Flights immediately after scuba diving using compressed gas to depths greater ? [ Training professional ]
Question 113-1 : Are to be avoided because of the possibility of decompression sickness can be performed without any danger are allowed if you fly no higher than 38000 ft should be avoided because hypoxia may develop
 Are to be avoided because of the possibility of decompression sickness.
Are to be avoided because of the possibility of decompression sickness. Hyperventilation is ?
Question 113-2 : A normal compensatory physiological reaction to a drop in partial oxygen pressure i e when climbing a high mountain an increased heart rate caused by an increasing blood pressure an increased heart rate caused by a decreasing blood pressure a reduction of partial oxygen pressure in the brain
 A normal compensatory physiological reaction to a drop in partial oxygen pressure (i.e. when climbing a high mountain).
A normal compensatory physiological reaction to a drop in partial oxygen pressure (i.e. when climbing a high mountain). How does an increase in altitude affect the haemoglobin oxygen saturation ?
Question 113-3 : As altitude increases the haemoglobin oxygen saturation decreases as altitude increases the haemoglobin oxygen saturation increases as altitude increases the haemoglobin oxygen saturation will remain constant at 57% from 24000 ft as altitude increases the haemoglobin oxygen saturation with remain constant at 97 5% from 10000 ft
 As altitude increases, the haemoglobin oxygen saturation decreases.
As altitude increases, the haemoglobin oxygen saturation decreases. How can vertigo be prevented in conditions of good visibility ?
Question 113-4 : By looking at the horizon by closing the e momentarily by looking approximately 5° to one side of an object by avoiding blinking
 By looking at the horizon.
By looking at the horizon. How are oxygen and carbon dioxide transported throughout the body ?
Question 113-5 : Circulation oxidisation diffusion metabolism
 Circulation.
Circulation. State the conditions which cause the 'black hole effect' and the danger to ?
Question 113-6 : The 'black hole effect' can be caused by flying over water at night on the approach to an airfield which can create the illusion that the aircraft is at a higher altitude than it is leading to a low approach being flown the 'black hole effect' can be caused by flying over featureless terrain on the approach to an airfield which can create the illusion that the aircraft is at a higher altitude than it is leading to a high approach being flown the 'black hole effect' can be caused by flying over water at night on the approach to an airfield which can create the illusion that the aircraft is at a higher altitude than it is leading to a high approach being flown the 'black hole effect' can be caused by flying under instruments with poor cockpit lighting and can lead to disorientation
 The 'black hole effect' can be caused by flying over water at night on the approach to an airfield which can create the illusion that the aircraft is at a higher altitude than it is, leading to a low approach being flown.
The 'black hole effect' can be caused by flying over water at night on the approach to an airfield which can create the illusion that the aircraft is at a higher altitude than it is, leading to a low approach being flown. Having a cold or an infection of the upper respiratory tract you ?
Question 113-7 : Should not fly because the congestion of the frontal sinuses may cause great pain which can seriously affect your ability to control yourself and the aircraft may accept to fly an ambulance flight because 'sinus squeeze' is rare and represents a minor danger to aviation must be careful when flying because the infection may cause hyperglycemia should not fly because the infection may cause hypoxia due to congestion in the nose
 Should not fly because the congestion of the frontal sinuses may cause great pain which can seriously affect your ability to control yourself and the aircraft.
Should not fly because the congestion of the frontal sinuses may cause great pain which can seriously affect your ability to control yourself and the aircraft. Glaucoma is due to ?
Question 113-8 : Increase in pressure of the liquid within the eye drop in pressure of the liquid around the eye damage to the eyeball due to high altitude excess light on the eyeball
Galactic radiation is ?
Question 113-9 : Steady and reasonably predictable unsteady and reasonably predictable steady but unpredictable unsteady and unpredictable
 Steady and reasonably predictable.
Steady and reasonably predictable. Free running circadian rhythms normally have a cycle of approximately ?
Question 113-10 : 24 hours 6 hours 8 hours 36 hours
Flying immediately following a dive with scuba diving equipment to a depth ?
Question 113-11 : Can cause decompression sickness even when flying at pressure altitudes below 18 000 ft prevents any dangers caused by dcs decompression sickness when climbing to altitudes not exceeding 30 000 ft has no influence on altitude flights will always lead to hypoxia
 Can cause decompression sickness even when flying at pressure altitudes below 18 000 ft.
Can cause decompression sickness even when flying at pressure altitudes below 18 000 ft. Hepatitis 'a' is transmitted through ?
Question 113-12 : Food or water which has been contaminated droplets in the air cause by the breath of an infected person insect bites bacteria in the form of spores via a puncture in the skin
 Food or water which has been contaminated.
Food or water which has been contaminated. Alcohol degrades ?
