The troposphere is the ? [ Preparation civilian ]
Question 126-1 : Part of the atmosphere below the tropopause part of the atmosphere above the stratosphere boundary between the mesosphere and thermosphere boundary between the stratosphere and the mesosphere
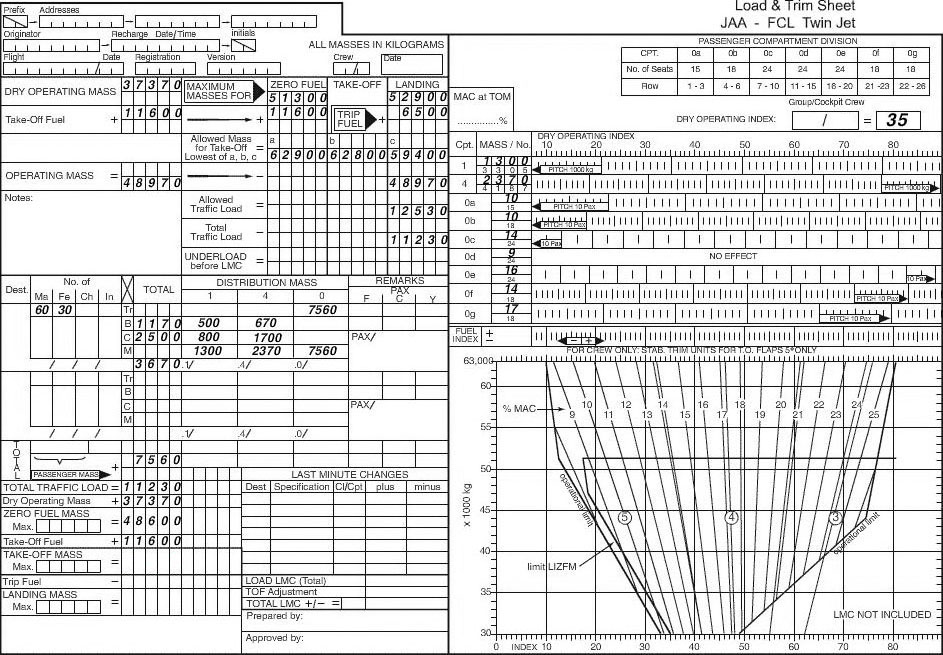 Part of the atmosphere below the tropopause
Part of the atmosphere below the tropopause The tropopause is a level at which ?
Question 126-2 : Temperature ceases to fall with increasing height water vapour content is greatest pressure remains constant vertical currents are strongest
 Temperature ceases to fall with increasing height.
Temperature ceases to fall with increasing height. The tropopause is lower ?
Question 126-3 : Over the north pole than over the equator in summer than winter in moderate latitudes south of the equator than north of it over the equator than over the south pole
 Over the north pole than over the equator
Over the north pole than over the equator The temperature at 10000 ft in the icao standard atmosphere is ?
Question 126-4 : 5°c 0°c 20°c 35°c
 -5°c.
-5°c. What of the following is the most important constituent in the atmosphere from ?
Question 126-5 : Water vapour nitrogen hydrogen oxygen
The average height of the tropopause at 50°n is about ?
Question 126-6 : 11 km 8 km 14 km 16 km
 11 km.
11 km. The height and the temperature of the tropopause are respectively in the order ?
Question 126-7 : 16 km and 75°c over the equator 8 km and 40°c over the equator 8 km and 75°c over the poles 16 km and 40°c over the poles
 16 km and -75°c over the equator.
16 km and -75°c over the equator. In the icao standard atmosphere the decrease in temperature with height below ?
Question 126-8 : 0 65°c per 100m 1°c per 100m 0 5°c per 100m 0 6°c per 100m
 0.65°c per 100m
0.65°c per 100m Which statement is correct regarding the icao standard atmosphere ?
Question 126-9 : At msl temperature is 15°c and pressure is 1013 25hpa at msl temperature is 15°c and the decrease in temperature with height is 1°c per 100m at msl temperature is 10°c and the decrease in temperature with height is 1°c per 100m at msl pressure is 1013 25 hpa and the decrease of temperature with height is 1°c per 100m
 At msl temperature is 15°c and pressure is 1013.25hpa
At msl temperature is 15°c and pressure is 1013.25hpa Qnh is defined as ?
