Which one of the following lists information given by a basic VOR/DME based Area Navigation System when tracking inbound to a phantom waypoint ?
Students > VFR
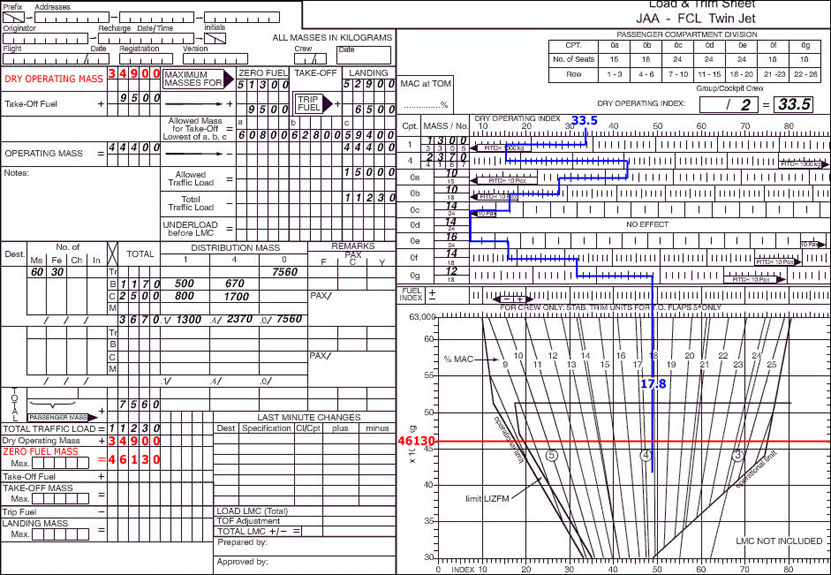
Which of the following lists information required to input a waypoint or 'Phantom Station' into a basic VOR DME based Area Navigation System ?
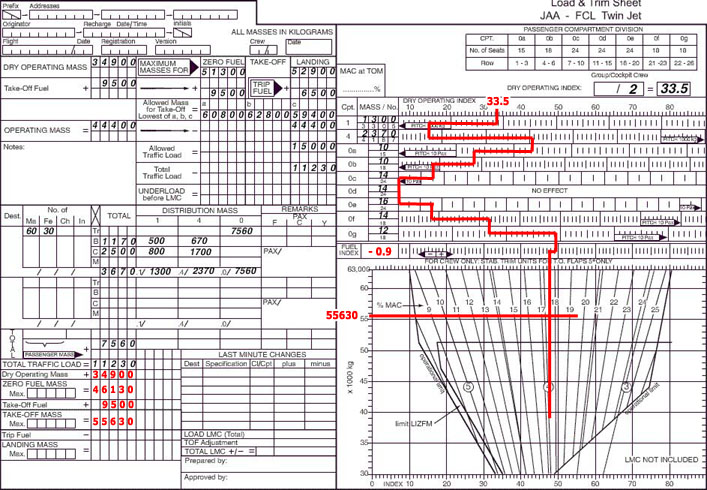
Which of the distances indicated will be shown on a basic VOR/DME based Area Navigation Equipment when using a 'Phantom Station' 2086 ?
