When 'secondary radar' is used an aircraft may be identified by one of the ? [ Theoretical lift off ]
Question 12-1 : Observation of compliance with an instruction to operate transponder from 'on' to 'stby' and back to 'on' to request pilot to switch from 'on' to 'stby' to request pilot to set transponder on position 'off' to request pilot to set transponder on position 'on'
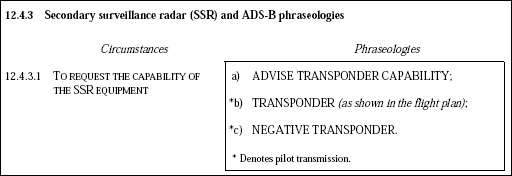 Observation of compliance with an instruction to operate transponder from 'on' to 'stby' and back to 'on'.
Observation of compliance with an instruction to operate transponder from 'on' to 'stby' and back to 'on'. When surveillance radar approaches are to be continued to the threshold of the ?
Question 12-2 : 4 nm from the touchdown 1 5 nm from the touchdown 3 nm from the touchdown 2 nm from the touchdown
 4 nm from the touchdown.
4 nm from the touchdown. When vectoring an aircraft to intercept the localizer course the final vector ?
Question 12-3 : 30 degrees 20 degrees 25 degrees 15 degrees
 30 degrees.
30 degrees. Whenever atis is provided the preparation and dissemination of the atis message ?
Question 12-4 : The air traffic services the meteorological office serving the aerodrome s both air traffic services and the meteorological office the unit as prescribed the states
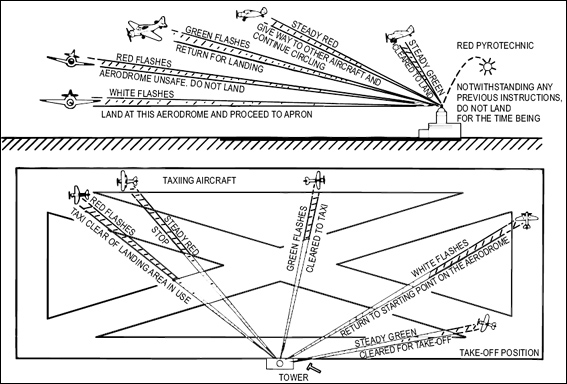 The air traffic services.
The air traffic services. Where a 'secondary surveillance radar' ssr is not available radar ?
Question 12-5 : To instruct the pilot to execute one or more changes of 30° or more to instruct the pilot to execute one or more changes of 45° to instruct the pilot to execute one or more changes of 10° to instruct the pilot to execute one or more changes of 20° or more
 To instruct the pilot to execute one or more changes of 30° or more.
To instruct the pilot to execute one or more changes of 30° or more. Which action shall be taken by an aircraft in the traffic pattern of an ?
Question 12-6 : The repeated switching on and off of the landing lights switching on and off three times the landing lights switching on and off four times the landing lights switching on and off four times the navigation lights
 The repeated switching on and off of the landing lights.
The repeated switching on and off of the landing lights. Which condition is requested so that an aerodrome may be considered controlled ?
Question 12-7 : The aerodrome shall be provided with a control tower the aerodrome shall be located within a controlled airspace the aerodrome shall be located within a control zone the aerodrome shall be located within a control zone ctr and provided with a control tower
 The aerodrome shall be provided with a control tower.
The aerodrome shall be provided with a control tower. Which does atc term 'radar contact' signify ?
Question 12-8 : Your aircraft has been identified on the radar display and radar flight instructions will be provided until radar identification is terminated you will be given traffic advisories until advised that the service has been terminated or that radar contact has been lost atc is receiving your transponder and will furnish vectors and traffic advisories until you are advised that contact has been lost your aircraft has been identified and you will receive separation from all aircraft while in contact with this radar facility
 Your aircraft has been identified on the radar display and radar flight instructions will be provided until radar identification is terminated.