Question 113-13 : Paradoxical sleep slow wave sleep stage 2 sleep stage 3 and 4 sleep
 Paradoxical sleep.
Paradoxical sleep. Among the measures that a pilot should take when in an area where gastro ?
Question 113-14 : Avoidance of ice in cold drinks avoidance of cooked meats avoidance of cooked fruits avoidance of curries or gassy foods
 Avoidance of ice in cold drinks.
Avoidance of ice in cold drinks. Among the factors which can cause illusions while taxiing are ?
Question 113-15 : Relative movement and cockpit height above the ground visibility and distance distance from the edge of the taxiway and taxi lighting distance from the edge of the taxiway and cockpit lighting
 Relative movement and cockpit height above the ground.
Relative movement and cockpit height above the ground. Among the factors which affect visual acuity are ?
Question 113-16 : Hypoxia age and angular distance from the fovea smoking colour blindness and angular distance from the fovea colour blindness alcohol and amount of light available colour blindness visibility and angular distance from the fovea
 Hypoxia, age and angular distance from the fovea.
Hypoxia, age and angular distance from the fovea. Among the factors which affect night vision are ?
Question 113-17 : Age cabin altitudes above 5000 ft smoking and alcohol age cabin altitudes above 5000 ft smoking and lack of vitamin c age cabin altitudes above 5000 ft smoking and lack of vitamin e age cabin altitudes above 5000 ft smoking and lack of vitamin b
 Age, cabin altitudes above 5000 ft, smoking and alcohol.
Age, cabin altitudes above 5000 ft, smoking and alcohol. A pilot should not fly immediately after donating blood because ?
Question 113-18 : You have an increased susceptibility to fainting the chance you get the bends is higher after blood donation your blood pressure is too low after blood donation your heart rate is too low after blood donation
 You have an increased susceptibility to fainting.
You have an increased susceptibility to fainting. An illusion of obtaining greater height above ground can occur when ?
Question 113-19 : Suddenly flying over small trees after prolonged flying over tall trees accelerating at low altitude decelerating at low altitude flying over high terrain in low visibility
 Suddenly flying over small trees after prolonged flying over tall trees.
Suddenly flying over small trees after prolonged flying over tall trees. After a cabin pressure loss at approximately 35000 ft the tuc time of useful ?
Question 113-20 : 30 40 seconds 10 15 seconds 3 4 minutes 5 minutes or more
 30-40 seconds.
30-40 seconds. Smoking cigarettes reduces the capability of the blood to carry oxygen because ?
Question 113-21 : Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon monoxide than it has for oxygen carbon monoxide in the smoke of cigarettes assists diffusion of oxygen in the alveoli carbon monoxide increases the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli the smoke of one cigarette can cause an obstruction in the respiratory tract
 Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon monoxide than it has for oxygen.
Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon monoxide than it has for oxygen. A pilot climbing in a non pressurised aircraft and without using supplemental ?
Question 113-22 : 20 000 ft 16 000 ft 12 000 ft 38 000 ft
 20 000 ft.
20 000 ft. Tetanus is transmitted through ?
Question 113-23 : Bacteria in the form of spores via a puncture in the skin droplets in the air cause by the breath of an infected person insect bites food or water which has been contaminated
 Bacteria in the form of spores via a puncture in the skin.
Bacteria in the form of spores via a puncture in the skin. Among the factors that increase tolerance to long duration g forces are ?
Question 113-24 : Bending forward or supine body position and tensing of the abdominal muscles correct use of pilot's harness and tensing of the abdominal muscles anti g suits and correct use of pilot's harness tensing the leg muscles and correct use of pilot's harness
 Bending forward or supine body position and tensing of the abdominal muscles.
Bending forward or supine body position and tensing of the abdominal muscles. Astigmatism is caused by ?
Question 113-25 : A mis shapened cornea a lack of vitamin a a lack of empty field a lack of accommodation
 A mis-shapened cornea.
A mis-shapened cornea. By 'long duration acceleration' we mean that it lasts more than ?
Question 113-26 : 1 second 20 seconds 1 minute 5 minutes
 1 second.
1 second. Below 70000 ft what gas makes up the major part of the atmosphere ?
Question 113-27 : Nitrogen oxygen carbon dioxide ozone
 Nitrogen.
Nitrogen. Barotrauma of the sinuses of the nose ?
Question 113-28 : Is caused by differences in pressure between the sinus cavities and the outside air pressure only arises in flying and not in diving is an irritation of the sinuses caused by the over use of nasal sprays is only caused by colds and their effects
 Is caused by differences in pressure between the sinus cavities and the outside air pressure.
Is caused by differences in pressure between the sinus cavities and the outside air pressure. Barotrauma is caused by an increase or decrease in the volume of the gases ?
Question 113-29 : Facial sinuses middle ear and dental cavities inner ear facial sinuses and stomach facial sinuses outer ear and stomach dental cavities outer ear and e
 Facial sinuses, middle ear and dental cavities.