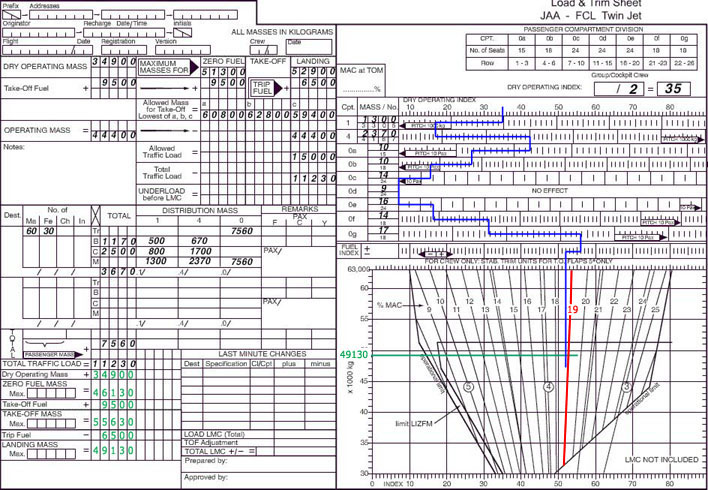
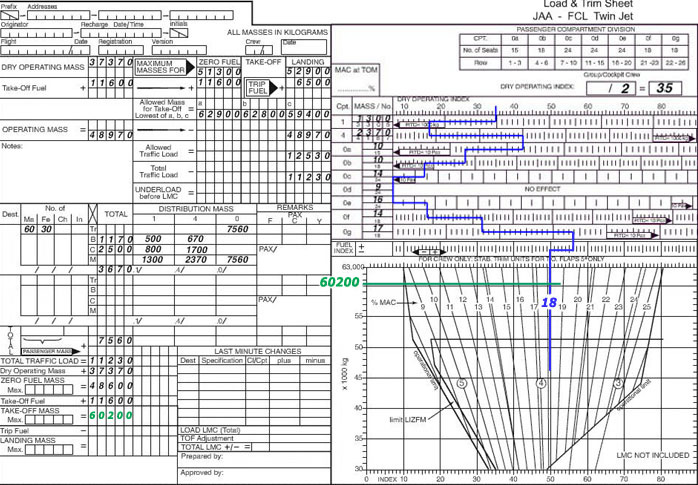
Which one of following inputs to an area navigation system r nav comes from an external not on board system Vor/dme radial/distance. brnav equipments are intended to help pilot so you will directly read distance to reach station . 
Which one of following sensors/systems self contained Inertial navigation system. brnav equipments are intended to help pilot so you will directly read distance to reach station . 
In relation to area navigation systems rnav which of following an air data input Inertial navigation system. brnav equipments are intended to help pilot so you will directly read distance to reach station . 
In flight management computer fmc of flight management system fms data relating to aircraft flight envelope computations stored in Performance database. . Question 56-8
In flight management computer fmc of flight management system fms data relating to v1 vr and v2 speeds stored in Performance database. . Question 56-9
In flight management computer fmc of flight management system fms data relating to flight plans stored in Performance database. . Question 56-10
In flight management computer fmc of flight management system fms data relating to stars and sids stored in Performance database. . Question 56-11
Under which of following circumstances does a vor/dme area navigation system switch to dead reckoning mode The system receiving information from only one vor. navigation computer vor/dme navigation the vor/dme area navigation system computer calculates track error in relation to desired track this data can easily be interfaced with automatic flight control when done so enables aircraft to automatically follow flight plan loaded into rnav computer the computer able to perform great circle navigation when receiving vor/dme stations if out of range system reverts to dr (dead reckoning) mode where it updates position means of last computed wind tas heading information operation in dr mode time limited. Question 56-12
In flight management computer fmc of flight management system fms data relating to cruising speeds stored in Performance database. . Question 56-13
Which facility associated with ils may be identified a two letter identification group Performance database. reference data airports (four letter icao identifier) vor/dme station data (three letter icao identifier) waypoint data (five letter icao identifier). Question 56-14
Under which of following circumstances does a vor/dme area navigation system switch to dead reckoning mode Vor/dme area navigation computer receiving neither radial nor distance data information from vor/dme stations. in navigation 'dead reckoning mode' the process of calculating one's current position using a previously determined position or fix advancing that position based upon known or estimated speeds over elapsed time course the rnav computer on board airplane will switch to dead reckoning mode when it lost radial or distance data information from vor/dme stations. Question 56-15
How does a vor/dme area navigation system selects dme stations to be used positioning The vor/dme area navigation system has its own nav tuner the system itself tunes dme stations providing most accurate position. dme stations that have best range geometry computing most accurate position on our course are automatically selected a rnav system which has its own nav tuner. Question 56-16
Apart from radials and distances from vor/dme stations what information required the vor/dme area navigation computer in order to calculate wind Heading from aircraft compass system true airspeed from air data computer. dme stations that have best range geometry computing most accurate position on our course are automatically selected a rnav system which has its own nav tuner. Question 56-17
The flight management system fms organized in such a way that The navigation database read only to pilot. you are not allowed to modify navigation database imagine that one pilot deleted one or more waypoints (by accident or negligence) you are flying after him it could be very dangerous for this reason navigational database read only but additional space exists so that crew created navigational data may be saved in computer memory such additional data will also be deleted at 28 days navigational update of database. Question 56-18
Precision rnav p rnav requires a track keeping accuracy of +/ nm 95% of flight time. Area navigation rnav (icao annex 11) a method of navigation permitting aircraft operations on any desired track within coverage of station referenced navigation signal or within limits of a self contained navigation system precision rnav (prnav) systems require rnp 1 (+/ 1 0nm 95% of flight time) for information basic rnav (b rnav) systems require rnp 5 (required navigation performance 5) b rnav requires only a track keeping accuracy of +/ 5nm or better 95% of flight time. Question 56-19