Your aircraft has been identified on the radar display and radar flight instructions will be provided until radar identification is terminated. Which of the following statements regarding alerting service is correct ?
Question 12-9 : Alerting service and flight information service may be provided by the same ats unit the distress phase is established when an aircraft is known or believed to be the subject of unlawful interference aircraft in the vicinity of an aircraft known or believed to be the subject of unlawful interference shall be informed about this the alert phase is established when no communication has been received from an aircraft within a period of thirty minutes after the time a communication should have been received
 Alerting service and flight information service may be provided by the same ats unit.
Alerting service and flight information service may be provided by the same ats unit. Which provisions on a vfr flight in class e airspace are correct ?
Question 12-10 : Service provided traffic information as far as practical atc clearance not required service provided air traffic control service atc clearance required service provided traffic information as far as practical atc clearance required service provided air traffic control service atc clearance not required
 Service provided: traffic information as far as practical; atc clearance: not required.
Service provided: traffic information as far as practical; atc clearance: not required. Which statement is correct ?
Question 12-11 : The lower limit of a tma shall be established at a height of at least 700 ft agl the lower limit of a cta shall be established at a height of at least 1500 ft agl the upper limit of a ctr shall be established at a height of at least 3000 ft amsl the lower limit of an uir may coincide with an ifr cruising level
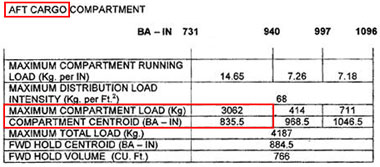 The lower limit of a tma shall be established at a height of at least 700 ft agl
The lower limit of a tma shall be established at a height of at least 700 ft agl Which statement regarding approach control service is correct ?
Question 12-12 : If it is anticipated that an aircraft has to hold for 30 minutes or more an expected approach time will be transmitted by the most expeditious means to the aircraft during a visual approach an aircraft is maintaining its own separation approach control have to advise the aircraft operators about substantial delays in departure in any event when they are expected to exceed 45 minutes an approach sequence shall be established according to the sequence of initial radio contact between aircraft and approach control
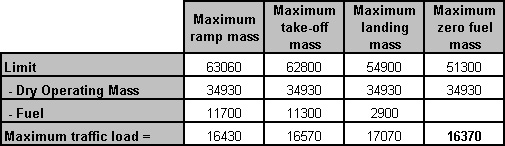 If it is anticipated that an aircraft has to hold for 30 minutes or more, an expected approach time will be transmitted by the most expeditious means to the aircraft.
If it is anticipated that an aircraft has to hold for 30 minutes or more, an expected approach time will be transmitted by the most expeditious means to the aircraft. While on ifr flight a pilot has an emergency which causes a deviation from an ?
Question 12-13 : The appropriate atc unit shall be notified of the action taken as soon as circumstances permit request an amended clearance or cancel the ifr flight plan submit a detailed report to atc within 24 hours squawk 7700
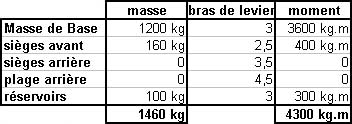 The appropriate atc unit shall be notified of the action taken as soon as circumstances permit.
The appropriate atc unit shall be notified of the action taken as soon as circumstances permit. Communications failure flight procedures.you are on a flight in accordance ?
