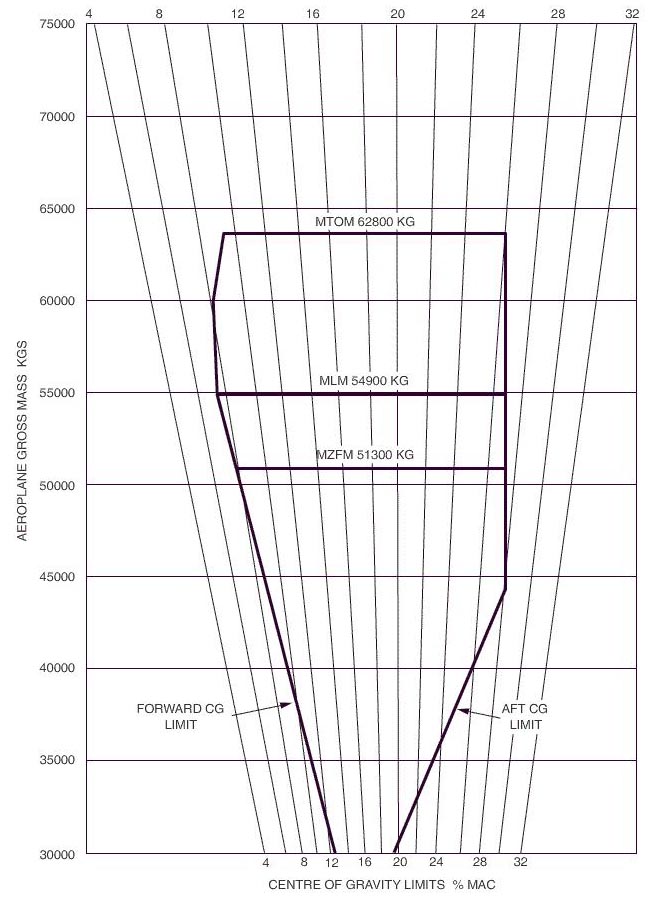
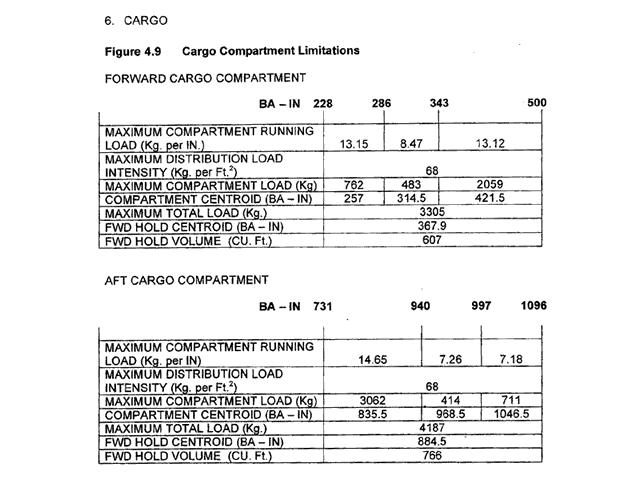
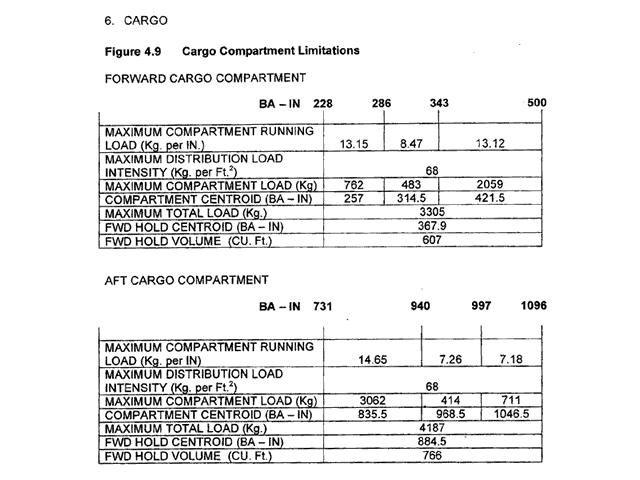
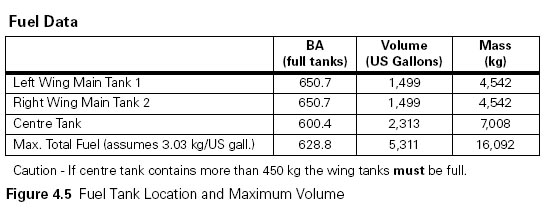
In order to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease exercise should ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 106-1 : Double the resting heart rate for at least 20 minutes three times a week double the resting heart rate for at least an hour five times a week triple the resting heart rate for 20 minutes once a week be avoided since raising the heart rate shortens the life of the heart
 Double the resting heart rate for at least 20 minutes, three times a week.