Question 126-10 : Qfe reduced to msl using the values of the standard atmosphere pressure at msl in the standard atmosphere pressure at msl in the actual atmosphere qfe reduced to msl using the values of the actual atmosphere
 Qfe reduced to msl using the values of the standard atmosphere.
Qfe reduced to msl using the values of the standard atmosphere. Which of the following statements is true ?
Question 126-11 : Qnh can be equal to qfe qnh is always lower than qfe qnh is always higher than qfe qnh is always equal to qfe
 Qnh can be equal to qfe.
Qnh can be equal to qfe. Which statement is true ?
Question 126-12 : Qnh can be lower as well as higher than 1013 25 hpa qnh can not be 1013 25 hpa qnh is lower than 1013 25 hpa at any time qnh can be 1013 25 hpa only for a station at msl
 Qnh can be lower as well as higher than 1013.25 hpa.
Qnh can be lower as well as higher than 1013.25 hpa. When the subscale is set to the qnh of an airfield the pressure altimeter ?
Question 126-13 : Elevation while landing zero while landing elevation while landing only if conditions are as in the icao standard atmosphere zero while landing only if conditions are as in the icao standard atmosphere
 Elevation while landing.
Elevation while landing. The radiation of the sun heats ?
Question 126-14 : The surface of the earth which heats the air in the troposphere the air in the troposphere mainly by absorbtion the water vapour in the air of the troposphere the air in the troposphere only directly if no clouds are present
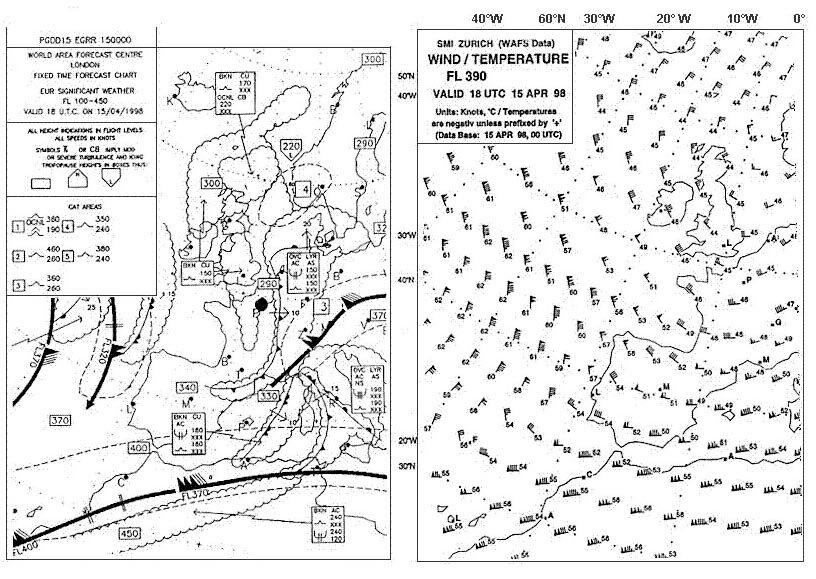 The surface of the earth, which heats the air in the troposphere.
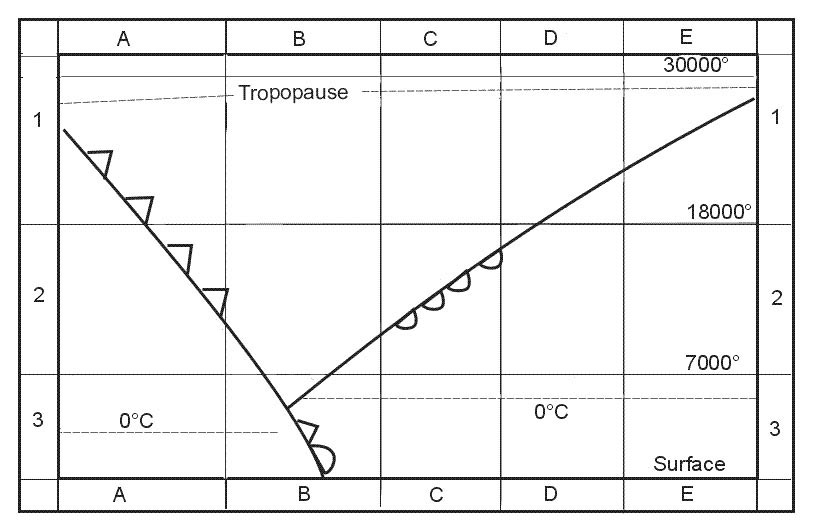
The surface of the earth, which heats the air in the troposphere. The vertical extent of the friction layer depends primarily on ?