Question 12-14 : You have to return to your current flight plan route you continue on heading 050 for 15 minutes you continue on heading 050 you continue on heading 050 for 30 minutes
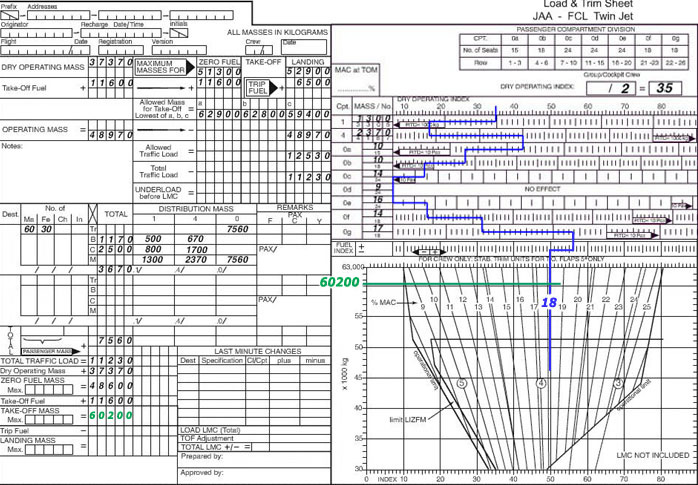 You have to return to your current flight plan route.
You have to return to your current flight plan route. You receive an ifr enroute clearance stating 'clearance expires at 0920' .what ?
Question 12-15 : If not airborne until 0920 a new clearance has to be issued do not take off before 0920 the take off clearance is expected at 0920 after 0920 return to the ramp and file a new flight plan
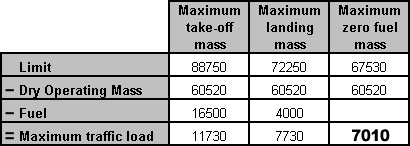 If not airborne until 0920, a new clearance has to be issued.
If not airborne until 0920, a new clearance has to be issued. Air traffic controle service.air traffic control units issue clearances for the ?
Question 12-16 : Preventing collision between aircraft under its control expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of traffic providing flight information service expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of traffic providing advisory service expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of traffic giving direct tracks expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of traffic
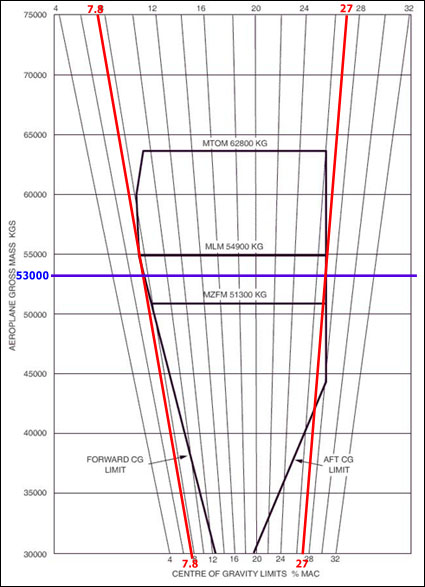 Preventing collision between aircraft under its control, expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of traffic.
Preventing collision between aircraft under its control, expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of traffic. The purpose of the ntz is to ?
Question 12-17 : Protect aircraft that are carrying out independent parallel approaches provide simultaneous operations on parallel runways in which one runway is used exclusively for approaches and the other runway is used exclusively for departures protect aircraft for vertical separation on parallel approaches protect aircraft that are carrying out a missed approach procedure
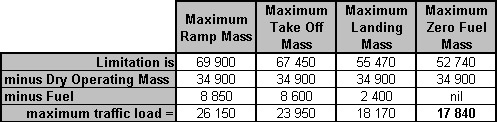 Protect aircraft that are carrying out independent parallel approaches.
Protect aircraft that are carrying out independent parallel approaches. When datalink communication are used accuracy of clock should be ?
Question 12-18 : 1 second of utc 30 seconds of utc 15 seconds of utc 1 minute of utc
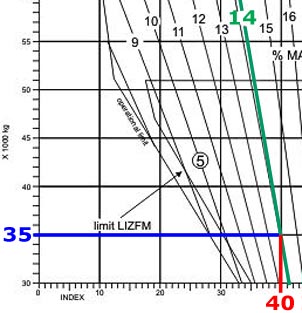
When in air space where vfr is permitted the pilot in command of an ifr flight ?