Double the resting heart rate for at least 20 minutes, three times a week. The physiological rhythms of a pilot in a new time zone will resynchronise to ?
Question 106-2 : 1 1 5 hours a day 2 2 5 hours a day 3 3 5 hours a day 4 4 5 hours a day
 1 - 1.5 hours a day.
1 - 1.5 hours a day. The duration of a period of sleep is governed primarily by ?
Question 106-3 : The point within your circadian rhythm at which you try to sleep the duration of your previous sleep the amount of time you have been awake the number of points you have in your 'credit/deficit' system
 The point within your circadian rhythm at which you try to sleep.
The point within your circadian rhythm at which you try to sleep. Hyperventilation is due to an excessive rate of breathing and can produce the ?
Question 106-4 : Dizziness tingling sensation in the fingers and toes nausea and blurred vision reduced heart rate and increase in visual acuity a state of overconfidence and reduced heart rate blue finger nails and lips
 Dizziness, tingling sensation in the fingers and toes, nausea and blurred vision.
Dizziness, tingling sensation in the fingers and toes, nausea and blurred vision. In order to get rid of excess nitrogen following scuba diving subsequent ?
Question 106-5 : 24 hours 3 hours after non decompression diving 36 hours after any scuba diving 48 hours after a continuous ascent in the water has been made
 24 hours.
24 hours. During flight in imc instrument meteorological conditions the most reliable ?
Question 106-6 : Visual sense interpreting the attitude indicator 'seat of the pants sense' vestibular sense visual sense by looking outside
 Visual sense, interpreting the attitude indicator.
Visual sense, interpreting the attitude indicator. The chemical substance responsible for addiction to tobacco is ?
Question 106-7 : Nicotine carbon monoxide tar the combination of nicotine tar and carbon monoxide
 Nicotine.
Nicotine. It is inadvisable to fly when suffering from a cold the reason for this is ?
Question 106-8 : The tissue around the nasal end of the eustachian tube is likely to be swollen thus causing difficulty in equalising the pressure within the middle ear and the nasal/throat area pain and damage to the eardrum can result particularly during fast descents although the change in air pressure during a climb at lower altitudes is very small it increases rapidly at high altitudes if the tissue in the eustachian tube of the ear is swollen gentle descents at high altitude would result in damage to the ear drum swollen tissue in the inner ear will increase the rate of metabolic production resulting in hyperventilation because it will seriously affect peripheral vision
 The tissue around the nasal end of the eustachian tube is likely to be swollen thus causing difficulty in equalising the pressure within the middle ear and the nasal/throat area. pain and damage to the eardrum can result, particularly during fast descents.
The tissue around the nasal end of the eustachian tube is likely to be swollen thus causing difficulty in equalising the pressure within the middle ear and the nasal/throat area. pain and damage to the eardrum can result, particularly during fast descents. Incapacitation is most dangerous when it is ?
Question 106-9 : Insidious intense obvious sudden
 Insidious.
Insidious. Concerning circadian rhythm disruption jet lag adjustment to destination time ?
Question 106-10 : 2 4 1 4 2 3 1 3
What seems to be the main role of orthodox sleep ?
Question 106-11 : It essentially allows for physical recovery it includes physical and mental recuperation associate with fatigue its main role is associated with activities of memory activities and restoration of attention capabilities via physical recovery it is characterised by an alternation of dream phases and paradoxical phases
 It essentially allows for physical recovery.