Question 126-15 : Stability wind speed roughness of surface wind speed roughness of surface temperature roughness of surface temperature local time temperature local time environmental lapse rate
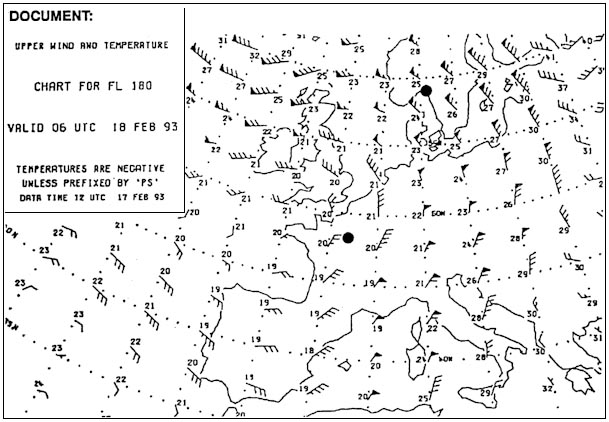 Stability, wind speed, roughness of surface.
Stability, wind speed, roughness of surface. The following temperatures have been observed over a station at 1200 utc ?
Question 126-16 : Assuming that the msl pressure is 1013 25 hpa the true altitude of an aircraft would actually be higher than the indicated altitude the temperature at 10000 ft is in agreement with the temperature in the international standard atmosphere the layer between 16000 ft and 18000 ft is absolutely unstable the height of the freezing level over the station is approximately 12000 ft
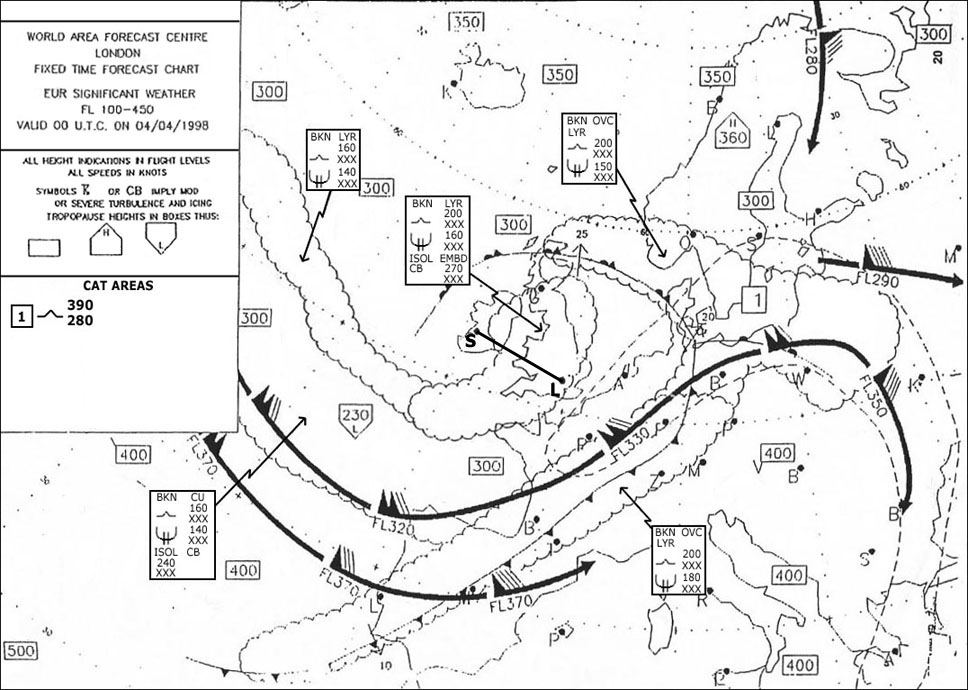 Assuming that the msl pressure is 1013.25 hpa the true altitude of an aircraft would actually be higher than the indicated altitude.