On what data a vor/dme area navigation system operating in dead reckoning mode Tas from air data computer heading from aircraft compass last computed w/v. navigation computer vor/dme navigation the vor/dme area navigation system computer calculates track error in relation to desired track this data can easily be interfaced with automatic flight control when done so enables aircraft to automatically follow flight plan loaded into rnav computer the computer able to perform great circle navigation when receiving vor/dme stations if out of range system reverts to dr (dead reckoning) mode where it updates position means of last computed wind tas heading information operation in dr mode time limited. Question 56-20
In flight management computer fmc of flight management system fms data relating to waypoints stored in Tas from air data computer heading from aircraft compass last computed w/v. . Question 56-21
A fms with only a multiple dme sensor operating shall have a position error 95% probability in a non precision approach equal or less than Tas from air data computer heading from aircraft compass last computed w/v. Icao doc 8168 departure procedures are normally based on rnp 1 where necessary appropriate they may be based on rnp 0 5 or rnp 0 3 departures are not associated with an rnp less than rnp 0 3 non precision approach procedures are normally based on rnp 0 5 (initial approach only) or rnp 0 3 (initial intermediate final approach) non precision approach procedures are not associated with an rnp less than rnp 0 3. Question 56-22
What the cross track deviation xtk indicated on an rnav system area navigation system The distance between actual position the great circle track between two active waypoints. Xtk the aircraft position relative to path xtk distance the shortest distance (shortest path) between actual aircraft position an active waypoint selected on track even if we are not on planned path. Question 56-23
In what piece of fms equipment will pilot enter waypoint information the route The control display unit (cdu). flight management system the flight management system (fms) comprised of following components flight management computer system (fmcs) autopilot/flight director system (afds) autothrottle (a/t) inertial reference systems (irs) global positioning system (gps) each of these components an independent system each can be used independently or in various combinations the term fms refers to concept of joining these independent components together into one integrated system which provides continuous automatic navigation guidance performance management the integrated fms provides centralized flight deck control of airplane's flight path performance parameters the flight management computer or fmc the heart of system performing navigational performance computations providing control guidance commands the primary flight deck controls are afds mcp two control display units (cdu's) two electronic flight instrument system (efis) control panels an fmc source selector switch the primary displays are cdus outboard display units inboard display units upper display unit the fmc uses crew entered flight plan information airplane systems data data from fmc navigation database performance database to calculate airplane present position pitch roll thrust commands required to fly an optimum flight profile the fmc sends these commands to autothrottle autopilot flight director map route information are sent to respective pilot's navigation displays the efis control panels are used to select desired information navigation display the mode control panel used to select autothrottle autopilot flight director operating modes the final preparation of flight via cdu are being completed the captain . Question 56-24
3d rnav fixing gives you Horizontal vertical profile guidance. Area navigation rnav (icao annex 11) a method of navigation permitting aircraft operations on any desired track within coverage of station referenced navigation signal or within limits of a self contained navigation system a 3d rnav system able to navigate in horizontal plane in addition has a guidance capability in vertical plane. Question 56-25
Which of following are stored in navigation database of flight management system fms 1 waypoints 2 details of radio navigation aids3 optimum altitudes4 company routes5 landing reference speedsthe combination regrouping all correct statements Horizontal vertical profile guidance. . Question 56-26
From which of following combination of navigational sources provide enough information to rnav equipment to calculate wind vector Irs air data computer. tothdaniel the right answer seems to be close but i cannot figure out how wind can be calculated without heading information the output data of an irs include present position acceleration true heading (ground speed calculated integrating measured acceleration) air data computer will provide tas. Question 56-27