Question 12-19 : 1 and 4 2 and 4 1 and 3 2 and 3
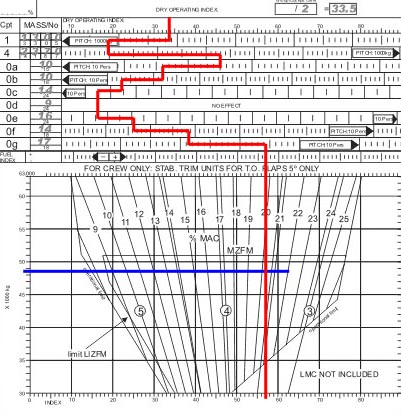 1 and 4.
1 and 4. An ats route designator ?
Question 12-20 : Has a maximum of six characters always starts with two alphabetical characters has a maximum of five characters begins with at least two numbers followed by an alphabetical character
Define the term 'psr' ?
Question 12-21 : Primary surveillance radar primary system radar parallel separation radar proximity surveillance radar
 Primary surveillance radar.
Primary surveillance radar. 'traffic to which the provision of atc is applicable but which in relation to a ?
Question 12-22 : Essential traffic local traffic uncontrolled traffic unidentified traffic
 Essential traffic.
Essential traffic. In class f airspace advisory service may be provided to ?
Question 12-23 : Ifr flights only vfr flights only all flights controlled flights only
 Ifr flights only.
Ifr flights only. Transition altitude 3000ft qnh 990 hpa calculate the transition level ?
Question 12-24 : Fl40 fl20 fl25 fl35
 Fl40.
Fl40. Clearance limit is a point ?
Question 12-25 : To which a specific clearance is valid to which a specific clearance is valid and this point is determined by the pic from which a specific clearance is valid where an airway clearance is amended
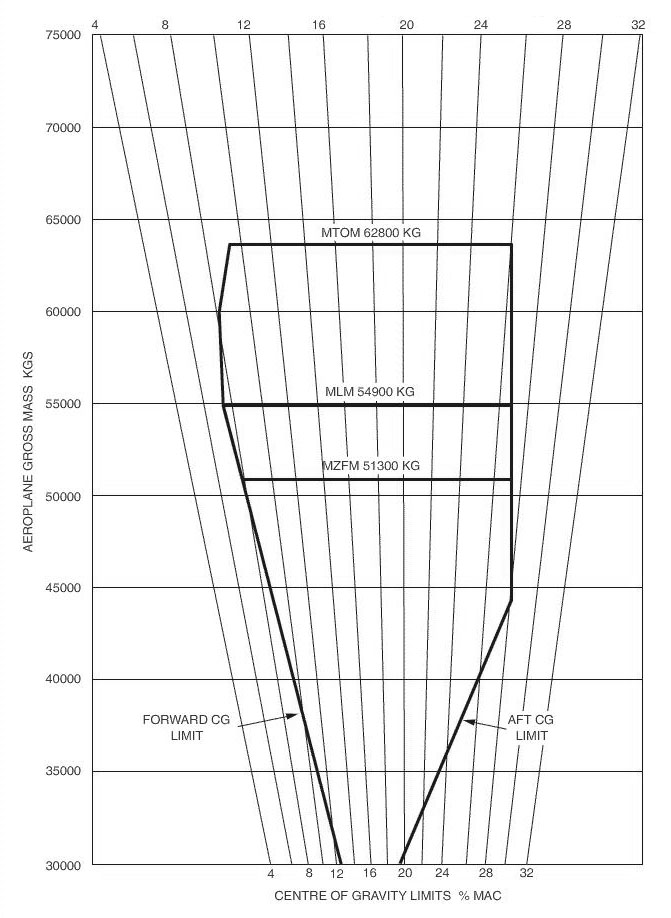 To which a specific clearance is valid.
To which a specific clearance is valid. A special air report shall be made ?