Assuming that the msl pressure is 1013.25 hpa the true altitude of an aircraft would actually be higher than the indicated altitude. A significant inversion at low height is a characteristic of ?
Question 126-17 : Nocturnal radiation the passage of cold front advection fog cumulus clouds
 Nocturnal radiation.
Nocturnal radiation. In order to reduce qfe to qnh which of the following item s must be known ?
Question 126-18 : Elevation of the airfield temperature at the airfield elevation of the airfield and the temperature at msl elevation of the airfield and the temperature at the airfield
 Elevation of the airfield.
Elevation of the airfield. The qnh is equal to the qfe if ?
Question 126-19 : The elevation = 0 t actual = t standard t actual < t standard t actual > t standard
 The elevation = 0
The elevation = 0 Which of the following conditions gives the highest value of the qnh ?
Question 126-20 : Qfe = 995 hpa elevation = 1600 ft 488m qfe = 1000 hpa elevation = 1200 ft 366m qfe = 1003 hpa elevation = 1200 ft 366m qfe = 995 hpa elevation = 1200 ft 366m
 Qfe = 995 hpa, elevation = 1600 ft (488m)
Qfe = 995 hpa, elevation = 1600 ft (488m) The pressure altitude is equal to the true altitude if ?
Question 126-21 : Standard atmospheric conditions occur the outside air temperature is standard for that height the air pressure is 1013 25 hpa at the surface the indicated altitude is equal to the pressure altitude
 Standard atmospheric conditions occur.
Standard atmospheric conditions occur. You must make an emergency landing at sea the qnh of a field on a nearby island ?
Question 126-22 : Less than 0 ft 0 ft more than 0 ft but less than 4000 ft 4000 ft
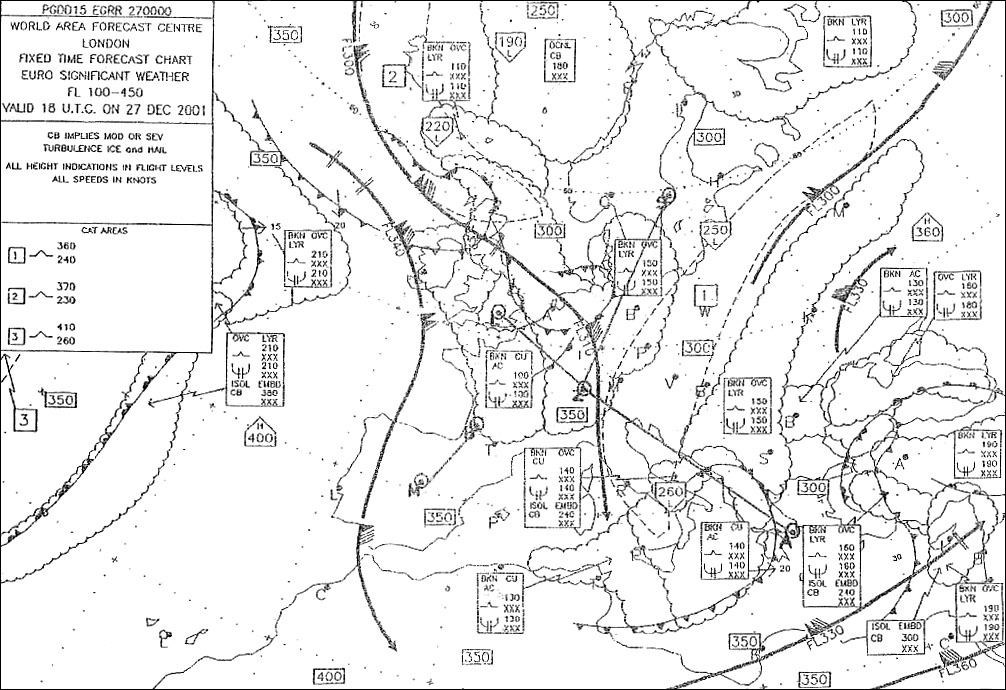 Less than 0 ft.
Less than 0 ft. The troposphere ?
