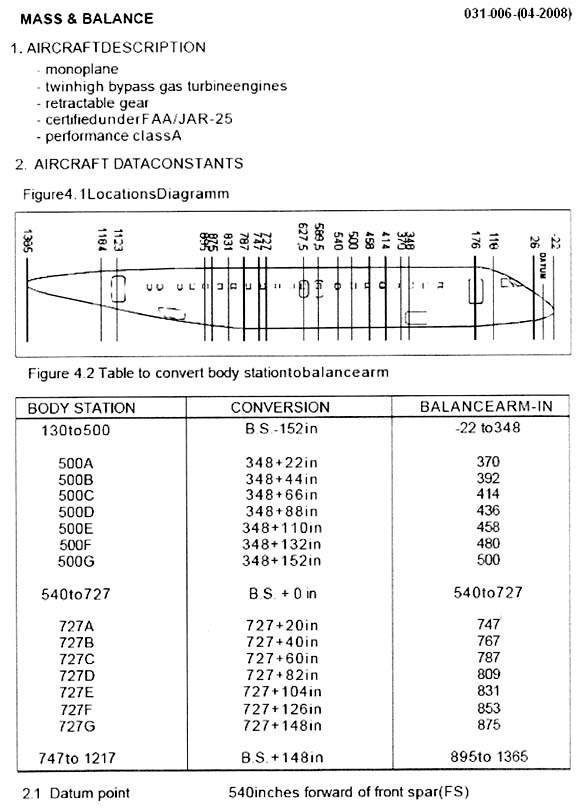
The respiratory process consists mainly of ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 103-1 : The diffusion of oxygen through the respiratory membranes into the blood transportation to the cells diffusion into the cells and elimination of carbon dioxide from the body the transportation of oxygen to the cells and the elimination of carbon monoxide the transportation of oxygen to the cells and the elimination of nitrogen the transportation of carbon dioxide to the cells and elimination of oxygen
 The diffusion of oxygen through the respiratory membranes into the blood, transportation to the cells, diffusion into the cells and elimination of carbon dioxide from the body.
The diffusion of oxygen through the respiratory membranes into the blood, transportation to the cells, diffusion into the cells and elimination of carbon dioxide from the body. Which of the following applies to carbon monoxide poisoning ?
Question 103-2 : Several days are needed to recuperate from a carbon monoxide poisoning a very early symptom of carbon monoxide poisoning is euphoria the human body shows no sign of carbon monoxide poisoning inhaling carbon monoxide leads to hyperventilation
 Several days are needed to recuperate from a carbon monoxide poisoning.
Several days are needed to recuperate from a carbon monoxide poisoning. How is oxygen mainly transported in the blood ?
Question 103-3 : Haemoglobin in the red blood cells white blood cells plasma blood fat
 Haemoglobin in the red blood cells.
Haemoglobin in the red blood cells. Which gas most readily combines with haemoglobin ?
Question 103-4 : Carbon monoxide nitrogen oxygen carbon dioxide
 Carbon monoxide.
Carbon monoxide. Which of the following is true concerning carbon monoxide ?
Question 103-5 : It is to be found in the smoke of cigarettes lifting up a smoker's 'physiological altitude' it combines 5 times faster to the haemoglobin than oxygen it has no physiological effect when mixed with oxygen it is always present in the lungs
 It is to be found in the smoke of cigarettes lifting up a smoker's 'physiological altitude'.
It is to be found in the smoke of cigarettes lifting up a smoker's 'physiological altitude'. An increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood leads to ?
Question 103-6 : An increased respiratory rate a decrease of acidity in the blood a reduction of red blood cells an improving resistance to hypoxia
 An increased respiratory rate.
An increased respiratory rate. In the alveoli gas exchange takes place external respiration which gas will ?
Question 103-7 : Carbon dioxide ambient air oxygen carbon monoxide
 Carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide. How can a pilot increase his tolerance to +gz ?
Question 103-8 : Tightening of the stomach muscles take an upright seat position relax the muscles and lean upper body forward tighten shoulder harness
 Tightening of the stomach muscles.
Tightening of the stomach muscles. Hypoxia is caused by ?
Question 103-9 : Reduced partial oxygen pressure in the lung reduced partial pressure of nitrogen in the lung an increased number of red blood cells a higher affinity of the red blood cells haemoglobin to oxygen
 Reduced partial oxygen pressure in the lung.