Facial sinuses, middle ear and dental cavities. Autokinesis can give the pilot the impression that ?
Question 113-30 : A star is another aircraft the aircraft is climbing lights from ships are stars lights are further away than in fact they are
 A star is another aircraft.
A star is another aircraft. At which altitude is it necessary to breathe 100% oxygen under pressure after a ?
Question 113-31 : Approximately 40 000 ft approximately 14 000 ft approximately 20 000 ft approximately 50 000 ft
 Approximately 40 000 ft.
Approximately 40 000 ft. At rest the cardiac output the quantity of blood the heart pumps in one minute ?
Question 113-32 : 5 litres/min 450 ml/min 45 litres/min 75 litres/min
 5 litres/min.
5 litres/min. Approximately how long will a blood/alcohol level of 60 mgm/100ml take to ?
Question 113-33 : 4 hours 20 hours 12 hours 1 hour
 4 hours.
4 hours. Any prolonged exposure to noise in excess of 90 db can result in ?
Question 113-34 : Noise induced hearing loss conductive hearing loss presbycusis effects of aging a ruptured ear drum
 Noise induced hearing loss.
Noise induced hearing loss. At which altitude may a degradation of night vision occur ?
Question 113-35 : From approximately 1600 m 3000 m 5000 m 5000 m 7000 m up to 5000 m
 From approximately 1600 m.
From approximately 1600 m. If a stop over is more than 24 hours the correct action is to ?
Question 113-36 : Move to the new time as soon as possible stay on home time and on arrival move to the new time stay on home time no adjustment is necessary
 Move to the new time as soon as possible.
Move to the new time as soon as possible. Cholera can be transmitted through ?
Question 113-37 : Food or water which has been contaminated droplets in the air cause by the breath of an infected person insect bites bacteria in the form of spores via a puncture in the skin
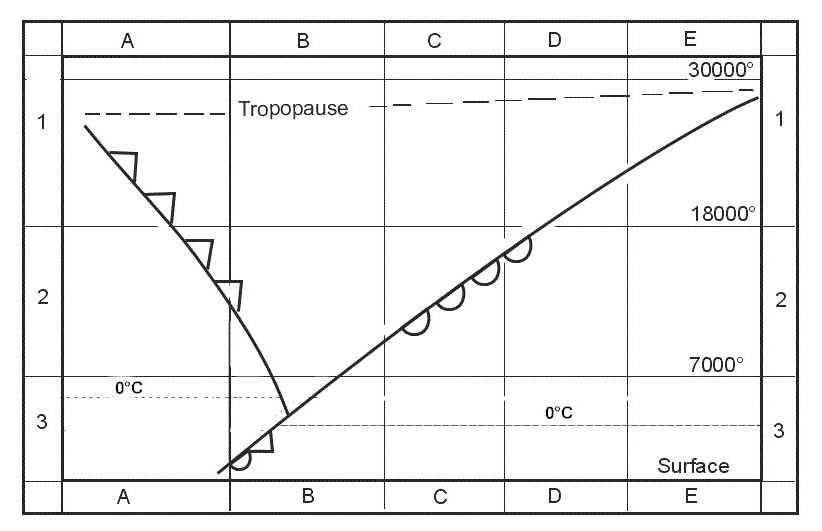 Food or water which has been contaminated.
Food or water which has been contaminated. Hypoxia is ?
Question 113-38 : A physical condition caused by a lack of oxygen to meet the needs of the body tissues leading to mental and muscular disturbances causing impaired thinking poor judgement and slow reactions a condition of lacking oxygen in the brain causing the circulatory system to compensate by decreasing the heart rate often produced during steep turns when pilots turn their heads in a direction opposite to the direction in which the aircraft is turning a physical condition caused by a lack of oxygen saturation in the blood while hyperventilating
 A physical condition caused by a lack of oxygen to meet the needs of the body tissues, leading to mental and muscular disturbances, causing impaired thinking, poor judgement and slow reactions.
A physical condition caused by a lack of oxygen to meet the needs of the body tissues, leading to mental and muscular disturbances, causing impaired thinking, poor judgement and slow reactions. A pilot may suffer from hypoxia ?
Question 113-39 : After decompression at high altitude and not using additional oxygen in time after decompression to 30 000 feet and using 100% oxygen via an oxygen mask if his rate of climb exceeds 5000 ft/min if he/she is flying an unpressurised airplane at an altitude of 15 000 feet and breathing 100% oxygen
 After decompression at high altitude and not using additional oxygen in time.
After decompression at high altitude and not using additional oxygen in time. The sleep pattern is closely associated with ?
Question 113-40 : Body temperature glucose level blood pressure heart rate
 Body temperature.
Body temperature. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
4479 Free Training Exam