It essentially allows for physical recovery. What are the main effects of a lack of sleep on performance ?
Question 106-12 : It increases fatigue reduces concentration and increases the risk of sensory illusions it increases fatigue and concentration difficulties but facilitates stress management by muscular relaxation it causes muscular spasms it reduces concentration and fatigue only with sleep loss greater than 48 hours
 It increases fatigue, reduces concentration and increases the risk of sensory illusions.
It increases fatigue, reduces concentration and increases the risk of sensory illusions. What is the effect of tiredness on attention ?
Question 106-13 : It reduces the ability to manage multiple matters it increases the ability to manage multiple matters it leads to one's attention being shared between different centres of interest it has no specific effects on attention
 It reduces the ability to manage multiple matters.
It reduces the ability to manage multiple matters. Which of the following statements are correct .1 modern aircraft allow for 50 ?
Question 106-14 : 2 3 1 4 2 3 4 1 2 4
 2, 3.
2, 3. With regard to central vision which of the following statements are correct .1 ?
Question 106-15 : 2 4 1 2 4 2 3 4 1 3
 2, 4.
2, 4. What is the procedure above 10000 ft altitude when faced with explosive ?
Question 106-16 : Don an oxygen mask and descend to below 10000 ft first inform atc descend to below 10000 ft and signal an emergency check the cabin altitude don an oxygen mask and maintain level flight
 Don an oxygen mask and descend to below 10000 ft.
Don an oxygen mask and descend to below 10000 ft. What is the approximate time of useful consciousness for a seated pilot ?
Question 106-17 : 45 seconds 12 seconds 5 minutes 3 seconds
 45 seconds.
45 seconds. Which is the procedure to be followed when symptoms of decompression sickness ?
Question 106-18 : Descend to the lowest possible level and land as soon as possible descend to the lowest possible level and wait for the symptoms to disappear before climbing again only medical treatment is of use only the prompt supply of oxygen is necessary
 Descend to the lowest possible level and land as soon as possible.
Descend to the lowest possible level and land as soon as possible. What is decompression sickness ?
Question 106-19 : A condition resulting from the formation of nitrogen bubbles in bodily tissues and fluids after a cabin pressure loss at high altitude a frequent disorder in commercial aviation due to the pressurisation curve of modern aircraft a disorder which is solely encountered below 18000 ft the formation of air bubbles in bodily tissues with no consequences for people's capabilities
 A condition resulting from the formation of nitrogen bubbles in bodily tissues and fluids after a cabin pressure loss at high altitude.
A condition resulting from the formation of nitrogen bubbles in bodily tissues and fluids after a cabin pressure loss at high altitude. Noise induced hearing loss nihl is caused by ?
Question 106-20 : Damage to the sensitive membrane in the cochlea due to overexposure to noise a blocked eustachian tube pressure differences on both sides of the eardrum reduced mobility of the ossicles
 Damage to the sensitive membrane in the cochlea due to overexposure to noise.
Damage to the sensitive membrane in the cochlea due to overexposure to noise. Excessive exposure to noise can damage ?
Question 106-21 : The sensitive membrane in the cochlea the semi circular canals the ossicles the eardrum
 The sensitive membrane in the cochlea.
The sensitive membrane in the cochlea. The inner ear is able to perceive .1 angular acceleration .2 linear ?
Question 106-22 : 1 and 2 and 3 are correct 2 and 3 are correct 1 is false 1 and 2 are correct 3 is false 2 is correct 1 and 3 are both false
 1 and 2 and 3 are correct.
1 and 2 and 3 are correct. Visual disturbances can be caused by .1 hyperventilation.2 hypoxia.3 ?
Question 106-23 : 1 2 and 4 are correct 1 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 2 and 3 are correct 2 3 and 4 are correct
 1, 2 and 4 are correct.
1, 2 and 4 are correct. Disorientation is more likely to occur when the pilot is .1 flying in imc.2 ?
Question 106-24 : 1 2 and 4 are correct 1 2 and 3 are correct 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 3 and 4 are correct
 1, 2 and 4 are correct.