Question 126-23 : Has a greater vertical extent above the equator than above the poles contains all oxygen of the stratosphere is the separation layer between the stratosphere and atmosphere reaches the same height at all latitudes
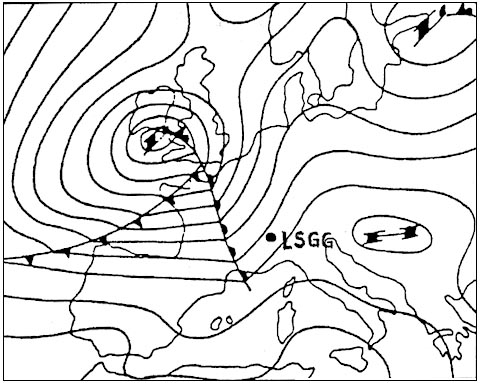 Has a greater vertical extent above the equator than above the poles.
Has a greater vertical extent above the equator than above the poles. For a given airfield the qfe is 980 hpa and the qnh is 1000 hpa the approximate ?
Question 126-24 : 160 metres 600 metres 540 metres 120 metres
 160 metres.
160 metres. Which is true of the temperature at the tropopause ?
Question 126-25 : It is higher in polar regions than in equatorial regions it is higher in equatorial regions than in polar regions it is highest in mid latitudes there is no significant difference with change of latitude
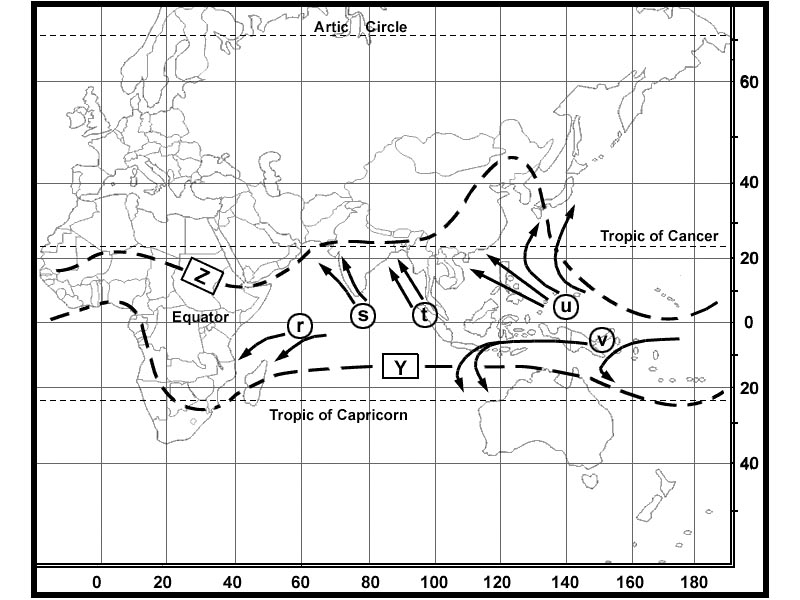 It is higher in polar regions than in equatorial regions
It is higher in polar regions than in equatorial regions Around paris on january 3rd at 1800 utc the surface temperature under shelter ?
Question 126-26 : Slightly below +3°c slightly above +3°c significantly above +3°c significantly below 0°c
 Slightly below +3°c.
Slightly below +3°c. On a clear sky continental ground surface wind calm the minimum temperature is ?
Question 126-27 : Half an hour after sunrise half an hour before sunrise at the moment the sun rises one hour before sunrise
 Half an hour after sunrise.