Question 12-26 : When experiencing severe icing or severe turbulence when experiencing light icing with an airprox if eat is delayed by at least 30 minutes
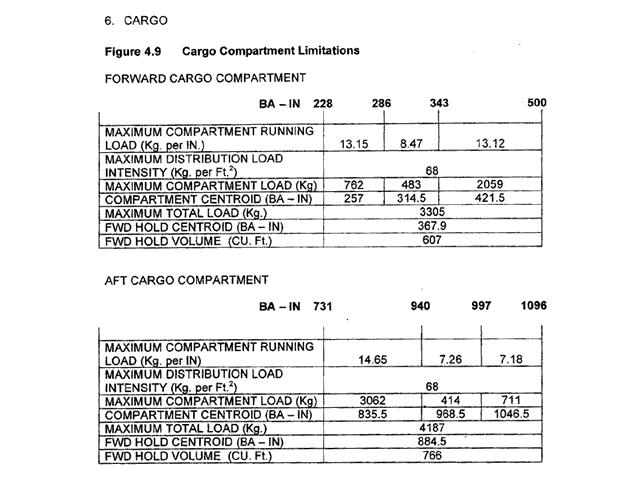 When experiencing severe icing or severe turbulence.
When experiencing severe icing or severe turbulence. A checklist of aip supplements currently in force shall be issued at intervals ?
Question 12-27 : Not more than one month not more than three months not more than 28 days not more than 2 months
 Not more than one month.
Not more than one month. A checklist of notam currently in force shall be issued at the aftn at ?
Question 12-28 : Not more than one month no more than 15 days not more than 28 days not more than 10 days
 Not more than one month.
Not more than one month. A notice containing information concerning flight safety air navigation ?
Question 12-29 : Aeronautical information circular aic airac notam aeronautical information publication aip
 Aeronautical information circular (aic).
Aeronautical information circular (aic). A notice providing information on rules of the air air traffic services and air ?
Question 12-30 : An airac an ats notam an advisory notam a notam rac
 An airac.
An airac. Aeronautical information service .name the accronym signifying the system aimed ?
Question 12-31 : Airac advisory notam ats notam notam rac
 Airac.
Airac. Aip supplements .temporary changes of 'long duration' and information of 'short ?
Question 12-32 : Three months or longer six months or longer one year or longer two months or longer
 Three months or longer.
Three months or longer. Aip .which part contains a brief description of areas and/or routes for which ?
Question 12-33 : Gen enr meteo ad
 Gen.
Gen. Aip .which part of the aip contains a brief description of the service s ?
Question 12-34 : Gen enr ad sar
 Gen.
Gen. Aip .which part of the aip contains a list with 'location indicators' ?
Question 12-35 : Gen enr ad loc
 Gen.
Gen. Aip .which part of the aip contains information relating to existing prohibited ?
Question 12-36 : Enr gen ad the aip does not contain this information
 Enr.
Enr. Aip .which part of the aip gives detailed information about refuelling ?
Question 12-37 : Ad sar gen fal
 Ad.
Ad. An airac is ?
Question 12-38 : An acronym for a system aimed at advance notification based on common effective dates of circumstances necessitating significant changes in operating procedures a publication issued by or with the authority of a state containing aeronautical information of a lasting character essential to air navigation a notice distributed by means of telecommunication containing information concerning the establishment condition or change in any aeronautical facility service procedure or hazard the timely knowledge of which is essential to personnel concerned with flight operations a package which consists of the following elements aip supplements to the aip notam aic checklists and summaries
 An acronym for a system aimed at advance notification based on common effective dates, of circumstances necessitating significant changes in operating procedures.
An acronym for a system aimed at advance notification based on common effective dates, of circumstances necessitating significant changes in operating procedures. In which section of aip are contained information elements relating to areas ?
Question 12-39 : Gen met com rac
 Gen.
Gen. Detailed description of meteorological information provided at the aerodrome ?
Question 12-40 : Gen met ad rac
 Gen.
Gen. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
439 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 12