Reduced partial oxygen pressure in the lung. Hypoxia can be caused by .1 low partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere ?
Question 103-10 : 1 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 2 3 are correct 4 is false 1 is false 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 and 2 are correct 3 and 4 are false
 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct. The symptoms of hypoxia include ?
Question 103-11 : Visual disturbances lack of concentration euphoria nausea and barotitis dull headache and bends dizziness hypothermia
Which of the following is/are the symptom s of hypoxia ?
Question 103-12 : Lack of concentration fatigue euphoria pain in the joints low blood pressure excessive rate and depth of breathing combined with pains in the chest area
 Lack of concentration, fatigue, euphoria.
Lack of concentration, fatigue, euphoria. Which statement applies to hypoxia ?
Question 103-13 : Sensitivity and reaction to hypoxia varies from person to person carbon monoxide increases the tolerance of the brain to oxygen deficiency you may become immune to hypoxia when exposed repeatedly to hypoxia it is possible to predict when how and where hypoxia reaction starts to set in
 Sensitivity and reaction to hypoxia varies from person to person.
Sensitivity and reaction to hypoxia varies from person to person. Hypoxia can be caused by ?
Question 103-14 : A lack of red blood cells in the blood or decreased ability of the haemoglobin to transport oxygen a lack of nitrogen in ambient air too much carbon dioxide in the blood increasing oxygen partial pressure used for the exchange of gases
 A lack of red blood cells in the blood or decreased ability of the haemoglobin to transport oxygen.
A lack of red blood cells in the blood or decreased ability of the haemoglobin to transport oxygen. Breathing 100% oxygen will elevate the pilot's physiological safe altitude to ?
Question 103-15 : 40 000 ft 10 000 ft 22 000 ft 45 000 ft
 40 000 ft.
40 000 ft. The most dangerous symptoms of hypoxia at altitude are ?
Question 103-16 : Euphoria and impairment of judgement dehydration sensation of heat and blurred vision the bends and the creeps
 Euphoria and impairment of judgement.
Euphoria and impairment of judgement. Dizziness and tumbling sensations when making head movements in a tight turn ?
Question 103-17 : 'pilot's vertigo' 'nystagmus' 'flicker vertigo' 'oculogravic illusion'
 'pilot's vertigo'.
'pilot's vertigo'. 'pilot's vertigo' ?
Question 103-18 : Is the condition of dizziness and/or tumbling sensation caused by contradictory impulses to the central nervous system cns is the sensation to keep a rotation after completing a turn is the sensation of climbing caused by a strong linear acceleration announces the beginning of airsickness
 Is the condition of dizziness and/or tumbling sensation caused by contradictory impulses to the central nervous system (cns).
Is the condition of dizziness and/or tumbling sensation caused by contradictory impulses to the central nervous system (cns). What can a pilot do to avoid 'flicker vertigo' when flying in the clouds ?
Question 103-19 : Switch strobe lights off dim the cockpit lights to avoid reflections engage the autopilot until breaking the clouds fly straight and level and avoid head movements
 Switch strobe-lights off.
Switch strobe-lights off. What do you do when you are affected by 'pilot's vertigo' .1 establish and ?
Question 103-20 : 1 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 2 and 3 are correct 4 is false 1 and 2 are correct 3 and 4 are false only 4 is false
 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct. Which flight manoeuvre will most likely induce vertigo turning the head while ?
Question 103-21 : Banking climbing descending flying straight and level
 Banking.
Banking. The semicircular canals of the inner ear monitor ?
Question 103-22 : Angular accelerations movements with constant speeds relative speed and linear accelerations gravity
 Angular accelerations.
Angular accelerations. Which part of the ear could be affected due to air pressure changes during ?
Question 103-23 : The eustachian tube and the tympanic membrane ear drum the semicircular canals the cochlea the saccules and utricles
 The eustachian tube and the tympanic membrane (ear drum).
The eustachian tube and the tympanic membrane (ear drum). Which part of the inner ear is responsible for the perception of sound ?
Question 103-24 : The cochlea the semicircular canals the sacculus and utriculus the eustachian tube
 The cochlea.
The cochlea. Which part of the vestibular apparatus is affected by changes in gravity and ?
Question 103-25 : The sacculus and utriculus the semicircular canals the cochlea the eustachian tube
 The sacculus and utriculus.
The sacculus and utriculus. Which part of the vestibular apparatus is responsible for the detection of ?
Question 103-26 : The semicircular canals the cochlea the sacculus and utriculus the eustachian tube
 The semicircular canals.