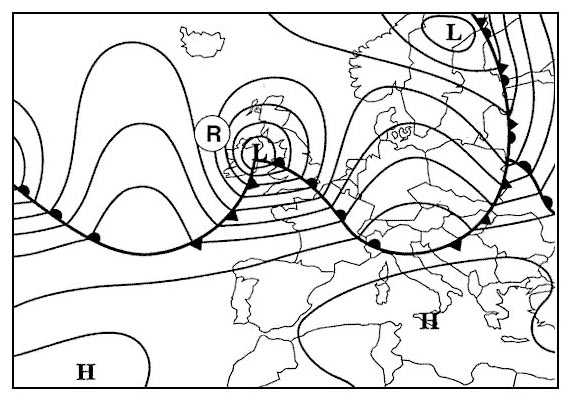
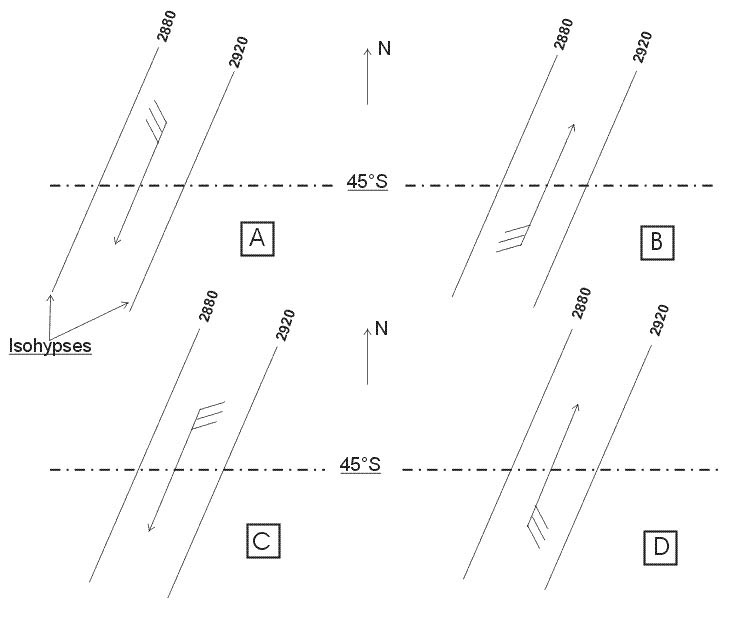
Half an hour after sunrise. An isohypse contour ?
Question 126-28 : Indicates the true altitude of a pressure level is the longest slope line of a frontal surface is the limit between two air masses of different temperature indicates the altitude of the zero degree isotherm
 Indicates the true altitude of a pressure level.
Indicates the true altitude of a pressure level. Before landing an altimeter set to qfe indicates ?
Question 126-29 : In standard atmosphere the height of the aircraft above the official airport elevation the flight level the aircraft's altitude above the mean sea level the height of the aircraft's wheels above the runway
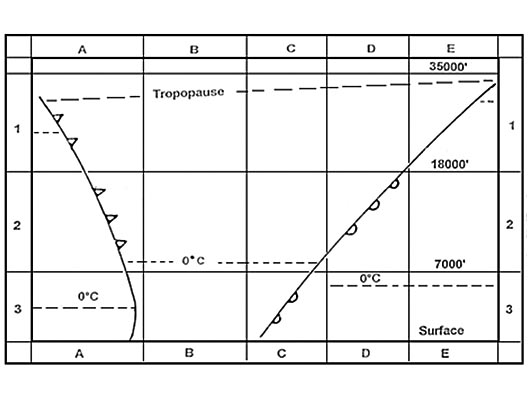 In standard atmosphere, the height of the aircraft above the official airport elevation.
In standard atmosphere, the height of the aircraft above the official airport elevation. In the mid latitudes the stratosphere extends on an average from ?
Question 126-30 : 11 to 50 km 0 to 11 km 50 to 85 km 85 to more than 200 km
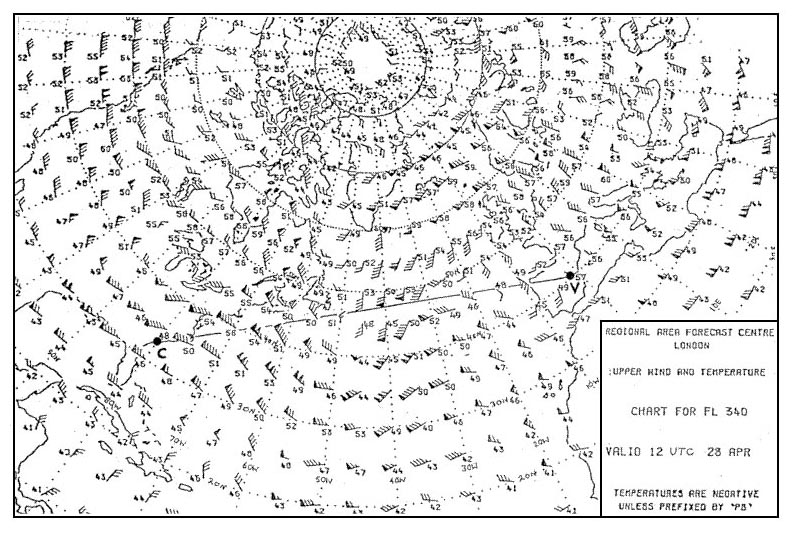 11 to 50 km.