1, 2 and 4 are correct. Positive linear acceleration when flying in imc instrument meteorological ?
Question 106-25 : Pitching up pitching down apparent sideward movement of objects in the field of vision vertigo
 Pitching up.
Pitching up. Linear acceleration when flying straight and level in imc instrumental ?
Question 106-26 : Climbing descending yawing spinning
 Climbing.
Climbing. Which of the following are the most favourable solutions to manage phases of ?
Question 106-27 : 1 4 1 2 1 3 3 4
 1, 4.
1, 4. During gas exchange the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli is ?
Question 106-28 : Lower than in the blood the same as in the atmospheric air higher than the pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood lower than the pressure of carbon dioxide in the atmospheric air
 Lower than in the blood.
Lower than in the blood. The rate and depth of breathing is primarily regulated by the concentration of ?
Question 106-29 : Carbon dioxide in the blood nitrogen in the air water vapour in the alveoli oxygen in the cells
 Carbon dioxide in the blood.
Carbon dioxide in the blood. A pressurized cabin helps to prevent .1 decompression sickness .2 the problem ?
Question 106-30 : 1 2 and 3 are correct 1 2 and 4 are correct 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 3 and 4 are correct
 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
1, 2 and 3 are correct. Healthy people are usually capable of compensating for a lack of oxygen up to ?
Question 106-31 : 10 000 12 000 feet 15 000 feet 20 000 feet 25 000 feet
 10 000 - 12 000 feet.
10 000 - 12 000 feet. When flying above 10000 feet hypoxia arises because ?
Question 106-32 : The partial oxygen pressure is lower than at sea level the composition of the blood changes the composition of the air is different from sea level the percentage of oxygen is lower than at sea level
 The partial oxygen pressure is lower than at sea level.
The partial oxygen pressure is lower than at sea level. Saturation of oxygen in the blood at sea level is approximately 98% this ?
Question 106-33 : 1 2 and 3 are correct 4 is false 1 2 and 4 are correct 3 is false 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 is false 1 3 and 4 are correct 2 is false
 1, 2 and 3 are correct, 4 is false.
1, 2 and 3 are correct, 4 is false. The severity of hypoxia depends on the .1 rate of decompression.2 physical ?
Question 106-34 : 1 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 2 and 3 are correct 4 is false 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 is false 1 and 3 are correct 2 and 4 are false
 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct. Which of the following statements concerning hypoxia is correct ?
Question 106-35 : It is a potential threat to safety it is never a problem at altitudes below 25 000 ft it activates the senses and makes them function better it has little effect on the body because the body can always compensate for it
 It is a potential threat to safety.
It is a potential threat to safety. Early symptoms of hypoxia could be .1 euphoria.2 decreased rate and depth of ?
Question 106-36 : 1 3 and 4 are correct 1 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 2 and 3 are correct 1 2 and 4 are correct
 1, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 3 and 4 are correct. One of the most dangerous symptoms of hypoxia concerning flight safety is ?
Question 106-37 : Impaired judgement reduced coordination of limb movements causing the pilot to spin cyanosis reducing then pilots ability to hear hyperventilation causing emotional stress
 Impaired judgement.
Impaired judgement. Which of the following symptoms can indicate hypoxia .1 blue lips and finger ?
Question 106-38 : 1 2 and 4 are correct 1 2 and 3 are correct 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 3 and 4 are correct
 1, 2 and 4 are correct.
1, 2 and 4 are correct. You are crossing the alps in a non pressurised aircraft at an altitude of 15 ?
Question 106-39 : Your judgement could be impaired the blood pressure can get too high the blood pressure can get too low you will get the bends
 Your judgement could be impaired.
Your judgement could be impaired. During a night flight at 10 000 feet you notice that your visual acuity has ?
Question 106-40 : Breathing extra oxygen through the oxygen mask closing one eye scanning sectors of the field of vision dim the instrument lights
 Breathing extra oxygen through the oxygen mask.
Breathing extra oxygen through the oxygen mask. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
4199 Free Training Exam
