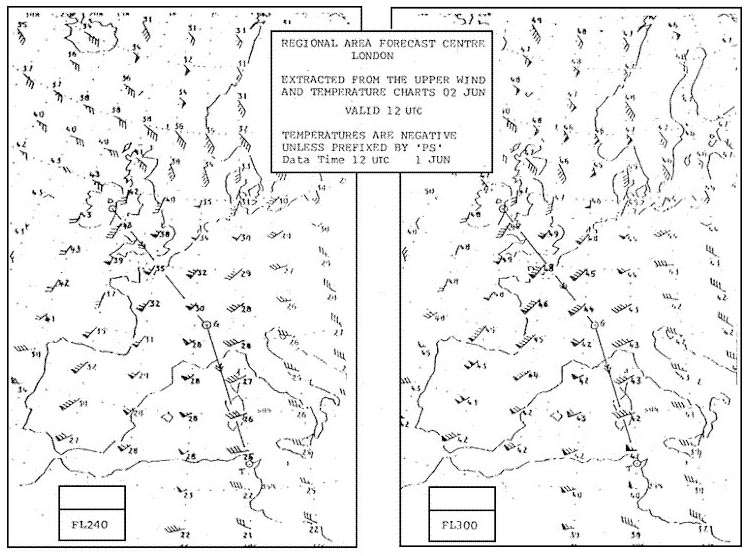
Wind speed over b is higher than over a. Which of the following constant pressure charts would be most relevant for ?
Question 127-28 : 150 hpa 200 hpa 250 hpa 300 hpa
 150 hpa.
150 hpa. By volume which of the following elements makes up the largest part of the ?
Question 127-29 : Nitrogen hydrogen oxygen noble gases
 Nitrogen.
Nitrogen. Which fl corresponds with the 400 hpa pressure level ?
Question 127-30 : Fl 240 fl 300 fl 340 fl 140
 Fl 240.
Fl 240. By volume what percentage of the air in the lower troposphere consists of water ?
Question 127-31 : 0 5% 5 10% 10 15% 20 30%
 0-5%.
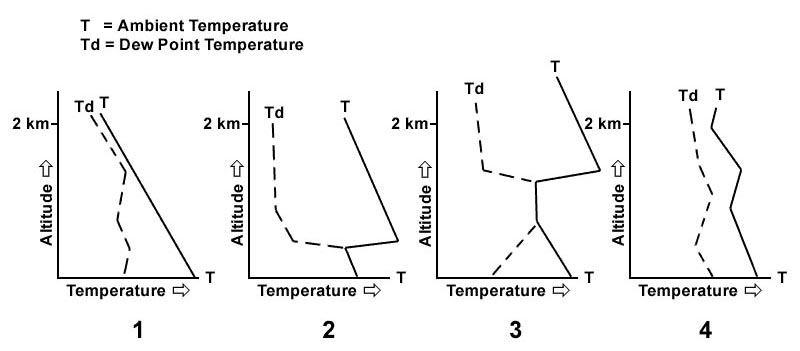
0-5%. Consider a parcel of air being forced upwards in the atmosphere the lapse rate ?
Question 127-32 : Will tend to descend to its original altitude will tend to ascend further will tend to remain at the new altitude will become conditionally unstable
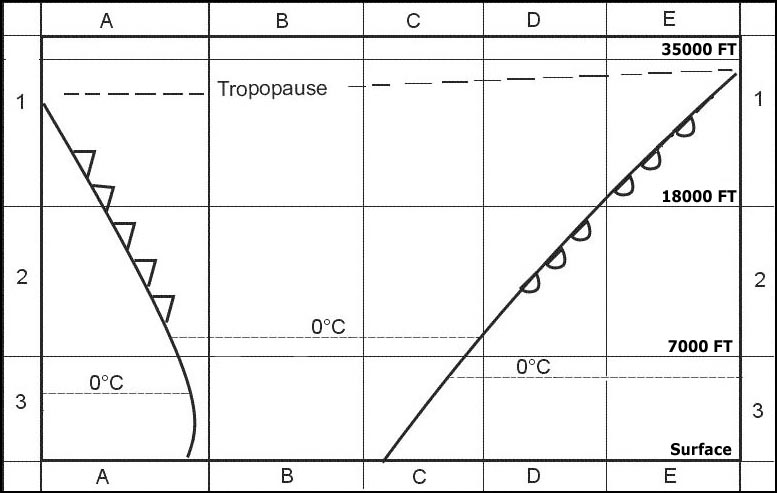 Will tend to descend to its original altitude.