11 to 50 km. An aircraft maintains a constant indicated altitude of 4500 ft from a 360 ?
Question 126-31 : 4485 ft 3135 ft 4815 ft 5175 ft
 4485 ft.
4485 ft. An aircraft maintains a constant indicated altitude of 5500 ft from a 1050 ?
Question 126-32 : 6146 ft 6796 ft 4854 ft 7446 ft
 6146 ft.
6146 ft. An aircraft maintains a constant indicated altitude of 6500 ft from a 600 ?
Question 126-33 : 4625 ft 6515 ft 5555 ft 5225 ft
 4625 ft.
4625 ft. An aircraft maintains a constant indicated altitude of 7500 ft from a 270 ?
Question 126-34 : 4824 ft 6204 ft 6876 ft 6474 ft
 4824 ft.
4824 ft. Between mean sea level and a height of 20 km the lowest temperature in the icao ?
Question 126-35 : 56 5°c 273°c 44 7°c 100°c
 -56.5°c.
-56.5°c. Considering the north atlantic area north of 60°n during winter the mean ?
Question 126-36 : 29 000 ft 56 000 ft 37 000 ft 20 000 ft
 29 000 ft.
29 000 ft. Considering the north atlantic at latitude 50°n during winter the mean height ?
Question 126-37 : 31 000 ft 23 000 ft 43 000 ft 54 000 ft
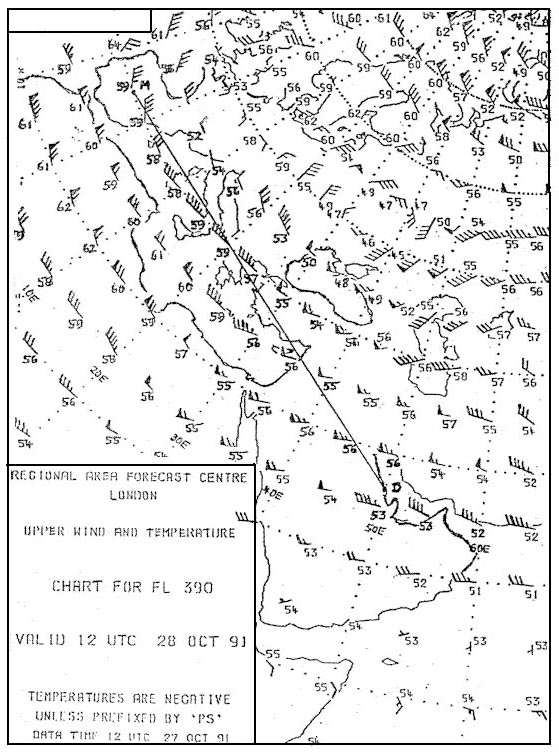 31 000 ft.
31 000 ft. If the qfe qnh and qff of an airport have the same value ?
Question 126-38 : The airport must be at msl the conditions must be as in the isa the airport must be at msl and the conditions must be as in the isa the 1013 25 hpa level must be at msl
 The airport must be at msl.
The airport must be at msl. In relation to the total weight of the atmosphere the weight of the atmosphere ?
Question 126-39 : 50% 1% 25% 99%
 50%.
50%. The icao standard atmosphere isa assumes that temperature will reduce at the ?
Question 126-40 : 1 98°c per 1000 ft up to 36090 ft after which it remains constant to 65617 ft 1 98°c per 1000 ft up to 36090 ft and will then rise at 0 3°c per 1000 ft up to 65617 ft when it will remain constant 2°c per 1000 ft up to 65617 ft after which it will remain constant to 104987 ft 2°c per 1000 ft up to 36090 ft and will then increase at 0 3°c per 1000 ft up to 65617 ft
 1,98°c per 1000 ft up to 36090 ft after which it remains constant to 65617 ft.
1,98°c per 1000 ft up to 36090 ft after which it remains constant to 65617 ft. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
4999 Free Training Exam