The semicircular canals. The vestibular apparatus ?
Question 103-27 : Reacts to linear/angular acceleration and gravity gives the impression of hearing reacts to pressure changes in the middle ear reacts to vibrations of the cochlea
 Reacts to linear/angular acceleration and gravity.
Reacts to linear/angular acceleration and gravity. Which of the following components belong to the middle ear ?
Question 103-28 : Ossicles otoliths endolymph semicircular canals
 Ossicles.
Ossicles. Through which part of the ear does the equalization of pressure take place when ?
Question 103-29 : Eustachian tube cochlea tympanic membrane external auditory canal
 Eustachian tube.
Eustachian tube. Concerning the effects of drugs and pilot's performance ?
Question 103-30 : The primary and the side effects have to be considered the side effects only have to be considered medication has no influence on pilot's performance only the primary effect has to be considered side effects are negligible
 The primary and the side effects have to be considered.
The primary and the side effects have to be considered. What is understood by air sickness ?
Question 103-31 : A sensory conflict within the vestibular system accompanied by nausea and vomiting an illness caused by evaporation of gases in the blood an illness caused by reduced air pressure an illness caused by an infection of the middle ear
 A sensory conflict within the vestibular system accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
A sensory conflict within the vestibular system accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Cigarette smoking has particular significance to the flyer because there are ?
Question 103-32 : A mild carbon monoxide poisoning decreasing the pilot's tolerance to hypoxia a mild carbon dioxide poisoning increasing the pilot's tolerance to hypoxia a mild carbon monoxide poisoning increasing the pilot's tolerance to hypoxia a suppressed desire to eat and drink
 A mild carbon monoxide poisoning decreasing the pilot's tolerance to hypoxia.
A mild carbon monoxide poisoning decreasing the pilot's tolerance to hypoxia. A pilot who smokes will lose some of his capacity to transport oxygen combined ?
Question 103-33 : 5 8% 0 5 2% 12 18% 20 25%
 5 - 8%.
5 - 8%. Flying at pressure altitude of 10 000 ft a pilot being a moderate to heavy ?
Question 103-34 : Above 10 000 ft of 10 000 ft lower than 10 000 ft of 15 000 ft when breathing 100% oxygen
 Above 10 000 ft.
Above 10 000 ft. Which of the following applies when alcohol has been consumed ?
Question 103-35 : Even after the consumption of small amounts of alcohol normal cautionary attitudes may be lost drinking coffee at the same time will increase the elimination rate of alcohol small amounts of alcohol increase visual performance acute effects of alcohol cease immediately when 100% oxygen is taken
 Even after the consumption of small amounts of alcohol, normal cautionary attitudes may be lost.
Even after the consumption of small amounts of alcohol, normal cautionary attitudes may be lost. Alcohol when taken simultaneously with drugs may ?
Question 103-36 : Intensify the effects of the drugs compensate for side effects of drugs show undesired effects only during night flights increase the rate of alcohol elimination from the blood
 Intensify the effects of the drugs.
Intensify the effects of the drugs. The proprioceptive senses seat of the pants sense are important for motor ?
Question 103-37 : Are completely unreliable for orientation when flying in imc instrument meteorological conditions indicate the difference between gravity and g forces allow the pilot to determine the absolute vertical at flight condition are important senses for flight training in imc instrument meteorological conditions
 Are completely unreliable for orientation when flying in imc (instrument meteorological conditions).
Are completely unreliable for orientation when flying in imc (instrument meteorological conditions). Sensory input to the 'seat of the pants' sense is given by ?
Question 103-38 : Subcutaneous pressure receptors and muscle activity sensors blood rushing into legs acceleration of the stomach nausea pressure of the heart on the diaphragm
 Subcutaneous pressure receptors and muscle activity sensors.
Subcutaneous pressure receptors and muscle activity sensors. Flying from frankfurt to moscow you will have a lay over of 4 days what time ?
Question 103-39 : Lt local time mez middle european time zt zonal time utc universal time coordinated
 Lt (local time).
Lt (local time). Orientation in flight is accomplished by .1 e .2 utriculus and sacculus.3 ?
Question 103-40 : 1 2 3 and 4 are correct only 1 and 4 are correct 2 3 and 4 are correct 1 is false 2 3 and 4 are false only 1 is correct
 1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct.
1, 2, 3 and 4 are correct. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
4079 Free Training Exam