Will tend to descend to its original altitude. What kind of turbulence is dependent on the sun's radiation and therefore ?
Question 127-33 : Convective turbulence mechanical turbulence orographic turbulence turbulence induced by wind speed
 Convective turbulence.
Convective turbulence. What is meant by qfe ?
Question 127-34 : The atmospheric pressure at the official aerodrome elevation the atmospheric pressure at the official aerodrome elevation reduced to mean sea level in standard atmospheric conditions the pressure at msl in standard atmospheric conditions the present atmospheric pressure at an aerodrome converted to mean sea level in accordance with the actual conditions
 The atmospheric pressure at the official aerodrome elevation.
The atmospheric pressure at the official aerodrome elevation. When the subscale of a pressure altimeter is set to the qfe of the destination ?
Question 127-35 : Zero at landing roll out airfield elevation at landing roll out more than the airfield elevation the aircraft's altitude above msl
 Zero at landing roll out.
Zero at landing roll out. If the subscale of an altimeter is set to qnh what will it indicate after ?
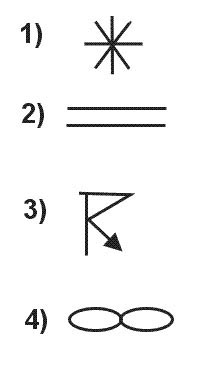
Question 127-36 : Aerodrome elevation less than aerodrome elevation when it is colder than standard more than aerodrome elevation when it is warmer than standard less than aerodrome elevation when pressure is lower than standard more than aerodrome elevation when pressure is higher than standard pressure altitude
 Aerodrome elevation.
Aerodrome elevation. The mean height of the tropical tropopause is ?
Question 127-37 : 44000 ft 49000 ft 54000 ft 59000 ft
 44000 ft.
44000 ft. An aircraft is flying from point a to point b at the flight level corresponding ?
Question 127-38 : Wind speed over b is higher than over paris the true altitude will be higher over b than over a wind speed over a is higher than over b the true altitude will be higher over b than over paris
 Wind speed over b is higher than over paris.
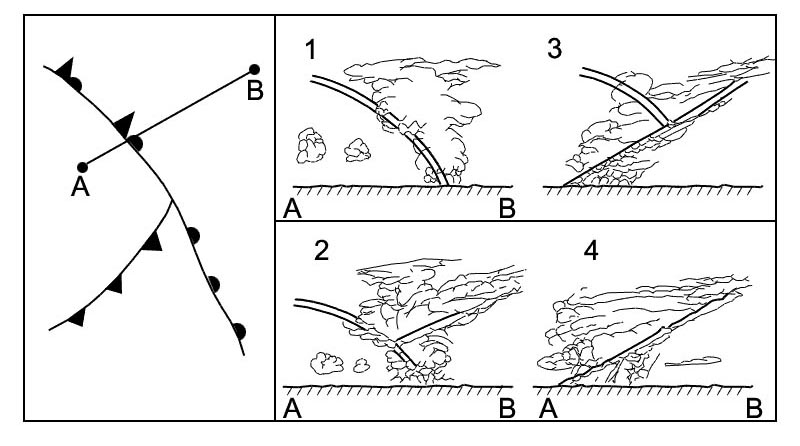
Wind speed over b is higher than over paris. A temperature inversion indicates a state of the atmosphere which is ?
Question 127-39 : Absolutely stable absolutely unstable indifferent conditionally unstable
 Absolutely stable.
Absolutely stable. Which fl corresponds with the 150 hpa pressure level ?
Question 127-40 : Fl 450 fl 390 fl 340 fl 300
 Fl 450.
Fl 450. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
5039 Free Training Exam