The flight management system fms organized in such a way that pilot can Insert additional temporary navigation data between two database updates. the navigational database read only but additional space exists so that crew created navigational data may be saved in computer memory such additional data will also be deleted at 28 days navigational update of database. Question 56-28
A pilot flying between two waypoints defined suitably located vor/dmes equipped with a simple 2d rnav system this pilot Reads cross track error the distance to go on cdi or hsi. The navigation computer of simple 2d rnav system computes navigational problems simple sine cosine mathematics solving triangular problems output data from navigation computer are desired magnetic track to next waypoint shown on cdi or hsi at course pointer distance from present position to next waypoint deviations (cross track error) from desired track as follows in enroute mode full scale deflection on cdi or hsi 5 nm in approach mode full scale deflection on cdi or hsi 1 25 nm in vor/dme mode full scale deflection of cdi or hsi 10°. Question 56-29
The control and display unit cdu on an fms Used the crew to input data into fmc. The navigation computer of simple 2d rnav system computes navigational problems simple sine cosine mathematics solving triangular problems output data from navigation computer are desired magnetic track to next waypoint shown on cdi or hsi at course pointer distance from present position to next waypoint deviations (cross track error) from desired track as follows in enroute mode full scale deflection on cdi or hsi 5 nm in approach mode full scale deflection on cdi or hsi 1 25 nm in vor/dme mode full scale deflection of cdi or hsi 10°. Question 56-30
A 2 dimensional rnav system has a capability in Used the crew to input data into fmc. a 2d rnav system able to navigate in horizontal plane only a 3d rnav system able to navigate in horizontal plane in addition has a guidance capability in vertical plane a 4d rnav system able to navigate in horizontal plane has a guidance capability in vertical plane in addition has a timing function. Question 56-31
A fix obtained rho rho navigation based on information from two Used the crew to input data into fmc. rho rho navigation uses distance from two sources position information rho rho navigation quite a bit more complicated than either theta theta (vor vor) or theta rho (vor dme) requires an onboard computer to do all but easiest calculations however it very accurate much more than any system that uses theta (vor) simple reason that dme so much more accurate than any other azimuth based navigation system . Question 56-32
The fms navigation data base usually contains 1 airport reference data 2 atc frequencies 3 company routes 4 navaid frequencies the combination regrouping all correct statements Used the crew to input data into fmc. rho rho navigation uses distance from two sources position information rho rho navigation quite a bit more complicated than either theta theta (vor vor) or theta rho (vor dme) requires an onboard computer to do all but easiest calculations however it very accurate much more than any system that uses theta (vor) simple reason that dme so much more accurate than any other azimuth based navigation system . Question 56-33
The inputs of information used to achieve rnav required accuracy may be 1 ndb2 irs3 vor/dme4 gnssthe combination regrouping all correct statements Used the crew to input data into fmc. rho rho navigation uses distance from two sources position information rho rho navigation quite a bit more complicated than either theta theta (vor vor) or theta rho (vor dme) requires an onboard computer to do all but easiest calculations however it very accurate much more than any system that uses theta (vor) simple reason that dme so much more accurate than any other azimuth based navigation system . Question 56-34
Benefits of area navigation include 1 shorter flight distance2 reduction in fuel and flight time 3 no radio contact within rnav airspace 4 reduction in number of ground tracking facilities5 pilot choice of vertical and horizontal separations the combination regrouping all correct statements Used the crew to input data into fmc. area navigation rnav (icao annex 11) a method of navigation permitting aircraft operations on any desired track within coverage of station referenced navigation signal or within limits of a self contained navigation system rnav can be used in all phases of flight and when implemented correctly can result in improved situational awareness the pilot reduced workloads both controller pilot reduced environmental impact from improved design of routes procedures reduced fuel consumption from shorter more direct routes. Question 56-35
A phantom station as used in a 2d rnav system A waypoint defined a radial a dme distance from a vor/dme station. Basic vor dme based area navigation system a 2d rnav system the navigation computer of simple 2d rnav system computes navigational problems simple sine cosine mathematics solving triangular problems input data to navigation computer is actual vor radial dme distance from selected vor station radial distance to phantom waypoint desired magnetic track inbound to phantom waypoint thus a phantom station a waypoint defined a radial a dme distance from a vor/dme station a 2d rnav system able to navigate in horizontal plane only. Question 56-36
Which of following nav aids will provide an rnav system with position A waypoint defined a radial a dme distance from a vor/dme station. Area navigation (rnav) can be defined as a method of navigation that permits aircraft operation on any desired course within coverage of station referenced navigation signals or within limits of a self contained system capability or a combination of these the computer in a basic rnav system transfers information given a vor/dme station (or two or more vor or two or more dme stations) into tracking distance indications to any chosen phantom station/waypoint this one of rnav's computer main functions a vdf not an rnav nav aids system ndb/adf will only provide a direction (angle) information whitout any distance from ground station. Question 56-37
On a modern commercial aircraft fms provides Lateral vertical navigation guidance performance management. the two functions common to all fms systems automatic navigation lnav (lateral navigation) flight path management vnav (vertical navigation) furthermore flight management system has ability to monitor direct both navigation performance of flight. Question 56-38
The addition of dme p to mls necessary to Obtain three dimensional positions. the mls precision distance measuring equipment (dme/p) functions same as navigation dme but there are some technical differences the beacon transponder operates in frequency band 962 to 1105 mhz responds to an aircraft interrogator the mls dme/p accuracy improved to be consistent with accuracy provided the mls azimuth elevation stations a microwave landing system (mls) an all weather precision landing system originally intended to replace or supplement instrument (ils) mls has a number of operational advantages including a wide selection of channels to avoid interference with other nearby airports excellent performance in all weather a small 'footprint' at airports an aircraft that enters scanned volume uses a special receiver that calculates its position measuring arrival times of beams. Question 56-39
The position of a waypoint can be inserted into computer of a 4d rnav system in different ways 1 alphanumeric icao identifier2 lat/long and altitude3 radial and distance from a vor station4 distance and bearing from another waypointthe combination that regroups all of correct statements Obtain three dimensional positions. Ecqb04 (revised) november 2017. Question 56-40
The purpose of fligh management system fms to provide Continuous automatic navigation guidance performance management. flight management system the flight management system (fms) comprised of following components flight management computer system (fmcs) autopilot/flight director system (afds) autothrottle (a/t) inertial reference systems (irs) global positioning system (gps) each of these components an independent system each can be used independently or in various combinations the term fms refers to concept of joining these independent components together into one integrated system which provides continuous automatic navigation guidance performance management the integrated fms provides centralized flight deck control of airplane's flight path performance parameters the flight management computer or fmc the heart of system performing navigational performance computations providing control guidance commands the primary flight deck controls are afds mcp two control display units (cdu's) two electronic flight instrument system (efis) control panels an fmc source selector switch the primary displays are cdus outboard display units inboard display units upper display unit the fmc uses crew entered flight plan information airplane systems data data from fmc navigation database performance database to calculate airplane present position pitch roll thrust commands required to fly an optimum flight profile the fmc sends these commands to autothrottle autopilot flight director map route information are sent to respective pilot's navigation displays the efis control panels are used to select desired information navigation display the mode control panel used to select autothrottle autopilot flight director operating modes the final preparation of flight via cdu are being completed the captain .
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2199 Free Training Exam
